16 Diagnosing Problems with Oracle Web Services Manager
Topics:
16.1 Diagnosing Policy Manager Problems Using the OWSM Policy Manager Page
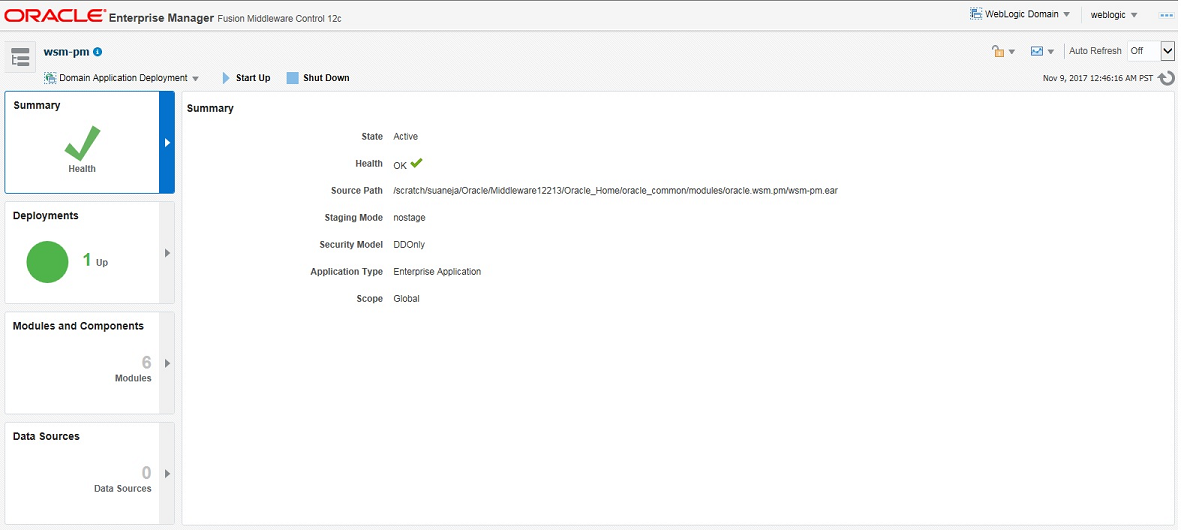
The OWSM Policy Manager manages all OWSM policies and needs to be running to use the OWSM policy framework. You can check the current state of the Policy Manager and review its response time, load, and other data from the OWSM Policy Manager page in Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control.
If the OWSM Policy Manager is not available, then any modifications that you make to policy attachments for ADF and WebCenter services and clients will not be saved to the OWSM repository.
To view the OWSM Policy Manager page:
From the Policy Manager page, you can perform one or more of the following tasks:
-
In the Summary section of the page, you can check the current state of the Policy Manager and identify the server to which it is deployed.
-
In the Deployments section of the page, you can view the Name, Status, State, Health, Type and Targets of the deployments.
-
In the Modules and Components section of the page, you can check the modules, components, test points and web services deployed. You can validate the connection to the Policy Manager by clicking the Test Point URL for wsm-pm. On the Validate Policy Manager page, click Validate Policy Manager.
-
In the Data Sources section of the page, you can check the data sources if any and their location.
Note:
You can also access the Validator page in a web browser using the following URL:
http://host:port/wsm-pm/validator
In this URL, host and port represent the host and port number on which the Policy Manager is running.
If the connection to the Policy Manager fails, an error message is displayed. If the connection to the Policy Manager is successful, the Policy Manager Validator page displays the following information:
-
The status of the Policy Manager.
-
The total number of OWSM policies in the OWSM repository
-
The name, latest version, and description of all the OWSM policies in the OWSM repository.
-
The total number of OWSM assertion templates in the repository
-
The name, latest version, and description of all the OWSM assertion templates in the OWSM repository.
-
The creation date and build label of the repository.
For details about the OWSM repository, see Managing the Oracle Web Services Manager Repository.
16.2 Overview of Common Problems with Oracle Web Services Manager
You may encounter some common problems while using OWSM. This section discusses those problems, as well as possible solutions.
Topics:
-
Overview of Key Store or Credential Store Errors After an Application Invokes a Web Service
-
Overview of Trust Certificate Error After Application Invokes a Web Service
-
About Troubleshooting SAML Assertion Errors During Identity Propagation
-
Overview of Policy Access Problems After an Application Invokes a Web Service
-
Overview of Problems Accessing Users in the Credential Store
-
Overview of Common User Authorization Problems After an Application Invokes a Web Service
-
Overview of Timestamp Errors After an Application Invokes a Web Service
16.2.1 Overview of Common Policy Manager Connection Problems
You might encounter some common Policy Manager connection issues. This section helps you diagnose and resolve those problems.
