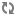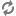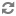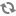You can also load your exported product data into CAS record stores using calls to the Record Store API, as in the following Java example:
package com.endeca.itl.recordstore.sample;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import com.endeca.itl.record.PropertyValue;
import com.endeca.itl.record.Record;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStore;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStoreConfiguration;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStoreException;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStoreLocator;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.RecordStoreWriter;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.TransactionId;
import com.endeca.itl.recordstore.TransactionType;
/**
* SampleWriter is an example of how to use the Record Store core and
* client utility classes to write records. It creates one record and
* writes it to the Record Store.
*/
public class SampleWriter {
// This should match the idPropertyName in your record store configuration.
public static final String PROPERTY_ID = "Endeca.FileSystem.Path";
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (args.length!=2) {
System.out.println("usage: <cas host> <cas port>");
System.exit(-1);
}
String casHost = args[0];
int casPort = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
// For better performance, create a linked list of records to write
// as a batch, rather than writing individual records.
Collection<Record> records = new LinkedList<Record>();
// The following lines, which add hard-coded values, are meant only to illustrate the API.
// You will want to replace these lines with code that processes your product data,
// which can include both property names and property values.
Record record = new Record();
record.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue("product.name","Acme Sport Shirt"));
record.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue("product.price","23.99");
record.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue("common.id", "a231ad32));
records.add(record);
RecordStoreLocator locator = RecordStoreLocator.create(casHost, casPort, "rs1");
RecordStore recordStore = locator.getService();
RecordStoreConfiguration config = new RecordStoreConfiguration();
config.setIdPropertyName("Endeca.FileSystem.Path");
config.setChangePropertyNames(new ArrayList<String>());
TransactionId tId = null;
try {
System.out.println("Setting record store configuration ...");
recordStore.setConfiguration(config);
System.out.println("Starting a new transaction ...");
tId = recordStore.startTransaction(TransactionType.READ_WRITE);
// Create a writer that writes records in batches of 100.
RecordStoreWriter writer = RecordStoreWriter.createWriter(recordStore, tId, 100);
System.out.println("Writing records ...");
// To perform a baseline update, delete all records in record store before writing new records.
writer.deleteAll();
writer.write(records);
writer.close();
// Commit the transaction to complete the write operation.
System.out.println("Committing transaction ...");
recordStore.commitTransaction(tId);
System.out.println("DONE");
} catch (RecordStoreException exception) {
exception.printStackTrace();
if (tId != null) {
try {
recordStore.rollbackTransaction(tId);
} catch (RecordStoreException anotherException) {
System.out.println("Failed to roll back transaction.");
anotherException.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
For more information about the Record Store API, refer to the Oracle Commerce Content Acquisition System API Guide and the Record Store API Reference (Javadoc).