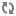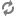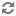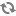To create a client application that consumes any of the CAS Web services, you need the particular Web service's WSDL file to generate client stubs.
A WSDL file specifies value types, exceptions, and available methods in a Web service in a programmatic fashion. Typically, a client developer uses a tool that parses the WSDL file and generates client-side stubs (also called proxy classes) and value types. These generated files include all the code necessary to serialize and deserialize SOAP messages and make the SOAP layer transparent to the client developer. The CAS WSDL files can be used with any language that has Web services support.
Among the tools that generate client stub code from the WSDLs are the following:
Specify the appropriate choice below as the package name when you generate stubs for a particular Web service:
com.endeca.itl.cas.api
com.endeca.itl.component.manager
com.endeca.itl.recordstore
For example, the CXF
wsdl2java utility takes the WSDL file and generates
fully annotated Java code with one of the following commands:
wsdl2java -p com.endeca.itl.cas.api -client CasCrawlerService.wsdl
wsdl2java -p com.endeca.itl.component.manager -client ComponentInstanceManager.wsdl
wsdl2java -p com.endeca.itl.recordstore -client RecordStore.wsdl
For details on using a WSDL code-generation utility, refer to the utility's documentation.
Keep in mind that the exact syntax of a class member depends on the output of the WSDL tool that you are using. Therefore, check the client stub classes that are generated by your WSDL tool for the exact syntax of the class members.