| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS Custom Encoders User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS Custom Encoders User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
Understanding the Encoder Framework
Parent, Child, and Sibling Nodes
Creating the Abstract Message Definition
Applying Custom Encoding to an XSD
To Apply the Custom Encoder to an XSD
Anchored and Detached Delimiters
Constant and Embedded Delimiters
Validating and Testing the Custom Message Definition
Validating the Custom Message Definition
Testing the Encoder Runtime Behavior
The parsing and serializing operations require data to be in byte-array form, so different methods for encoding and decoding data must be used to accommodate different input and output data formats. These different methods incorporate various stages of character conversion using specific character sets.
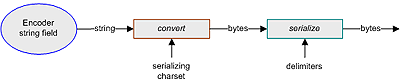
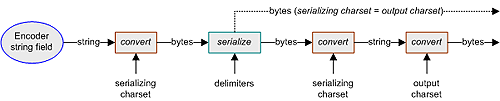
Internally, the encoder requires the data input and output to be in bytes. The encoding process uses the serializing charset, as illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 24 Encoding Process
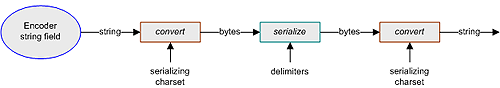
The encodeToString() method requires conversion to produce an output string after encoding from a byte[] field. This method also requires conversion when encoding from a string field, since the parser requires the data in bytes, and conversion again to produce an output string. The encodeToString() process uses the serializing charset, as illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 25 encodeToString()
The encodeToBytes() method requires conversion to produce bytes after encoding from a string field. Following serialization, this method also requires conversion to produce an output (in bytes) having a different format from that used by the parser. If the same format is desired, then the output charset is left undefined, the serializing charset property is substituted by default, and the double conversion is bypassed. The encodeToBytes() process uses both the serializing charset and the output charset, as illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 26 encodeToBytes()
Encodes an XML representation of a message into an OutputStream object, encoded in custom format.
Encodes an XML representation of a message into a Writer object, encoded in custom format.
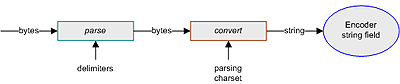
Internally, the decoding process requires conversion when decoding to a string field, since the input is in bytes as required by the parser. The decoding process uses the parsing charset, as illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 27 Decoding Process
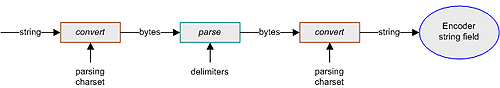
The decodeFromString() method requires conversion of the input string, since the parser requires the data in bytes. This method requires a second conversion when decoding to a string field. The decodeFromString() process uses the parsing charset, as illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 28 decodeFromString()
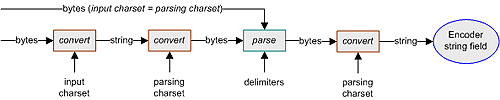
The decodeFromBytes() method requires conversion if the input data has a different byte format from that used by the parser. If the same format is desired, then the input charset is left undefined, the parsing charset is substituted by default, and the double conversion is bypassed. After parsing, this method requires further conversion if decoding to a string field. The decodeFromBytes() process uses both the input charset and the parsing charset, as illustrated in the following figure.
Figure 29 decodeFromBytes()
Decodes an InputStream object encoded in custom format into an XML-encoded message.
Decodes a Reader object encoded in custom format into an XML-encoded message.
The following figure illustrates how the delimiter gets set and passed into the parser.
Figure 30 Setting Delimiters
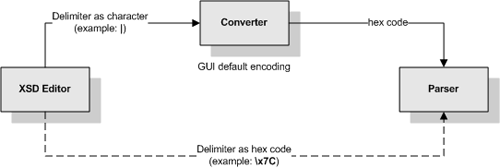
As an example, if you select a delimiter in the XSD Editor by hex code (such as \x7C), it is passed directly into the parser. If you type the delimiter in as a pipe (|), however, then the pipe character is first converted to hex code, using the GUI’s encoding, and then sent to the parser.