Overview of Using Business Rules With Order Management
Set up a business rule in Oracle Order Management to implement a dynamic decision at run time that automates a company policy, does a calculation, or does some processing.
A business rule is a statement that describes how to implement a business policy or make a business decision. It can implement logic.
-
Enforce a spending policy.
-
Constrain a process so it meets a regulatory requirement.
-
Calculate a discount or premium.
-
Provide an offer according to a customer value.
Here are some business requirements you can meet with a business rule.
-
If customer is Computer Service and Rentals, then use orchestration process y to fulfill the sales order.
-
If destination is Japan, then route shipment through Pacific Northwest Warehouse.
A business rule keeps rule logic separate from the underlying application code, which allows a business analyst to modify rule logic without using programming code and without interrupting your business process.
Here's an example of a business rule.
-
If the sales order is valued at $50,000 or more, then make sure a representative calls the customer before sending an invoice.
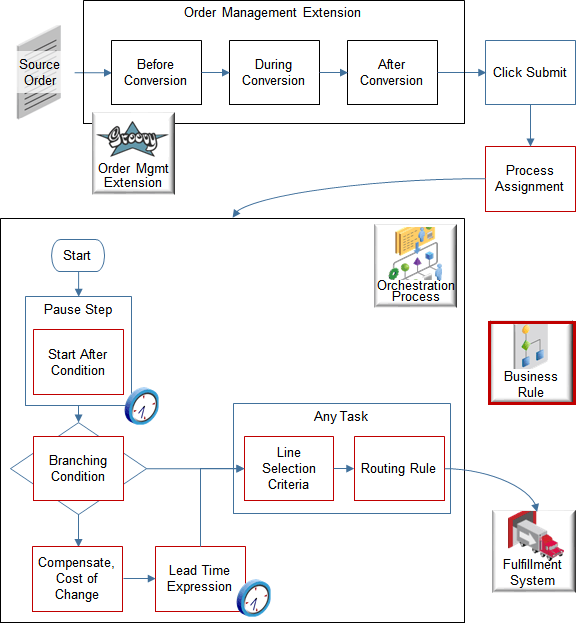
You can use business rules and order manage extensions together during a sales order's lifecycle:
Note
|
Type of Business Rule |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Process Assignment |
Assign the orchestration process that Order Management runs to process order lines. For example:
For details, see Assign Orchestration Processes. |
|
Process a sales order.
Process a change order.
|
Set up a rule that affects processing, such as branch in an orchestration process, do a complex calculation that determines planning lead time, or manage a change that happens to the sales order. For example:
|
|
Routing Rule |
Set up a rule that routes a fulfillment request to a fulfillment system according to an attribute on the sales order, order line, or orchestration process. For example:
For details, see Overview of Connecting Order Management to Your Fulfillment System. |
When Should I Use An Extension?
Order Management converts each source order that you create in Order Management or that it receives from a source system so it can optimize order fulfillment. You can use an order management extension to:
-
Populate order attributes before conversion.
-
During conversion.
-
Populate order attributes after conversion.
For example:
-
Populate an attribute on the order line. If the item is a widget, then populate the Request Date attribute.
-
Convert a measurement. If the item is a widget, then convert the value in the Size attribute from centimeters to inches in the order line.
-
Create order lines from one item. For example, if the item is a laptop that includes a docking station, then convert the item into one order line for the laptop and another line for the docking station.
See Overview of Creating Order Management Extensions.
Use Visual Information Builder to Create Rules
You can use Visual Information Builder to create some types of rules, which is a rule editor that supports a simplified drag-and-drop interface. It helps you visualize data, visualize your business processes, implement your business logic, and implement your business rule sets.
We strongly recommend that you use only Visual Information Builder for routing and assignment rules.
Use these pages to access the editors:
|
Editor for Oracle Business Rules |
Editor for Visual Information Builder |
|---|---|
|
Manage External Interface Routing Rules |
Manage External Integration Routing Rules for Sales Orders |
|
Manage Orchestration Process Assignment Rules |
Manage Process Assignment Rules for Sales Orders |
Examples of Creating Business Rules
Visual Information Builder
See:
-
Route Requests from Order Management to Fulfillment Systems Without Cross-References
-
Integrate Order Management Without Cross-Referencing Customer Attributes
Oracle Business Rules
See:
|
Page |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Manage Orchestration Process Definitions |
Get details about the rules that you set up on an orchestration process. Get details about the rules that pause an orchestration process. Get details about the rules that control status. |
Learn how to use business rules with extensible flexfields. For details, see Overview of Setting Up Extensible Flexfields in Order Management.
Examples That Include Orchestration Process Attributes
|
Orchestration Process Attribute |
Details |
|---|---|
|
Cost of Change |
|
|
Compensation Pattern |
|
|
Lead-Time Expression |
|
|
Line Selection Criteria |
|
|
Branching Condition |
|
|
Start-After Condition |
Pause Orchestration Processes for Events |
You use the Manage Orchestration Process Definitions page to set these attributes. For details, see Guidelines for Setting Up Orchestration Process Steps.