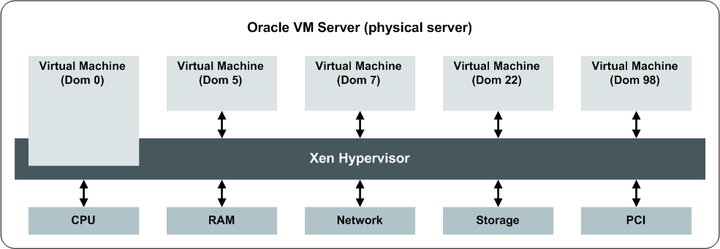
Oracle VM Server is a component of the Oracle VM product. Oracle VM Server is based on the Xen hypervisor. Oracle VM Server can be managed using Oracle VM Manager, or it can be managed as a standalone product with OpenStack.
Xen is a bare-metal (type 1) hypervisor. The hypervisor is controlled from a privileged environment (which is also itself a virtual machine) called Domain0, or Dom0. Dom0 controls the physical devices on the system, and connects them to the other virtual machines. Dom0 is also responsible for launching virtual machines called domU(s) using tools run from the user space. When launching a virtual machine, Xen connects domU to storage and network resources.
Since dom0 is itself a virtual machine, any memory assigned to it cannot be used for domUs. Sufficient dom0 memory is important for performance and correct operation, so it is important to adhere to the minimum memory requirements. See Section 3.1, “System Requirements” for information on the memory requirements for using Oracle VM Server as a compute node.
The libvirt driver is used to connect Oracle VM Server to OpenStack. The libvirt driver fully supports Xen. On Oracle VM Server compute node, the libvirt driver is used natively (libvirt runs in a Docker container on Oracle Linux compute nodes). All other OpenStack compute node services are run in Docker containers on dom0.
The version of Oracle VM Server supported is Oracle VM Server Release 3.4.2, which uses Oracle’s Unbreakable Enterprise Kernel Release 4 (also known as UEK R4), an upstream Linux kernel hardened and shipped by Oracle. As a result, Oracle VM Server uses the latest versions of hardware drivers and Open vSwitch.