Understanding Data
Introduction
User Defined Data in Communication Cloud Service enables a flexible and customizable data handling mechanism. It facilitates efficient mapping, transformation, and formatting of data sourced from consuming service/application. This ensures that the final communication content is accurate and tailored to your business needs.
- Definition and reuse of Field as per business requirement.
- Inclusion of Document, Layout or Content for each and every occurrence of the Field's data available in either Array or List Type Field.
- Transformation of data to produce new data to be included in the output.
- User Defined Data – It is the top-level configuration within your Operations Company. Field Group, Structure, and Format configurations are associated to a User Defined Data configuration.
- Field Group – It enables you to group different Fields together logically based on their characteristics.
- Field – It is a unique data point where you can populate a value of type: Date, Number, String, Array, List, File, and more. It enables you to easily iterate based on field data or transform existing field as needed. Use Field Iteration for ordering of data in Array or List Field Types. Use Field Transform to transform existing data and produce new data like concatenated data fields or addition of some data fields and more.
- Structure – You can configure data structure to identify a complete set of Fields mapping the specific JSON data structure passed onto Communication Cloud Service to accomplish a specific business operation. The JSON data can either be provided by the consuming application/service or can be created by Communication Cloud Service based on the XML data provided by the consuming application/service.
- Format – You can define a data format specific to your business requirement that can be used across Fields in multiple communications through Content Components in the Content Editor.
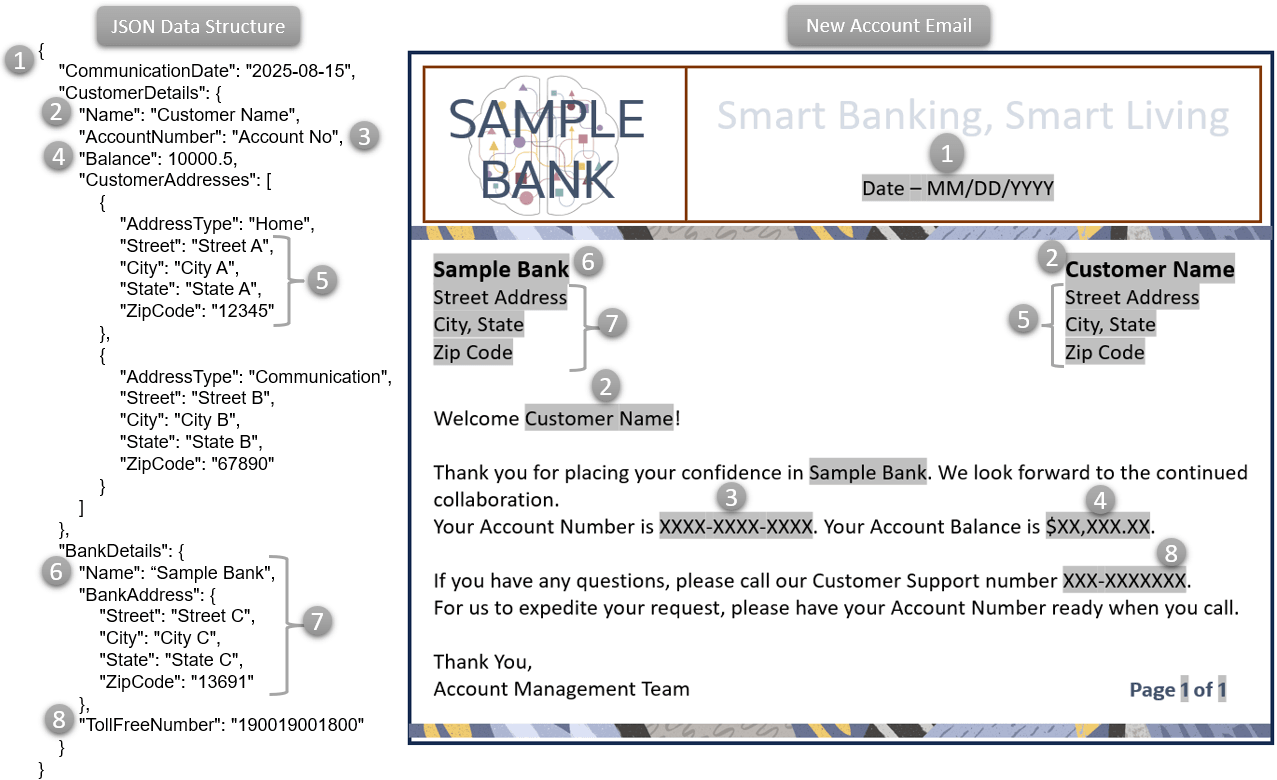
{
"CommunicationDate": "2025-08-15",
"CustomerDetails": {
"Name": "Customer Name",
"AccountNumber": "Account No",
"Balance": 10000.5,
"CustomerAddresses": [
{
"AddressType": "Home",
"Street": "Street A",
"City": "City A",
"State": "State A",
"ZipCode": "12345"
},
{
"AddressType": "Communication",
"Street": "Street B",
"City": "City B",
"State": "State B",
"ZipCode": "67890"
}
]
},
"BankDetails": {
"Name": "Bank A",
"BankAddress": {
"Street": "Street C",
"City": "City C",
"State": "State C",
"ZipCode": "13691"
},
"TollFreeNumber": "190019001800"
}
}
- Create the following Fields:
- CommunicationDate - Field Type = Date and Default Value = 2025-08-15.
- CustomerDetails - Field Type = Object and Parent Field for the following Child Fields:
- Name - Field Type = String
- AccountNumber - Field Type = String
- Balance - Field Type = Number
- CustomerAddresses - Field Type = Array. Create AddressDetails Field with Field Type = Object. Create the following Fields as Child Fields to AddressDetails Field. Then to the CustomerAddresses Field add Iteration associated to AddressDetails Field to order and display multiple Addresses with following details:
- AddressType - Field Type = String
- Street - Field Type = String
- City - Field Type = String
- State - Field Type = String
- ZipCode - Field Type = String
- BankDetails - Field Type = Object and Parent Field for the following Child Fields:
- Name - Field Type = String
- BankAddress - Field Type = Object and Parent Field for the following Child Fields:
- Street - Field Type = String
- City - Field Type = String
- State - Field Type = String
- ZipCode - Field Type = String
- TollFreeNumber - Field Type = Number, Default Value = 190019001800
- Create a Structure namely New Account Email of Type Object. Create a Structure Version, associate all above fields and add JSON Path to the JSON Structure received from the consuming service/application.
Using this Structure and its Fields within Document, Layout, or Content, where these Fields are mapped to the Content Controls/Components, you can generate New Account Email. You can then distribute it to all your newly registered customers. The following image illustrates an example of a Sample Bank that distributes New Account Email to its newly registered customers. The Fields involved in it are highlighted in gray and mapped to the data received in JSON Structure:
Functionalities
- Flexible - It accommodates various data formats and structures, making it more adaptable to your business needs. You can define data unique to your business processes and preferred data formats.
- Efficient - Its flexible and customizable data handling mechanism minimizes the need for frequent template updates, saving time and resources.
- Accurate - It also allows efficient mapping, transformation, and formatting of data from consuming service/application. This ensures that your communication content is accurate and tailored to your business and customer needs.
Configuration Movement
The User Defined Data, Field Group, Field, Structure, and Format configurations follow the configuration movement process; that is, if you configure any one of them in one tenancy (non-production), you can move the configuration to different tenancies (pre-production and production) sequentially.
For more information refer, Understanding Configuration Movement topic.
Video Tutorials
User Defined Data in Communication Cloud Service video:
Learn how to map incoming JSON data to content and layouts using User Defined Data, with step-by-step instructions for configuring containers, field groups, fields, structures, and formats. The video also covers field mapping, data transformation, and formatting options.