| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS Custom Encoders User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS Custom Encoders User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
Understanding the Encoder Framework
Parent, Child, and Sibling Nodes
Creating the Abstract Message Definition
Applying Custom Encoding to an XSD
To Apply the Custom Encoder to an XSD
Anchored and Detached Delimiters
Constant and Embedded Delimiters
Validating and Testing the Custom Message Definition
Validating the Custom Message Definition
Testing the Encoder Runtime Behavior
Using Custom Encoders in JBI Projects
To Use a Custom Encoder in a JBI Project
One of the parsing techniques that can be applied to the decoding of an input data stream is that of matching a specific byte pattern within a data sequence. You can accomplish this in a Custom Encoder by using the Match and Align field-node properties, when the Node Type is either delimited or fixedLength. During the decode operation, a field is successfully matched if it complies with the value of the Match property, interpreted according to the value of the Align property, as set for that field.
The value you enter for the Match property defines the byte pattern for the data you want to match. As an example, a value of abc has been entered into the value field shown in the following figure. This provides a reference for the Alignment property, as shown in the next section.
If the Node Type property is set to fixedLength, and the Fixed Length Type property is specified as determined by regex match, the Alignment property is automatically set to regex and the regular expression (regex) must be entered into the Match value field.
Selecting the No Match check box reverses the situation, resulting in a match if the field contents (data) are not equal to the byte pattern entered in the Match field.
Figure 4 Match Property
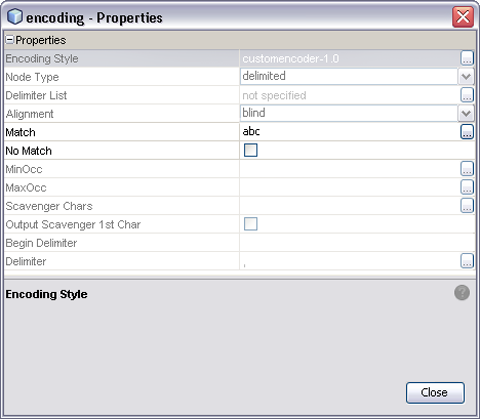
The align property supplements the match property, specifying criteria on which to base the match. The default value is blind; if this is specified, the match property has no meaning.
Figure 5 Align Property Menu
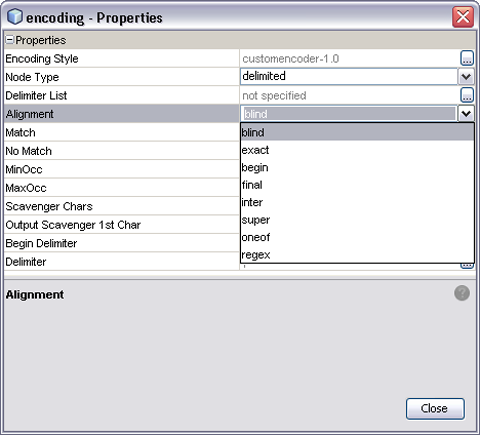
Table 7 Align Parameter Options
|
Note - The value entered for the match property is interpreted as a Latin1 string, rather than following the specified encoding.