It includes the following topics:
16.2.1.1 Understanding Common Policy Manager Connection Problems
When a connection to the Policy Manager fails, one or more of the following error messages are displayed:
-
WSM-06157: The repository database is not configured correctly or not running. -
WSM-06160: The policy manager application has not been deployed or is not running. -
WSM-06161: The policy manager application has not been deployed. -
WSM-06162: The policy manager application is not running or is not configured correctly. -
WSM-06159: Cannot connect to the policy manager due to credential issue. -
WSM-02120: Unable to connect to the policy access service.
Problems connecting to the Policy Manager are commonly caused by the following:
-
The Policy Manager is down.
You can determine if the Policy Manager is down as follows:
-
The state of the Policy Manager in the General area of the OWSM Policy Manager home page, as described in "Diagnosing Policy Manager Problems Using the OWSM Policy Manager Page" is shown as
Shutdown. -
The status of the
wsm-pminternal application on the Domain home page in Fusion Middleware Control is Down, as shown in Figure 16-2. To access the Domain home page, select Home from the WebLogic Domain menu in the top left-hand corner of the page.Figure 16-2 OWSM Policy Manager Shutdown (Farm Page)
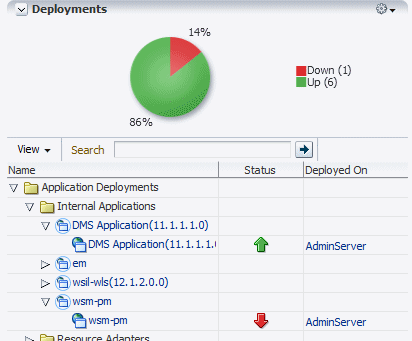
Description of "Figure 16-2 OWSM Policy Manager Shutdown (Farm Page)" -
An error dialog box displays when you attempt to access the OWSM policy management pages in Fusion Middleware Control. This error information is also written to the diagnostic log file, as described in "Reviewing Sample Logs" in Administering Web Services.
-
-
The domain is configured to use auto-discovery with SSL.
OWSM supports an auto-discovery feature that it uses to locate and connect to the OWSM Policy Manager. If the domain is configured to use auto-discovery with SSL, then the auto-discovery logic will always try to connect to an SSL-enabled server. To ensure that the secure connection is maintained, the auto-discovery logic will not attempt to connect to a Policy Manager on a non-SSL server, even if the SSL-enabled server goes down. Therefore, even though there is a Policy Manager running, because it is running on a non-SSL enabled server, it is ignored and an error message is displayed.
-
The credential required to access the Policy Manager is invalid or is not authorized.
-
The repository may not be configured correctly.
-
The cross-component wiring for the Policy Manager and Agent may not be current.
16.2.1.2 Solving Policy Manager Connection Problems
You can use the following information to fix the most common Policy Manager connection problems:
-
If the Policy Manager is down, then restart the wsm-pm application as described in "Starting and Stopping Applications" in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.
-
If the domain is configured to use auto-discovery with SSL, then
-
Verify that the wsm-pm Policy Manager application is targeted to an SSL server. Use the WebLogic Server Administration Console as described in "Target an Enterprise application to a server" in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Online Help.
-
Verify that SSL has been configured correctly and that there are no SSL certificate issues. For additional information, see About Configuring Keystores for SSL
-
If the SSL-enabled server is down, restart the server and the Policy Manager application, as described in "Starting and Stopping Oracle Fusion Middleware" in Administering Oracle Fusion Middleware.
-
Verify that the service table and component configuration are correctly configured for SSL. For more information, see Cross-Component Wiring for Auto-Discovery of Policy Manager
-
If you want to use the Policy Manager on a non-SSL enabled server, then modify the auto-discovery configuration. For more information, see "Understanding Configuring the Policy Manager Connection Using Fusion Middleware Control" and Configuring the Policy Manager Connection Using WLST
-
-
If there is a credential issue when attempting to access the Policy Manager, then check the user account. By default, the OWSM run time uses the OracleSystemUser account. If you are not using the default user accounts, you need to modify the configuration as described in About Modifying the Default User
-
If there is a problem with the repository configuration, then
-
Verify that the database and MDS schema are setup correctly. This configuration is performed as part of the installation process. For more information, see "Creating the Database Schemas" in Installing and Configuring the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure.
