Creating a Data Export File
The data export to file feature enables you to export data from an Oracle Fusion Cloud Enterprise Performance Management application to a data file. You can use the data file to load data into an ERP application or an external system.
When creating a data export to file application, note the following:
-
When dimensions are created, the order of the column in the data file is used to assign the column order. The first column in file is assigned ACCOUNT data column.
-
It is recommended that you export only a year at a time. If date ranges cross a year boundary, data may be duplicated.
-
Data Rule—The POV category is not validated.
-
Data Load Mapping—Target values are not validated for data export to file applications.
-
Data Load Execution—When the option to export the data file is enabled, Data Management creates an output data file. The name of the data file is
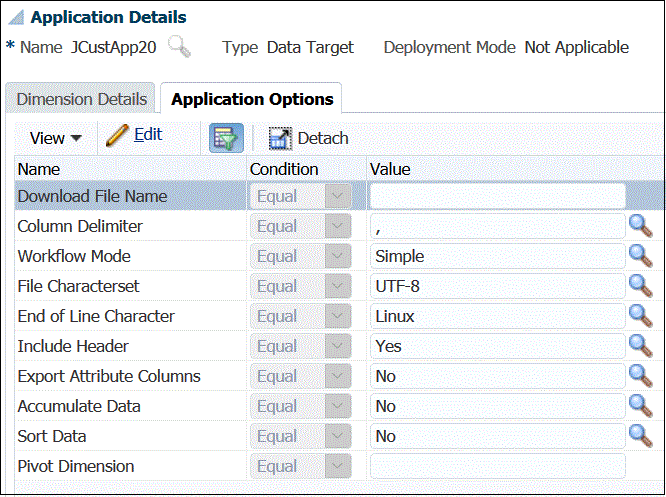
<Target App Name>_<Process ID>.dat, and it is written to the<APPL ROOT FOLDER>/outboxdirectory. You can access the data file from the Process Details page from theOUTPUT filecolumn.When the data load rule is executed, Data Management exports the data.
-
Check Rules can be created from a data export file. Check rules cannot be based on target values.
-
Write-back is not applicable from data export files.
- In this release, only numeric data types are supported.
-
The custom target application option is still available for exporting production data to external systems. Data Management supports both the custom target and data export to file application options. Eventually, the data export to file option will supersede the custom target application option due to its enhanced functions and capabilities.
The data export to file option is largely backward compatible with the file format of the custom target application option, but small differences exist, which may cause regression issues.
For this reason, you are urged to migrate your existing custom target applications to Data Export to File applications. To do this, select the System Maintenance process called the Upgrade Custom Application option, which can be run for one custom application or all. See Upgrade Custom Applications for more information.
The Upgrade Custom Application process converts existing custom applications to the file formats used by the data export to file option. It retains all the existing setup. When the custom target applications have been converted, you can run same data rule as before. Before using the conversion program, reconcile any differences in the file formats. For example, the header row in the data export to file option contains the name of the dimension and not UD1, UD2 etc.
To define a data export to file target application: