Daten zwischen Cloud-Datenbanken in der gleichen Region replizieren
Hier erfahren Sie, wie Sie Oracle Cloud Infrastructure GoldenGate einrichten, um Daten zwischen zwei autonomen KI-Datenbanken zu replizieren.
Überblick
Mit Oracle Cloud Infrastructure GoldenGate können Sie unterstützte Datenbanken in der gleichen Region replizieren. In den folgenden Schritten wird beschrieben, wie Sie eine Zieldatenbank mit Oracle Data Pump instanziieren und Daten von der Quelle in das Ziel replizieren.
Dieser Schnellstart ist auch als LiveLab verfügbar: Workshop anzeigen.
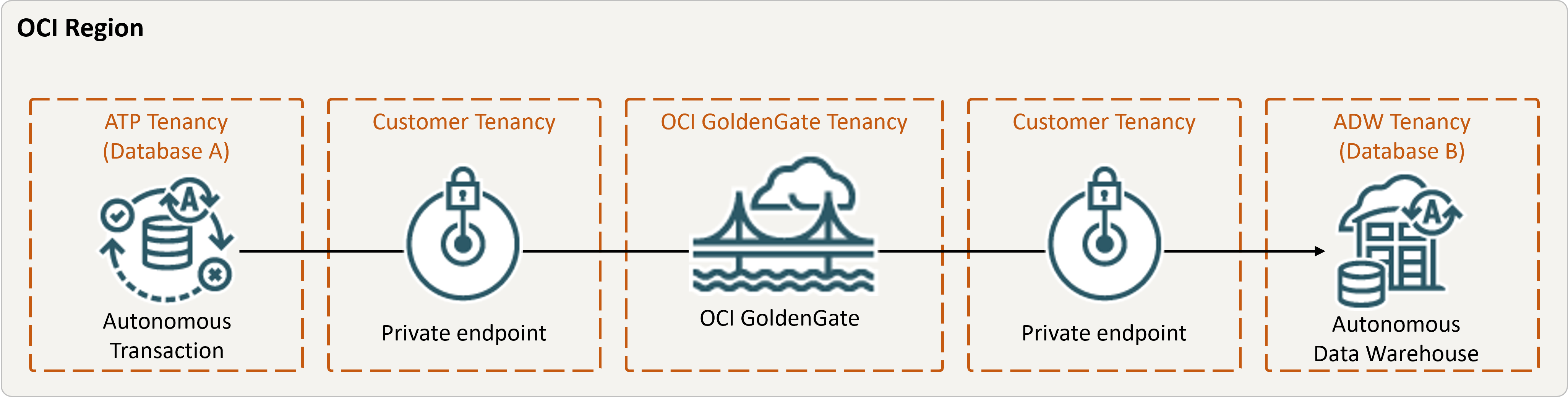
Beschreibung der Abbildung Same-region.png
Bevor Sie beginnen
Sie benötigen Folgendes, um fortzufahren:
- Eine vorhandene Quelldatenbank
- Eine vorhandene Zieldatenbank
- Die Quell- und Zieldatenbanken müssen sich in einem einzelnen Mandanten in der gleichen Region befinden.
- Wenn Sie Beispieldaten benötigen, laden Sie Archive.zip herunter, und befolgen Sie die Anweisungen unter Übung 1, Aufgabe 3: ATP-Schema laden.
Aufgabe 2: Integrierten Extract erstellen
Ein integrierter Extract erfasst fortlaufende Änderungen an der Quelldatenbank.
Aufgabe 3: Daten mit Oracle Data Pump (ExpDP) exportieren
Mit Oracle Data Pump (ExpDP) können Sie Daten aus der Quelldatenbank in Oracle Object Storage exportieren.
Aufgabe 4: Zieldatenbank mit Oracle Data Pump (ImpDP) instanziieren
Mit Oracle Data Pump (ImpDP) können Sie Daten aus der Datei SRC_OCIGGLL.dmp, die aus der Quelldatenbank exportiert wurde, in die Zieldatenbank importieren.