VLAN Overview
A VLAN enables you to isolate and secure the network by creating a smaller, more focused virtual LAN within the overall network. The gateway uses the ports of the Oracle IB switch.
Use the following information to plan your VLAN:
-
Each gateway can only have one untagged public-network, which has a default of vlan 1.
-
Each gateway can have multiple tagged public networks.
-
Each tagged public network can have a range of VLANs.
-
The ports on each gateway share a VLAN. Therefore, the VLAN range of the public networks that terminate on the same gateway ports cannot overlap. For example, if you want all ports to have a 2-4096 vlan range, create one public network terminated on a LAG with all four ports. The Oracle Fabric OS software automatically checks and blocks incorrect overlapping operations.
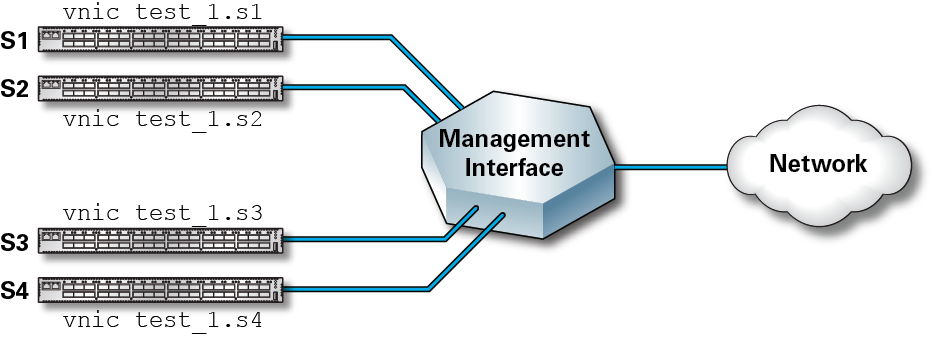
In this figure, no isolation exists and all hosts (s1, s2, s3, and s4) are visible to each other on the network. This scenario might not be useful in situations where you want some hosts to be isolated from others. You can use VLANs to achieve this isolation.
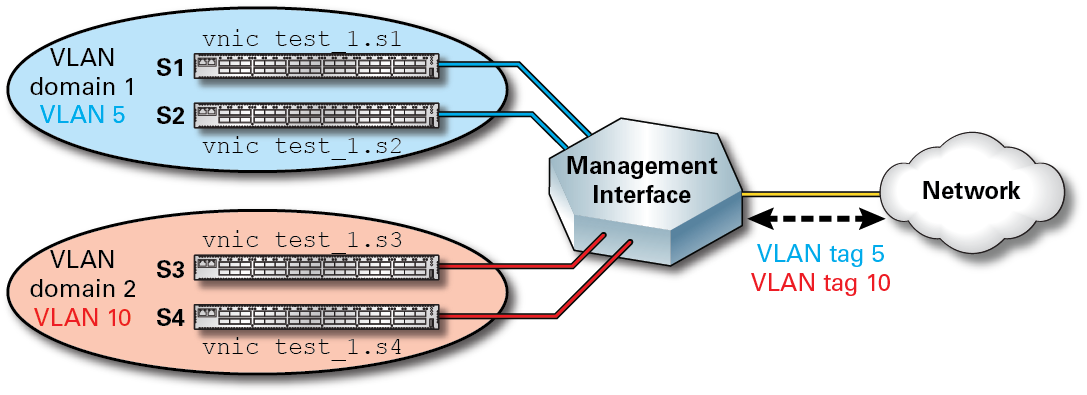
In this figure, configured VLAN packets are tagged with unique VLAN IDs and are transmitted and received on specific vNICs to support communication between specified servers. For example, the packets that are supported on vNICs in VLAN 5 are transmitted and received on interfaces that support VLAN 5. As a result, only hosts s1 and s2 know about each other, and traffic to and from those hosts is kept isolated from hosts s3 and s4 in VLAN 10. Servers s3 and s4 know only about each other and traffic for hosts s3 and s4 is also kept isolated from traffic related to VLAN 5.