


|

|
|
|
|
What Is a Single-machine Configuration
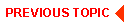
A single-machine configuration consists of one or more local or remote clients that communicate with one or more servers residing on a single machine running one or more business applications. Even though it may include multiple applications, this type of configuration is considered a single domain because it is administered as a single entity. All the managed elements (services, servers, and so on) of all the applications in this configuration are defined in and controlled from one BEA Tuxedo configuration file. The basic parts of a single-machine configuration when installed and running on a single machine are illustrated in the following diagram.
A Single-machine BEA Tuxedo Configuration
Parts of a Single-machine Configuration

|
|

|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2000 BEA Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
|