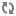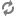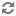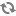This sample program shows how to read records from the Record Store.
The
SampleReader.java class is an example of how to
use the core and client utility classes to read records. The sample program
gets the ID of the last-committed generation and reads its records from the
Record Store.
The code works as follows:
Using the
RecordStoreLocatorutility class, a connection is made to the Record Store Server.RecordStoreLocator locator = RecordStoreLocator.create(casHost, casPort, "rs1"); RecordStore recordStore = locator.getService();
In a
tryblock, theRecordStore.startTransaction()core method creates a READ transaction and then theRecordStore.getLastCommittedGenerationId()core method gets the ID of the last generation that was committed to the Record Store.TransactionId tId = null; try { System.out.println("Starting a new transaction ..."); tId = recordStore.startTransaction(TransactionType.READ); System.out.println("Getting the last committed generation ..."); GenerationId gId = recordStore.getLastCommittedGenerationId(tId);The
RecordStoreReader.createBaselineReader()utility method is used to create a baseline reader. The reader transfers a maximum of 100 records per transfer.System.out.println("Reading records ..."); RecordStoreReader reader = RecordStoreReader.createBaselineReader(recordStore, tId, gId, 100); int count = 0;In a
whileloop, thehasNext()method tests whether the reader has another record to read. If true, thenext()method retrieves the record, the record is written out, and the record-read count is increased by one. When there are no more records to read, theclose()method closes the reader, and the number of records is printed out.while (reader.hasNext()) { Record record = reader.next(); System.out.println(" RECORD: " + record); count++; } reader.close(); System.out.println(count + " record(s) read");The client program uses the
RecordStore.commitTransaction()core method to commit the read transaction. .System.out.println("Committing transaction ..."); recordStore.commitTransaction(tId); System.out.println("DONE");
Example 8. SampleReader.java
package com.endeca.itl.recordstore.sample;
import com.endeca.itl.record.Record;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.GenerationId;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStore;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStoreException;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStoreLocator;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStoreReader;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.TransactionId;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.TransactionType;
/**
* SampleReader is an example of how to use the Record Store core and
* client utility classes to read records. It gets the ID of the
* last-committed generation and reads its records from the Record Store.
*/
public class SampleReader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length!=2) {
System.out.println("usage: <cas host> <cas port>");
System.exit(-1);
}
String casHost = args[0];
int casPort = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
RecordStoreLocator locator = RecordStoreLocator.create(casHost, casPort, "rs1");
RecordStore recordStore = locator.getService();
TransactionId tId = null;
try {
System.out.println("Starting a new transaction ...");
tId = recordStore.startTransaction(TransactionType.READ);
System.out.println("Getting the last committed generation ...");
GenerationId gId = recordStore.getLastCommittedGenerationId(tId);
System.out.println("Reading records ...");
RecordStoreReader reader = RecordStoreReader.createBaselineReader(recordStore, tId,
gId, 100);
int count = 0;
while (reader.hasNext()) {
Record record = reader.next();
System.out.println(" RECORD: " + record);
count++;
}
reader.close();
System.out.println(count + " record(s) read");
System.out.println("Committing transaction ...");
recordStore.commitTransaction(tId);
System.out.println("DONE");
} catch (RecordStoreException exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
if (tId != null) {
try {
recordStore.rollbackTransaction(tId);
} catch (RecordStoreException anotherException) {
System.out.println("Failed to roll back transaction.");
anotherException.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}