-
Verify that the JDBC configuration is correct. The JDBC configuration is defined when you create the domain using the Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard. For more information, see "Configuring Your WebLogic Domain" in Installing and Configuring the Oracle Fusion Middleware Infrastructure.
-
-
If there is a problem with the cross-component wiring, then
-
Verify that the service table entry corresponding to the OWSM Policy Manager contains the correct URL.
-
Verify that the wiring between the OWSM Agent Hook and the OWSM Policy Manager is in the
wiredstate.
-
For more information, see the following topics:
16.2.2 Overview of Key Store or Credential Store Errors After an Application Invokes a Web Service
You may need information to diagnose and resolve common problems that cause key store or credential store errors after an application invokes a web service.
Topics:
16.2.2.1 Understanding Common Key or Credential Store Errors
If a key store or credential store problem occurs after an application invokes a web service, then an error message similar to the following is displayed:
-
WSM-00056: The key <alias_name> is not retrieved -
WSM-00256: The property "Keystore Sign Alias" is not set -
WSM-0024: Unable to read key from KSS keystore -
WSM-00340: Key does not exist in the KSS keystore
Key store and credential store errors are commonly caused by the following problems:
-
For the JKS keystore:
-
The alias for the signature key or encryption key in the OWSM keystore configuration does not exist in the OWSM keystore.
-
The signature key, encryption key, or OWSM keystore password is not synchronized between the keystore file and the keystore configuration for OWSM. That is, at least one of the passwords does not have identical values in both locations.
-
The signature key is not set.
-
There is a missing key in the credential store.
-
-
For the KSS keystore:
-
The keystore may have not been initialized or the necessary permissions are not granted.
-
The key does not exist in the keystore. The key you entered on the domain configuration Message Security screen cannot be found in the keystore.
-
16.2.2.2 Solving Key and Credential Store Problems
You can use the following information to fix common key store and credential store problems.
-
Verify that the alias for the signature key and encryption key in the OWSM keystore configuration exists in the OWSM keystore file, as follows:
-
Use Fusion Middleware Control to identify the alias for the signature key and encryption key in the OWSM keystore configuration by performing the procedure in Configuring the OWSM Keystore
-
Verify that the aliases identified in step 1 exist in the OWSM keystore file.
For a JKS keystore:
Use the
keytool -listcommand on the OWSM keystore file, as described in step 4 of Generating Private Keys and Creating the Java Keystore For detailed information about using the keytool utility, see the keytool - Key and Certificate Management Tool document at the following URL:http://download.oracle.com/javase/6/docs/technotes/tools/windows/keytool.htmlNote:
If you are unable to locate the document at the above URL, you can access it by searching for it on the Search Java SE Technical Documentation web page at:
-
Ensure each alias is synchronized in both the keystore file and the OWSM keystore configuration in the credential store. If they are not, you can edit the alias in the OWSM keystore configuration by performing the procedure described in Configuring the OWSM Keystore You can edit the alias in the OWSM keystore file using the
keytool -changealiascommand.Note:
Before you edit an alias, be sure that doing so will not affect any other web service.
-
If the alias for the signature key or encryption key does not exist in the OWSM keystore file, add it as described in Generating Private Keys and Creating the Java Keystore
For a KSS keystore:
Use Fusion Middleware Control to manage the contents of the keystore and ensure that the alias matches. For more information, see "Managing Keys and Certificates with the Keystore Service" in Securing Applications with Oracle Platform Security Services.
-
-
-
Ensure the passwords are synchronized, as follows:
For a JKS keystore, ensure that the signature key, encryption key, and OWSM keystore file passwords are each synchronized in the keystore file and the keystore configuration for OWSM, as follows:
-
Use
keytoolto reset the passwords in the OWSM keystore file. Because the passwords are not visible, resetting them is the only method to ensure that they have identical respective values in both locations.-
Use the
keytool -storepasswdcommand to reset the OWSM keystore file password. -
Use the
keytool -keypasswdcommand to reset the signature key password and encryption key password.
-
-
Use Fusion Middleware Control to reset the passwords in the OWSM keystore configuration to the same respective values you set in step 1, as described in Configuring the OWSM Keystore
-
16.2.3 Overview of Trust Certificate Error After Application Invokes a Web Service
You may need information to help you diagnose and resolve a trust certificate error that occurs after an application invokes a web service.
