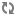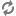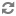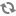This section describes how search interfaces perform record searches on specified dimensions and properties, which are known as the members of the search interface. It also describes the components of search interfaces and the JSON syntax for configuring these components.
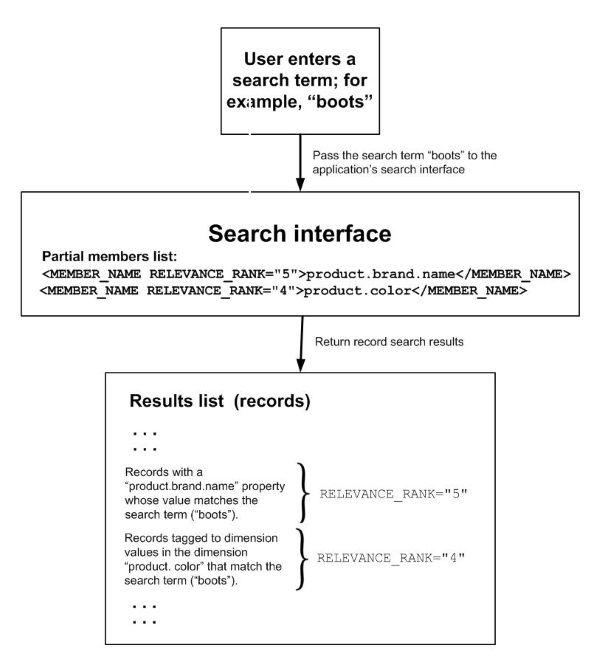
The following diagram illustrates how a search interface selects the records that appear in the results list, given a particular search term ("boots") entered by the user:
As shown in the diagram, this sample search interface includes the following members, among others:
The records in this example are sorted according to the RELEVANCE_RANK value of the member that they match. The RELEVANCE_RANK values are used for sorting only with certain relevance ranking modules. For more information, see How relevance ranking modules use RELEVANCE_RANK values .
Note
A search interface does not in any way define or control the behavior of the user interface of your front end application.
The dimensions and properties included in a search interface are known as its members. Because a search interface normally includes multiple members, keyword searches made through search interfaces in most cases return larger result sets than searches on individual dimensions or properties.
Search interfaces are almost always implemented with relevance ranking, a feature that makes it possible to sort the records returned by the search interface so that items of greater interest to users are listed before items of lesser interest.You can also configure relevance ranking for specific queries, rather than as a feature of a search interface. For information about relevance ranking, see Sorting keyword search results.
You configure a search interface for record searches in a file named
appname.recsearch_config.xml. In this file, you
specify both attributes and members of the search interface. Create your
version of
appname.recsearch_config.xml in the following
folder:
app-name\config\mdex\app-name.recsearch_config.xml.
A search interface is configured by a SEARCH_INTERFACE element in recsearch_config.xml. As a model for your own search interface configuration, use the following SEARCH_INTERFACE element in the version of recsearch_config.xml provided in the Discover Electronics reference application:
<SEARCH_INTERFACE CROSS_FIELD_BOUNDARY="ALWAYS" cross
FIELD_RELEVANCE_RANK="0"
DEFAULT_RELRANK_STRATEGY="All" NAME="All">
<MEMBER_NAME RELEVANCE_RANK="8">product.id</MEMBER_NAME>
<MEMBER_NAME RELEVANCE_RANK="7">product.sku</MEMBER_NAME>
<MEMBER_NAME RELEVANCE_RANK="6">product.code</MEMBER_NAME>
<MEMBER_NAME RELEVANCE_RANK="5">product.brand.name</MEMBER_NAME>
<MEMBER_NAME RELEVANCE_RANK="4">product.category</MEMBER_NAME>
<MEMBER_NAME RELEVANCE_RANK="3">product.name</MEMBER_NAME>
<MEMBER_NAME RELEVANCE_RANK="2"
SNIPPET_SIZE="25">product.short_desc</MEMBER_NAME>
<MEMBER_NAME RELEVANCE_RANK="1">product.long_desc</MEMBER_NAME>
</SEARCH_INTERFACE> You must specify values for the following attributes of the SEARCH_INTERFACE element:
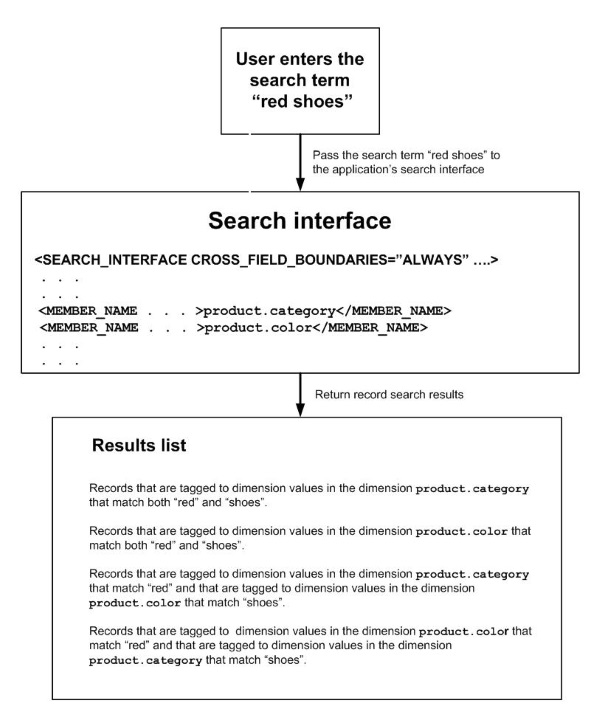
CROSS_FIELD_BOUNDARY: Specifies when parts of a search term can be individually matched with different members; for example, given the search term "red shoes", when can matches be made between "red" and one member, and between "shoes" and another member? The possible values
are:
ALWAYS, which causes the search engine always to look for matches between members of the search interface and the parts of a search term. ALWAYS is the recommended setting for most purposes.
