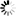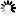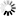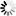To track manager status in Python, the API can be queried repeatedly using the URI to access the Manager object and the managerRunState property value can be tested to determine whether or not the Oracle VM Manager instance has RUNNING runtime status. To keep the script polite, use the time library to sleep between requests. Since this is functionality that may be used repeatedly at different stages in a program, it is better to define it as a function:
...
def check_manager_state(baseUri,s):
while True:
r=s.get(baseUri+'/Manager')
manager=r.json()
if manager[0]['managerRunState'].upper() == 'RUNNING':
break
time.sleep(1)
return;
In this function, the while True: statement
creates an infinite loop. The requests library session object
is used to submit a GET request to the appropriate URI and the
response content is converted from JSON into a python data
object. The object is a list that contains a dictionary with
all of the Manager object properties as keys. We use an
if statement to test the managerRunState property
to see whether it matches the string value 'RUNNING'. If a
match is found, the infinite loop is broken and the function
can return. If a match is not found, the
time.sleep statement causes the function to wait
for one second before submitting the next request, so that
requests take place over a sensible period.
Usually, you would insert a call to this function directly after you authenticate, as described in Section 2.6.1, “Authenticating”. You may even incorporate this code into your authentication process, so that it is called whenever an authentication request is made within your application.