Topics:
16.2.3.1 Understanding a Trust Certificate Error
The trust certificate error commonly occurs when the web service is advertising its certificate in the Web Services Description Language (WSDL) and the client may not be configured correctly to trust that certificate or its issuer.
If a trust certificate problem occurs after an application invokes a web service, the following error message is displayed:
WSM-00138: The path to the certificate is invalid due to exception
16.2.4 About Troubleshooting SAML Assertion Errors During Identity Propagation
You may need information to help you troubleshoot SAML assertion problems that occur during identity propagation.
Topics:
16.2.4.1 Understanding Common SAML Assertion Problems
If a problem occurs when an application attempts to propagate a user's identity by calling a different application, then you will see InvalidSecurityToken, FailedAuthentication, and SAML assertion issuer related errors.
SAML assertion errors are commonly caused by the following problems:
-
The SAML issuer name for the SAML token is not configured or is configured incorrectly.
-
The
subject.precedenceconfiguration override is set incorrectly.
16.2.4.2 Troubleshooting SAML Assertion Problems
You can use the following information to troubleshoot the most common Policy Manager connection problems:
-
To troubleshoot the SAML issuer name configuration:
Verify that the SAML Issuer Name that the client is using is among the issuers configured in the Oracle WebLogic Server domain. To do so, perform the steps described in SAML Trusted Issuers and DN Lists Using Fusion Middleware Control
If the SAML Issuer Name that the client is using is not configured as an issuer in the Oracle WebLogic Server domain, Oracle recommends changing the issuer name on the client by updating its
saml.issuer.nameoverride to one of the issuers configured in the domain.If you cannot change the issuer name on the client, you can add its issuer name to the Oracle WebLogic Server domain by performing the steps in the SAML Trusted Issuers and DN Lists Using Fusion Middleware Control
-
To troubleshoot the subject.precedence configuration override:
-
Set the
subject.precedenceoverride value in your current client policy to false to change the identity to a different user. By default, thesubject.precedenceoverride is set to true. -
Set the appropriate Credential Store Framework key override on the client policy that contains the user name and password of the user you want to send to the service. If an entry for this user does not exist in the Credential Store Framework, you must add it. For more information, see Adding Keys and User Credentials to Configure the Credential Store
-
Ensure the appropriate Web Services Identity Permission is set for the client application by performing the steps in About SAML Web Service Client Configuration for Identity Switching
-
16.2.5 Overview of Policy Access Problems After an Application Invokes a Web Service
You may need information to help you diagnose and resolve problems that cause policy access errors that occur after an application invokes a web service.
Topics:
16.2.5.1 Understanding Common Policy Access Problems
If a policy access problem occurs after an application attempts to invoke a web service, then an error message similar to the following is displayed:
-
WSM-06156: The policy URI is missing, empty or contains invalid characters. -
WSM-06158: The referenced policy does not exist in the repository. -
WSM-02017: The document was not found in the repository.
Policy access issues that occur after an application invokes a web service are commonly caused by the following problems:
-
The Policy Manager is down
-
The policy URI is missing or the policy name is misspelled.
-
The policy does not exist in the repository
-
The policy attachment is not in effect due to a cache delay.
16.2.6 Overview of Problems Accessing Users in the Credential Store
You may need information to help you diagnose and resolve problems that prevent OWSM from locating a user in the credential store.
Topics:
16.2.6.1 Understanding Common User Access Problems
If OWSM cannot access a user in the credential store, then an error such as the following is displayed:
WSM-00015: The user name is missing
User access issues are commonly caused by the following problems:
-
The credential map
oracle.wsm.securitydoes not exist in the credential store. -
The user is not listed in the map used by OWSM.
-
The CSF key for the entry does not exist in the credential store.
16.2.6.2 Solving User Access Problems
You can use the following information to fix common user access problems.
Verify that the credential map oracle.wsm.security exists in the credential store. OWSM only reads from this credential store map.
To determine if the oracle.wsm.security credential map exists in the credential store, refer to the procedure in Adding Keys and User Credentials to Configure the Credential Store
If your application uses a credential map other than oracle.wsm.security, ensure that any users that OWSM needs to access are duplicated in the oracle.wsm.security credential map.
16.2.7 Overview of Common User Authorization Problems After an Application Invokes a Web Service
You may need information to help you diagnose and resolve problems that cause user authorization issues that occur after an application invokes a web service.
