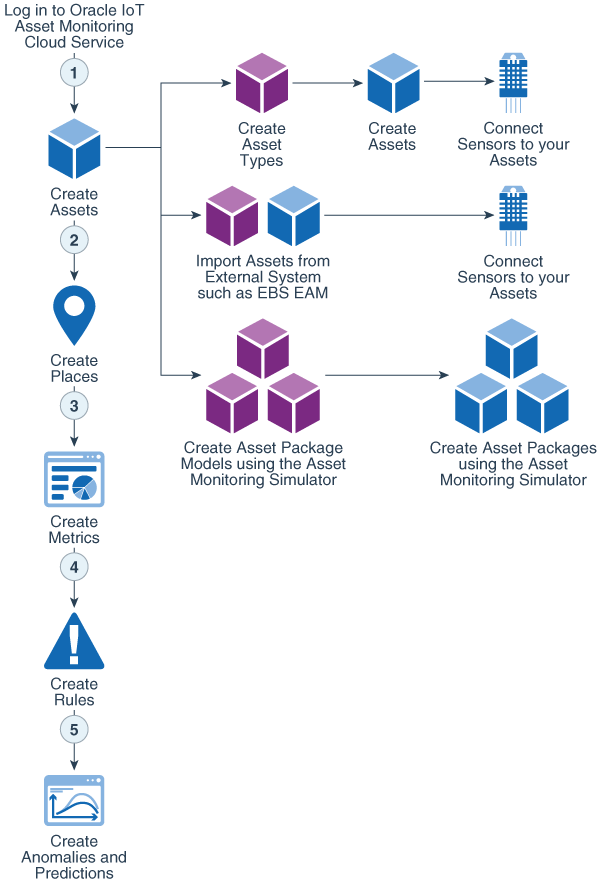
Typical Workflow for Using Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud Service
To implement Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud Service, start by importing or creating the assets and asset types. Once you have associated sensor devices with your assets, you can start locating and monitoring your assets.
If you are learning about Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud Service, or wish to try out its various features, use the digital twin simulator that comes along with the product. This eliminates the need to connect actual sensors, and to create assets and asset types. See Simulate Asset Sensors with the Built-In Simulator for more information.
This image represents the workflow for implementing Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud Service:
| Task | Description | More Information |
|---|---|---|
|
Create the Device Models |
Create device models to let data be transmitted from a device to Oracle Internet of Things Intelligent Applications Cloud. Perform this task in Oracle Internet of Things Intelligent Applications Cloud Management Console if you do not have your device models in the IoT platform already. |
Create Device Models in Oracle Internet of Things Intelligent Applications Cloud |
| Register and Activate the Devices |
Register the devices with the Oracle Internet of Things Intelligent Applications Cloud and provision the client software so that it communicates with the Oracle Internet of Things Intelligent Applications Cloud. Perform this task in Oracle Internet of Things Intelligent Applications Cloud Management Console if you do not have your devices on the IoT platform already. |
Register and Activate Devices in Oracle Internet of Things Cloud Service |
| Assign the Device Models to the Cloud Service | Assign the device models to the Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud
Service, so that they can be seen and used in the Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud
Service.
Perform this task in Oracle Internet of Things Intelligent Applications Cloud Management Console. |
Assign Device Models to the Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud Service Application |
|
Create Assets |
Start by creating your business assets and asset types in Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud Service. You can monitor both indoor and outdoor assets. If you are already managing your assets in an asset management system, such as Maintenance Cloud or Oracle Enterprise Asset Management, you can import your assets into Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud Service. The next step is to associate sensor devices, such as location sensors and temperature/humidity sensors, with your assets. Bluetooth and RFID devices are examples of indoor sensors. GPS devices are examples of outdoor sensors. |
|
|
Create Places |
Create places to define the storage and usage locations of your asset. You can search for your places in the map view and zoom into the available assets. If an asset moves out of its permitted place, Oracle IoT Asset Monitoring Cloud Service can generate an incident that is reported to the operations manager. Create outdoor places by drawing a geofence on the map. For indoor places, you can additionally make use of floor plans and altitude data. |
|
|
Create Metrics/KPIs |
KPIs or Key Performance Indicators help you track key metrics for your monitored assets, such as assets connected, assets available, and assets utilization. You can also create custom KPIs to track the metrics that are relevant to your business processes. So, for example, you could create a metric to track the average hourly temperature reported by a temperature sensor. You can track KPIs from the dashboard and the map view for the assets visible in the map. You can also track individual KPIs for an asset from the assets page. |
|
|
Create Rules |
Create rules to generate incidents, warnings, or alerts based on location, threshold, or alert conditions. So, for example you can create a location rule to generate an incident when an asset moves out of its designated location. You can create a threshold rule, say, to generate an alert when a pump device reports a blocked filter. You can also use rules to trigger asset actions. For example, you can configure a rule to power off an overheating asset. Incidents: Use incidents to report issues and work with the maintenance staff for resolutions. Alerts: Use alerts to trigger other rules, or to pass messages to integrated enterprise applications. Warnings: Use warnings to create a log of issues that don’t require your immediate attention. Actions: Use asset actions to execute device-related actions for your asset. |
|
|
Create Anomalies and Predictions |
Use anomalies to detect deviations from normal asset behavior, and to flag and address device issues in time. You can create point-in-time anomalies that look for deviations in a KPI value that exceed a threshold value. For example, point-in-time anomalies can help detect an HVAC device that is overheating . You can also use pattern-based anomalies to look for telltale patterns in sensor data generated by an asset. For example, you may use pattern-based anomalies to look for vibration anomalies in a forklift asset. Predictions use historical and transactional data to identify risks to your assets. You can either use internal Oracle Internet of Things Intelligent Applications Cloud data or import and use external device data to help make predictions for your asset. Predictions help warn you of impending asset failure in advance. Preventive maintenance can help save the costs associated with asset breakdown or unavailability. |