Editing Encoding Properties
Once the encoding style is applied, you can edit detailed encoding rules at
the node level using the special encoding node under the element's annotation node.
The following figure shows the majority of encoding properties associated with various nodes.
Figure 2 Encoding Properties Dialog
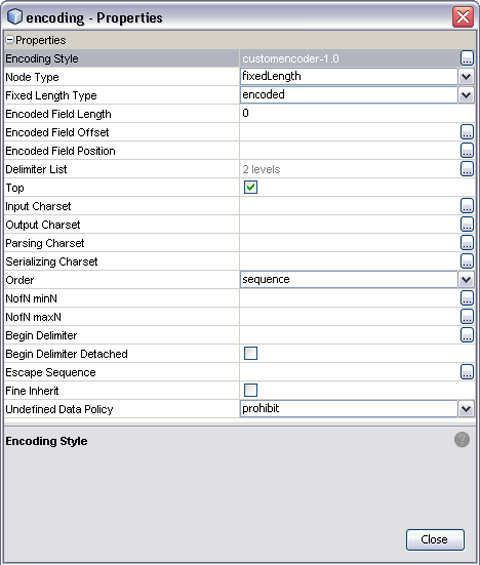
Encoding Properties
Table 1 General Properties
|
|
|---|
Encoding
Style |
Specifies the encoding style, for example: customencoder-[version]. |
Node Type |
Specifies the format for parsing
and serialization.
The options are:
group, which provides organizational grouping for purposes such as repetition. Does not apply to Choice Element nodes. array, which is a delimited structure. If repeated, occurrences are separated by the repeat delimiter. The last occurrence may be terminated by a normal delimiter. Does not apply to Choice Element nodes. delimited, which is a delimited structure. If repeated, occurrences are separated by a normal delimiter. Does not apply to Choice Element nodes. See Specifying Delimiters for additional information. fixedLength, which indicates a fixed length and is specified by non-negative integer (or zero to indicate end of parent node data). Does not apply to Choice Element nodes. transient, which appears only in an internal tree as a scratchpad field. It does not appear in external data representation, and can only have transient node types as children.
The default value is delimited. See also Node Type Default Values (following this
table) for more information. |
Delimiter List |
|
Order |
Specifies the ordering of the selected group node or complex type
element node’s children during the parsing process.
sequence specifies that the child nodes must appear in the sequence given in the metadata. any specifies that the child nodes must remain grouped, but the groups can appear in any order. mixed specifies that the child nodes can appear in any order.
Does not apply to choice
element nodes. See Order Property for additional information. |
|
Table 2 Root Node Properties
|
|
|---|
Top |
Specifies whether or not parsing/serializing encoding
is supported for descendant nodes. The default value is true (checked box). |
Input Charset |
Specifies the
character set of the input data. This is only needed if the parsing
is done upon byte array data and the character set that the byte
array data is encoded against is not safe for delimiter scanning. If this
property is not specified, the value specified for the Parsing Charset property will be
used. This property is displayed only when the Top property is set to true
(checked box). Applies to root node only. See Data Encoding for additional information. |
Output Charset |
Specifies the
character set of the output data if it needs to be different from
the serializing character set. If this property is not specified, the value specified
for the Serializing Charset property will be used. This property is displayed only when
the Top property is set to true (checked box). See Data Encoding for additional information.
Note - This character
set may be unsafe for delimiter scanning.
|
Parsing Charset |
Specifies the character set used
to decode byte array data into string during parsing. It is recommended to
use UTF-8 for DBCS data, since the hex value of some ASCII delimiter
may coincide with a hex value contained within a double-byte character. This property
is displayed only when the Top property is set to true (checked box). See Data Encoding
for additional information. |
Serializing Charset |
Specifies the character set used to encode string data into byte
array data during serialization of the data. This property is displayed only when
the Top property is set to true (checked box). See Data Encoding for additional
information. |
Escape Sequence |
Global-level escape sequence, which should be set only at the root level.
This property is displayed only when the top property is set to true
(checked box).. |
Fine Inherit |
When set to true (checked box), enables the following delimiters to
be inherited individually from the parent nodes:
Otherwise, once a delimiter level is specified
for a child node, it overrides the relevant delimiter level as a whole
on parent nodes. This setting is global, so the flag only needs to
be set on a root element. The default value is false (unchecked box). Displayed only
when the top property is set to true (checked box). |
Undefined Data Policy |
Specifies whether
or not undefined (trailing) data is allowed and/or will be mapped. This property
is displayed only when the top property is set to true (checked box).
The options are as follows:
map specifies that undefined (trailing) data is allowed and will be mapped to field named undefined with the predefined namespace urn:com.sun:encoder:instance. skip specifies that undefined (trailing) data is skipped silently. prohibit specifies that undefined (trailing) data is not allowed, and if present an exception will be thrown.