Topics:
16.2.7.1 Understanding Common User Authorization Problems
If your system fails to authorize a user, then a message similar to the following might be displayed:
java.security.AccessControlException: access denied (oracle.wsm.security.WSFunctionPermission
Generally, failure to authorize a user is not really a problem but rather intended behavior; that is, the system was unable to authorize the user for the action that the user was attempting.
16.2.8 Overview of Timestamp Errors After an Application Invokes a Web Service
You may need information to help you diagnose and resolve problems that can cause a timestamp error after an application invokes a web service.
Topics:
16.2.8.1 Understanding the Causes a Timestamp or clockSkew Error
If a timestamp problem occurs after an application invokes a web service, then an error similar to the following is displayed:
WSM-00060: Error validating timestamp
The problem manifests itself as a timestamp validation or clockSkew error, as follows:
Caused By: FAULT CODE: InvalidSecurityToken FAULT MESSAGE: Found invalid condition "on or after" in SAML assertion. Current Time:Fri Feb 11 22:16:42 IST 2011, clockSkew:300000 milli seconds, NotOnOrAfter Time:Fri Feb 11 14:21:42 IST 2011.
This problem usually happens if your server and client clocks are more than five minutes apart after they are converted to the same time zone.
16.2.8.2 Solving Timestamp or clockSkew Errors
Change your client or server clock in one of the following ways so that they are within five minutes, both set to the correct time:
-
Adjust the Clock Skew as described in Configuring Security Policy Enforcement Using Fusion Middleware Control
-
Set the system clock.
-
Use an ntp server to maintain the time.
16.2.9 Overview of Multiple Authentication Security Policy Errors After an Application Invokes a Web Service
You can diagnose and resolve multiple authentication policy errors that occur after an application invokes a web service.
Topics:
16.2.9.1 Understanding Common Multiple Authentication Security Policy Errors
If a multiple authentication security policy problem occurs after an application invokes a web service, a multiple policy error (WSM-01823) is displayed in the log. For example, this error appears if multiple authentication policies are attached to a subject.
Multiple authentication policy errors commonly occur when more than one authentication policy is attached to a subject. This situation can happen if you have two policy sets that each attach an authentication policy to the same resource type, such as a web service. For example, if you have two policy sets defined in the OWSM repository for your domain and one defines the policy scope as Domain("domain_name") and the other as Domain ("*").
The following listing illustrates an example of this scenario.
wls:/base_domain/serverConfig> displayWSMPolicySet('default-domain-ws-domain_gpa')
Policy Set Details:
-------------------
Display Name: default-domain-ws-domain_gpa
Type of Resources: SOAP Web Service
Scope of Resources: DOMAIN("base_domain")
Description: Global policy attachments for Web Service Endpoint resources.
Enabled: true
Policy Reference: URI=oracle/wss11_saml_or_username_token_with_message_protection_service_policy, category=security, enabled=true
wls:/base_domain/serverConfig> displayWSMPolicySet('default-domain-ws-domain')
Policy Set Details:
-------------------
Display Name: default-domain-ws-domain
Type of Resources: SOAP Web Service
Scope of Resources: DOMAIN("*")
Description: Global policy attachments for Web Service Endpoint resources.
Enabled: true
Policy Reference: URI=oracle/wss_saml_or_username_token_service_policy, category=security, enabled=true
In this example, there are two policy sets with different names and different authentication policies pointing to the same resource type on the domain.
Note:
If the authentication policies attached to the subject are exact duplicates of each other, including any configuration overrides, the policy attachment is viewed as a duplicate and the configuration is valid.
16.2.9.2 Solving Multiple Authentication Security Policy Errors
Use the following steps to verify if you have multiple policy sets attempting to attach authentication policies:
For more information, see Determining the Secure Status of an Endpoint
16.3 Overview of Policy Attachment Issues Using WLST
You use WLST commands to diagnose policy attachment issues.
This section contains the following topics:
16.3.1 Understanding the Use of listWSMPolicySubjects Command to Identify Policy Attachment Issues
To ensure that there are no conflicts between directly-attached policies and policies attached globally using policy sets, use the listWSMPolicySubjects (detail="true") WLST command.
This command displays a list of the web services or web service clients in a domain including endpoint configuration, the effective set of policies attached to each endpoint, the secure status of the endpoint, any configuration overrides and constraints, and if the endpoint has a valid configuration. For information about using this command, see "Viewing the Web Services in a Domain Using WLST" in Administering Web Services.
Note:
An endpoint is considered secure if the policies attached to it (either directly, or externally using a policy set) enforce authentication, authorization, or message protection behaviors.
