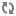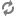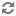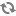This sample program shows how to write records to the Record Store.
The
SampleWriter.java class is an example of how to use
the core and client utility classes to write records. The sample Java program
creates one record and writes it to the Record Store.
The code works as follows:
The PROPERTY_ID variable uses the setting of the Record Store instance
idPropertyNameconfiguration property, which is used to identify the records.public static final String PROPERTY_ID = "Endeca.FileSystem.Path";
A sample record is created with the
Recordclass and added to the records Collection.Collection<Record> records = new LinkedList<Record>(); Record record = new Record(); record.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(PROPERTY_ID, "id1")); record.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue("property.name", "property.value")); records.add(record);Using the
RecordStoreLocatorutility class, a connection is made to the Record Store Server.RecordStoreLocator locator = RecordStoreLocator.create(casHost, casPort, "rs1"); RecordStore recordStore = locator.getService();
In a
tryblock, a READ_WRITE transaction was created by theRecordStore.startTransaction()core method and theRecordStoreWriter.createWriter()method is used to create a writer. This example writer writes a maximum of 100 records per transfer.try { System.out.println("Setting record store configuration ..."); recordStore.setConfiguration(config); System.out.println("Starting a new transaction ..."); tId = recordStore.startTransaction(TransactionType.READ_WRITE); RecordStoreWriter writer = RecordStoreWriter.createWriter(recordStore, tId, 100); ...The writer first writes a "Delete All" record, then writes the sample record, and finally closes the writer. Note that the record is written twice (the first time as part of a collection and the second as an individual record), in order to demonstrate both methods.
System.out.println("Writing records ..."); writer.deleteAll(); writer.write(records); writer.close();The client program uses the
RecordStore.commitTransaction()core method to commit the write transaction.System.out.println("Committing transaction ..."); recordStore.commitTransaction(tId); System.out.println("DONE");
After the transaction is committed, the Record Store will have a new record generation.
Example 7. SampleWriter.java
package com.endeca.itl.recordstore.sample;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import com.endeca.itl.record.PropertyValue;
import com.endeca.itl.record.Record;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStore;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStoreConfiguration;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStoreException;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStoreLocator;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStoreWriter;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.TransactionId;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.TransactionType;
/**
* SampleWriter is an example of how to use the Record Store core and
* client utility classes to write records. It creates one record and
* writes it to the Record Store.
*/
public class SampleWriter {
// This should match the idPropertyName in your record store configuration.
public static final String PROPERTY_ID = "Endeca.FileSystem.Path";
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length!=2) {
System.out.println("usage: <cas host> <cas port>");
System.exit(-1);
}
String casHost = args[0];
int casPort = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
Collection<Record> records = new LinkedList<Record>();
Record record = new Record();
record.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(PROPERTY_ID, "id1"));
record.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue("property.name", "property.value"));
records.add(record);
RecordStoreLocator locator = RecordStoreLocator.create(casHost, casPort, "rs1");
RecordStore recordStore = locator.getService();
RecordStoreConfiguration config = new RecordStoreConfiguration();
config.setIdPropertyName("Endeca.FileSystem.Path");
config.setChangePropertyNames(new ArrayList<String>());
TransactionId tId = null;
try {
System.out.println("Setting record store configuration ...");
recordStore.setConfiguration(config);
System.out.println("Starting a new transaction ...");
tId = recordStore.startTransaction(TransactionType.READ_WRITE);
RecordStoreWriter writer = RecordStoreWriter.createWriter(recordStore, tId,
100);
System.out.println("Writing records ...");
writer.deleteAll();
writer.write(records);
writer.close();
System.out.println("Committing transaction ...");
recordStore.commitTransaction(tId);
System.out.println("DONE");
} catch (RecordStoreException exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
if (tId != null) {
try {
recordStore.rollbackTransaction(tId);
} catch (RecordStoreException anotherException) {
System.out.println("Failed to roll back transaction.");
anotherException.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}