ON_FAILURE, which causes the search engine to look for matches between members of the search interface and parts of a search term only if it cannot match the entire search term to any member of the search interface.
NEVER, which requires that the entire search term (that is, all words that the user entered to search for) must be found within the same member.
CROSS_FIELD_RELEVANCE_RANK: Specifies the relevance rank for cross-field matches. The value should be an unsigned 32-bit integer.The default value for CROSS_FIELD_RELEVANCE_RANK is 0; as a result, cross field matches are ranked lower than matches against a single field.
DEFAULT_RELRANK_STRATEGY: A default relevance ranking strategy. This attribute is ignored by Assembler-based applications.
NAME: The name of the search interface. This name must not be the same as the name of any dimensions or properties within your application.
STRICT_PHRASE_MATCH: This attribute is deprecated and its use is not recommended.
Note
The dimensions and properties in a search interface used for records searches must be enabled for record searches. All dimensions are enabled for dimension search. For more information, see Introduction: configuring dimensions and Endeca record properties .
The following diagram illustrates the effect of setting CROSS_FIELD_BOUNDARY to "Always":
To be useful, a search interface should include two or more members. Individual dimensions and properties can be searched without being members of a search interface.
The members can be dimensions or properties of indexed records. Every member must be enabled for record search. Each member of the search interface is specified in a separate MEMBER_NAME subelement of the SEARCH_INTERFACE element; for example:
<MEMBER_NAME RELEVANCE_RANK="2" SNIPPET_SIZE="25">product.short_desc</MEMBER_NAME>
where:
RELEVANCE_RANK="2"is a value used to sort records that are not sorted by the search interface's relevance ranking strategy. Records tagged to members with lower RELEVANCE_RANK values are displayed before records tagged to members with higher values. Do not omit relevance rank values for members.SNIPPET_SIZE="25" enables snippeting for a MEMBER_NAME.The value of SNIPPET_SIZE specifies the maximum number of words that a snippet can contain. Omitting this attribute or setting its value to zero disables snippeting. (Snippets are useful for document searches, but are not ordinarily used by eCommerce sites.) For information about snippeting, refer to the MDEX Engine Developer's Guide.
Note
RELEVANCE_RANK and SNIPPET_SIZE are the only attributes of the MEMBER_NAME element.
Search interfaces can contain both wildcard-enabled and non-wildcard-enabled members. Only wildcard-enabled members will return wildcard-expanded results, however. Wildcard search can be enabled for particular dimensions and properties; for information about how to do this, see Parameters of dimensions and properties in index-config.json .
To specify the search interface that your application uses, specify the name of the search interface as the value of the defaultSearchKey property of the navigationStateBuilder component in assembler-context.xml; for example:
<property name="defaultSearchKey" value="All" />
where:
Note
Most applications use only a single search interface. If you create more than one search interface for a single application, you must provide customized logic that determines when each search interface is used. This document does not discuss how to provide such customized logic.
You can also specify that keyword searches be made against a specific record property, rather than through a search interface. To do this, specify the record property as the value of the value attribute of the defaultSearchKey property of the navigationStateBuilder component in assembler-context.xml; for example:
<property name="defaultSearchKey" value="product.code" />
where:
value is set to the record property
product.code. All keyword searches will be against
this record property alone.