If your configuration includes policies attached globally using policy sets, you can view information about the policy sets using the following commands:
-
listWSMPolicySets()— Displays a list of the policy sets in the repository. For information about using this command, see Viewing a List of Policy Sets -
displayWSMPolicySet()— Displays the configuration of a specific policy set. For information about using this command, see Displaying the Configuration of a Policy Set
To view the effective policies for an endpoint using Fusion Middleware Control, see Viewing Policies Attached to a Web Service Using Fusion Middleware Control
For more information about determining if the endpoint is secure and has a valid configuration, see Determining the Secure Status of an Endpoint
16.3.2 Viewing a Sample Configuration Output with Globally and Directly Attached Policies
You use the listWSMPolicySubjects(detail=true) command for viewing a valid configuration. Because you can specify the priority of a global or directly attached policy (using the reference.priority configuration override), the effective field indicates if directly attached policies are in effect for the endpoint.
The global and directly attached security policies are shown in bold.
Note:
To simplify endpoint management, all directly attached policies are shown in the output regardless of whether they are in effect for the endpoint. In contrast, only globally attached policies that are in effect for the endpoint are displayed.
Application: /WLS/base_domain/jaxwsejb30ws
Assembly: #jaxwsejb
Subject: WS-Service({http://www.oracle.com/jaxws/tests/concrete}WsdlConcreteService#WsdlConcretePort)
URI="oracle/wss_saml_or_username_token_service_policy", category=security, policy-status=enabled;
source=global policy set "default-domain-ws-domain", scope="DOMAIN('*')";
reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="reference.priority", value="10"
URI="oracle/mex_request_processing_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/mtom_encode_fault_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/max_request_size_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
Property name="max.request.size", value="-1"
URI="oracle/request_processing_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/soap_request_processing_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/ws_logging_level_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
Property name="logging.level", value=""
URI="oracle/test_page_processing_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/wsdl_request_processing_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/wss10_saml20_token_with_message_protection_service_policy", category=security, policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=false
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="LOCAL_ATTACHMENT"
The policy subject is secure in this context.
16.3.3 Viewing a Sample Valid Configuration Output with Directly Attached Policies Only
You use listWSMPolicySubjects(detail=true) command for viewing a valid configuration.
The following example shows sample output from the command with directly attached policy shown in bold.
Application: /WLS/base_domain/jaxwsejb30ws
Assembly: #jaxwsejb
Subject: WS-Service({http://www.oracle.com/jaxws/tests/concrete}WsdlConcreteService#WsdlConcretePort)
URI="oracle/mex_request_processing_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/mtom_encode_fault_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/max_request_size_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
Property name="max.request.size", value="-1"
URI="oracle/request_processing_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/soap_request_processing_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/ws_logging_level_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
Property name="logging.level", value=""
URI="oracle/test_page_processing_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/wsdl_request_processing_service_policy", category=wsconfig,
policy-status=enabled; source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="IMPLIED_FEATURE"
URI="oracle/wss10_saml20_token_with_message_protection_service_policy", category=security, policy-status=enabled;
source=local policy set; reference-status=enabled; effective=true
Property name="local.policy.reference.source", value="ANNOTATION"
The policy subject is secure in this context.
16.4 About Diagnosing Problems With a Domain Configuration Using WLST
You use WLST commands to diagnose domain configuration issues.
This section contains the following topics:
16.4.1 Understanding the Use of checkWSMStatus Command to Identify Domain Configuration Issues
To ensure that there are no problems with the configuration of your domain, use the checkWSMStatus WLST command. The checkWSMStatus command returns the status of the policy manager (wsm-pm), the agent (agent), the credential store and keystore configuration (credstore), Oauth2 configuration (oauth2), and Policy Manager history (pmHistory). The status of the components can be checked together or individually.
This command can be run after the provisioning of your WSM-protected web service; there is no need to wait until after the first invocation.
Note:
The Policy Manager (wsm-pm) application must be deployed and running for the checkWSMStatus command to function correctly.
For more information about the arguments for this command, see "checkWSMStatus command" in the WLST Command Reference for Infrastructure Components.
16.4.2 Viewing checkWSMStatus Output Showing Status
The checkWSMStatus command returns the status of the credential store and keys, the Policy Manager, and the enforcement agent for the domain.
The following example illustrates this for the domain base_domain:
wls:/base_domain/serverConfig> checkWSMStatus(verbose='true')
Health check for server "EXAMPLESERVER":
Credential Store Configuration:
PASSED.