This setting is global, so the flag only
needs to be set on a root element. |
|
Table 3 Leaf Node Properties
|
|
|---|
Match |
Defines match pattern. If alignment
is regex, then this field holds the regex match pattern. See Matching Data Patterns for
more information. |
No Match |
Flag indicating if the match condition should be reverted. The flag acts
as a logical NOT against the match condition. See Matching Data Patterns for more information. |
Alignment |
|
NofN minN |
Specifies the
minimum number of child nodes that must contain data. If absent, then so
such constraint exists. |
NofN maxN |
Specifies the maximum number of child nodes that must
contain data. If absent, then so such constraint exists. |
MinOcc |
Specifies the minimum number of
occurrences of a repeating node. The value specified here overrides the minOccurs value in
XSD's element declaration. This property is needed only when the order is
mixed; so in the XSD, repeating choice group must be used, and the minOccurs specified in
the XSD does not actually represent the minimum occurrence. |
MaxOcc |
Specifies the maximum number of
occurrences of a repeating node. The value specified here overrides the maxOccurs value in
XSD's element declaration. This property is needed only when the order is
mixed; so in the XSD, repeating choice group must be used, and the maxOccurs specified in
the XSD does not actually represent the maximum occurrence. |
Scavenger Chars |
Specifies the characters to
be stripped out when parsing the data, if they appear at the start
of the byte stream for this element. |
Output Scavenger 1st Char |
Specifies the character
to be stripped out when serializing the data, if it appears as the
first character of the output byte stream from this element (even occurring before
the begin delimiter, if any). |
Delimiter |
Displayed for delim Node Type only. Once delimiters are specified,
the value field displays the delimiter characters (read only). |
Begin Delimiter |
Once begin delimiters
are specified, the value field displays the delimiter characters (read only). |
Begin Delimiter
Detached |
Specifies whether the begin delimiter is anchored or detached. The default value is
false (unchecked box), indicating an anchored delimiter. |
Array Delimiter |
Displayed for array Node Type only.
Once delimiters are specified, the value field displays the delimiter characters (read only). |
Fixed
Length |
Displayed for fixedLength Node Type only.
The options are:
regular specifies a fixed-length field whose length is measured from the beginning of the message. encoded specifies a fixed-length field whose length is the sum of the encoded field length and an offset, measured from either the zero position or the current parsing position. determined by regex match specifies a fixed-length field whose length is determined by a regular expression at runtime. deducted from end specifies a fixed-length field whose length is measured from the end of the message.
|
Length |
Displayed only for fixedLength
Node Type with the regular option. Specifies the length of the field in terms
of bytes (as a positive integer). The default value is 0. |
Offset |
Displayed only for
fixedLength Node Type with the regular option. Specifies the offset of the field in
terms of bytes (as a positive long integer) from the zero position where
the first sibling starts. The default value is 0. |
Encoded Field Length |
Displayed only
for fixedLength Node Type with the encoded option, and specification is required. Specifies the
length of the encoded field in terms of bytes (as a positive integer).
The default value is 0. |
Encoded Field Offset |
Displayed only for fixedLength Node Type with
the encoded option, and specification is optional. Specifies the offset in terms of
bytes (as a positive long integer) from the position where the first sibling
starts. |
Encoded Field Position |
Displayed only for fixedLength Node Type with the encoded option,
and specification is required. Specifies the offset in terms of bytes (as a
positive long integer) between the current parsing position and the position from which
the Encoded Field Length is defined. |
Length From End |
Displayed only for fixedLength Node Type with
the deducted from end option. |
|
Node Type Default Values
The basic default value for the nodeType property is delimited. If, however,
the node is the child of a parent node whose Node Type is
fixedLength or transient, then the child takes on the same Node Type as
the parent. See the following table for additional information.
Note - This rule does not apply to Choice Element nodes.
Table 4 Node Type Default Values
|
|
|---|
array |
delimited |
delimited |
delimited |
fixed |
fixed |
group |
delimited |
transient |
transient |
|
Order Property
To illustrate how the order property works, consider the simple tree structure shown
in the following diagram, where a is an element node, b is a
non-repeating field node, and c is a repeating field node. The value
set for the order property allows the field nodes to appear as shown in
following table.
Figure 3 Order Property Example
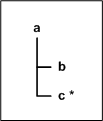
Table 5 Order Property Example
|
|
|---|
sequence |
b, c1, c2 |
any |
b, c1, c2, or c1, c2, b |
mixed |
b,
c1, c2, or c1, c2, b, or c1, b, c2 |
|
Data Encoding
For Java CAPS to correctly handle data in byte-oriented protocol, the encoding method
for inbound and outbound Encoders and the native code used for parsing must
be specified in the Encoding properties. If you do not specify otherwise, UTF-8
is assumed to be the encoding method in each case.
Supporting UTF-8 by default allows the use of the Unicode character set in
both ASCII and non-ASCII based environments without further specification. Java CAPS also supports
ASCII for English, Japanese, and Korean locales, and the localized country-specific encoding methods shown
in the following table.
The data encoding you specify when configuring the Encoding properties modifies the Java
methods used for encoding and decoding. The encoding and decoding processes differ from
one another depending upon which Java method you use, and whether you are
encoding to or decoding from bytes or strings. The diagrams shown in About Data Parsing and Serialization
illustrate these differences.
The encoding options available to you depend on the locale specified by your
version of Java CAPS. UTF-8 is the default in all locales.
Table 6 Partial Listing of Supported Encoding Options According to Locale
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
UTF-8 |
UTF-8 |
UTF-8 |
UTF-8 |
UTF-8 |
ASCII |
ASCII |
ASCII |
GB2312 |
Big5 |
EBCDIC |
EUC-JP |
EUC-KR |
|
|
UTF-16 |
SJIS |
MS949 |
|
|
|
MS932 |
|
|
|
|