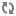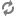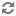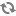Call the
CasCrawler.startCrawl() method to start a crawl.
The syntax of the method is:
CasCrawler.startCrawl(CrawlId crawlId, CrawlMode crawlMode)
The
crawlId parameter is a
CrawlId object that has the crawl ID set. The
crawlMode parameter is one of the following
CrawlMode data types:
CrawlMode.FULL_CRAWLperforms a full crawl and creates a crawl history.CrawlMode.INCREMENTAL_CRAWLperforms an incremental crawl and updates the crawl history. There are several cases in which theCrawlModeautomatically switches over fromINCREMENTAL_CRAWLto run aFULL_CRAWL. A full crawl runs in the following cases:
This method does not return a value.
To start a crawl:
Make sure that you have created a connection to the CAS Server. (A
CasCrawlerobject namedcrawleris used in this example.)Instantiate a
CrawlIdobject and then set its Id in the constructor.For example:
// Create a new crawl Id with the name set to Demo. CrawlId crawlId = new CrawlId("Demo");Call the
CasCrawler.startCrawl()method with the crawl ID and the appropriate crawl mode. To catch exceptions, use a try block with the appropriate catch clauses.For example:
try { crawler.startCrawl(crawlId, CrawlMode.INCREMENTAL_CRAWL); } catch (CrawlNotFoundException e) { System.out.println(e.getLocalizedMessage()); }
If the
CasCrawler.startCrawl() method fails, it throws an
exception:
CrawlInProgressExceptionoccurs if the CAS Server is already running the specified crawl.CrawlNotFoundExceptionoccurs if the specified crawl (thecrawlIdparameter) does not exist or is otherwise not found.InvalidCrawlConfigExceptionoccurs if the configuration is invalid. You can callgetCrawlValidationFailures()to return the list of crawl validation errors.ItlExceptionoccurs if other problems prevent the crawl from running.
As shown in step 3, use a
try block to catch these exceptions.