Message(s):
keystore.pass.csf.key : Property is configured and its value is "keystore-csf-key".
Description: The "keystore.pass.csf.key" property points to the CSF alias that is mapped to the username and password of the keystore. Only the password is used; username is redundant in the case of the keystore.
keystore-csf-key : Credentials configured.
keystore.sig.csf.key : Property is configured and its value is "sign-csf-key".
Description: The "keystore.sig.csf.key" property points to the CSF alias that is mapped to the username and password of the private key that is used for signing.
sign-csf-key : Credentials configured.
Sign Key : Key configured.
Alias - orakey
Sign Certificate : Certificate configured.
Alias - CN=weblogic, OU=Orakey Test Encryption Purposes Only, O=Oracle, C=US
Expiry - June 28, 2020 11:17:12 AM PDT
keystore.enc.csf.key : Property is configured and its value is "enc-csf-key".
Description: The "keystore.enc.csf.key" property points to the CSF alias that is mapped to the username and password of the private key that is used for decryption.
enc-csf-key : Credentials configured.
Encrypt Key : Key configured.
Alias - orakey
Encrypt Certificate : Certificate configured.
Alias - CN=weblogic, OU=Orakey Test Encryption Purposes Only, O=Oracle, C=US
Expiry - June 28, 2020 11:17:12 AM PDT
Policy Manager:
PASSED.
Message(s):
OWSM Policy Manager connection state is OK.
OWSM Policy Manager connection URL is "host.example.com:1234".
Enforcement Agent:
PASSED.
Message(s):
Enforcement is successful.
Service URL: http://host:port/Diagnostic/DiagnosticService?wsdl
Health check status on server EXAMPLESERVER is PASSED.
Health check status for system is PASSED.16.4.3 Viewing checkWSMStatus Output Showing Credential Store Failure
You can use the checkWSMStatus command to see the credential store failures.
In the following example, the checkWSMStatus command returns a failure for the credential store because it is missing the key keystore-csf-key.
wls:/base_domain/serverConfig> checkWSMStatus('credstore',target='EXAMPLESERVER')
Health check for server "EXAMPLESERVER":
Credential Store Configuration:
FAILED.
Message(s):
keystore.pass.csf.key : Property is configured and its value is "keystore-csf-key".
Description: The "keystore.pass.csf.key" property points to the CSF alias that is mapped to the username and password of the keystore. Only the password is used; username is redundant in the case of the keystore.
keystore-csf-key : Credentials configured.
keystore.sig.csf.key : Property is configured and its value is "sign-csf-key".
Description: The "keystore.sig.csf.key" property points to the CSF alias that is mapped to the username and password of the private key that is used for signing.
sign-csf-key : Credentials configured.
Sign Key : Key not configured.
oracle.wsm.security.SecurityException: WSM-00111 : Keystore is not properly configured. Check your keystore configurations.
Credential Store Diagnostic Messages:
Message(s):
The alias orakey is either not present in the keystore or is configured incorrectly. Check the contents of the keystore and the password for the alias "orakey". The password of the alias "orakey" should be the same as the password stored in the csf key=sign-csf-key
NOTE:- All the above commands are based on the Domain level configurations. The actual alias may have been overridden at runtime due to configuration override.
Health check status on server EXAMPLESERVER is FAILED.
Health check status for system is FAILED.
16.4.4 Viewing checkWSMStatus Output With OAuth2 Global Policy Set Configured
The OAuth2 global policy set is Configured for ws-client (SOAP client) subject type. Since the command checks for the OAuth2 related configuration in the GPA attached at the domain level, the steps to create GPA for is also listed.
Example:
beginWSMSession();
createWSMPolicySet('oauthTestPolicySet','ws-client','Domain("jrfServer_domain")');
attachWSMPolicy('oracle/http_oauth2_token_client_policy');
attachWSMPolicy('oracle/oauth2_config_client_policy');
setWSMPolicyOverride('oracle/oauth2_config_client_policy','token.uri','http://myhost.us.example.com:14100/ms_oauth/oauth2/endpoints/oauthservice/tokens');
setWSMPolicyOverride('oracle/http_oauth2_token_client_policy','oauth2.client.csf.key','basic.client.credentials');
validateWSMPolicySet();
commitWSMSession()
wls:/test_domain1/serverConfig>checkWSMStatus('oauth2')
OAuth2 Client Configuration Status:
Message(s):
OAuth2 Client Configuration Checks for type SOAP Client: PASSED
Successful OAuth Configurations for Client Type(s): WS_CLIENT
Health check status on server jrfServer_admin is PASSED.
Health check status for system is PASSED.16.4.5 Viewing checkWSMStatus Output With OAuth2 Global Policy Set Not Configured
You can view the checkWSMStatus output With OAuth2 global policy set is not configured.
In the following example, no OAuth2 global policy sets are configured.
wls:/test_domain1/serverConfig>checkWSMStatus('oauth2')
OAuth2 Client Configuration Status:
Message(s):
No OAuth2 client policy (oauth2_config_client_policy or oauth token policy) attached in the domain for client type(s): REST_CLIENT, WS_CLIENT, SCA_REST_REFERENCE, SCA_REFERENCE
Health check for server "jrfServer_admin":
Health check status on server jrfServer_admin is FAILED.
Health check status for system is FAILED.
16.5 Common Oracle Web Services Manager Exceptions for WS-Trust Use Cases
You can fix the exception and error that occur during an end-to-end WS-Trust use case scenario, study the probable causes and recommended solutions, and use this to diagnose and solve common OWSM exceptions for WS-Trust use cases.
Table 16-1 lists the common OWSM exceptions and errors that can occur during an end-to-end WS-Trust use case scenario. The probable cause and recommended solutions are also provided. For details about how to configure the supported WS-Trust use cases, see the following chapters in Use Cases for Securing Web Services Using Oracle Web Services Manager:
Table 16-1 Common OWSM Exceptions and Errors for WS-Trust Use Cases
| Exception/Error | Possible Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
Override the |
|
|
When communicating with any service over an SSL channel, a valid SSL certificate for the service must be available in the trusted keystore for the JRE distribution being used in the environment. In most cases, the SSL certificate is found in the following directory: This exception can occur due to either of the following:
|
Ensure that a valid SSL certificate for the service has been imported into the trusted keystore at |
|
|
This exception occurs because both the client and the service do not have an STS trust config policy attached. For a simple WS-Trust use case, the STS trust config policy must be attached to either the client or the service application. Because there are no policies attached, the client does not know which STS to communicate with to get the SAML token. |
Attach an STS trust config policy to the client or service application as required for your configuration. For more information, see About WS-Trust Configuration |
|
|
The web service provider or Relying Party is not able to validate the Issuer's signature on the incoming SAML token. |
Make sure that you have imported the issuer's public key/certificate into the JKS/KSS keystore that the service is using. For detailed procedures, see Overview of Configuring Keystores for Message Protection |
|
|
The SAML assertion issuer name is not configured in the trusted issuers list in the domain in which the Relying Party service is deployed. |
Add the issuer to the list of trusted issuers in the domain in which the service is running. For detailed procedures, see: |
|
|
This exception can be thrown when a third party STS server is protected using a policy that does not have a compatible client policy in OWSM. Any STS endpoint that the client is trying to communicate with is protected with a security policy. Oracle STS uses OWSM which provides compatible client and service policies. In this case, the client should not have any trouble finding the corresponding client policy. |
The OWSM trust client has been tested with most common STS servers so it is unlikely that this exception will occur. In the event that this exception is thrown, a possible workaround is to attach a new or cloned version of the |
16.6 Managing third party server integration with OWSM
The Access tokens required to access third party servers become invalid in certain scenarios.
Access tokens do not generally expire, however your access token will become invalid if an user explicitly rejects your application from their settings or if a Twitter admin suspends your application. If your application is suspended, then there will be a note on your application page saying that it has been suspended.
Note:
You should plan for an user’s access token invalidity at any time and you will need to re-authorize the user in any such cases.If and when the token expires, the applications have no way of being notified and will have to rely on the error returned by their applications when invoking Twitter API. In such case when access token has expired, the error code will indicate that and the users will have to use the console (apps.twitter.com) to regenerate access token and update credential store with new value.
If the consumer secret is changed, there is no additional work required. The applications just need to use new consumer secret. Here is an excerpt from Twitter documentation :
If your consumer key and secret become compromised for any reason, you may need to reset it to re-gain secure control of your application’s identity and the actions taken in its name. Resetting your consumer key does not reset the strings representing your users (their “access tokens”) but does make your access tokens invalid when used with the former key. When your existent access tokens are used with your new consumer key and secret, they will continue functioning as expected. Your new consumer key and secret will be represented by completely different strings than its previous incarnation.