| Oracle® Communications EAGLE Database Administration - GTT User's Guide Release 46.8 F11880-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Communications EAGLE Database Administration - GTT User's Guide Release 46.8 F11880-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This procedure is used to provision a load shared mated
application in the database using the
ent-map and
chg-map commands. A load shared mated
application is a mated application containing entries whose RC (relative cost)
values are equal. The
ent-map and
chg-map commands use these parameters
to provision a load shared mated application.
:pc/pca/pci/pcn/pcn24 –
The point code of the primary signaling point that is to receive the message.
:mpc/mpca/mpci/mpcn/mpcn24 – The point code of the
backup signaling point that is to receive the message.
Note:
The point codes can be either an ANSIpoint code (pc/pca,
mpc/mpca), ITU-I or ITU-I spare point code (pci,
mpci), a 14-bit ITU-N or 14-bit ITU-N
spare point code (pcn,
mpcn), or a 24-bit ITU-N (pcn24,
mpcn24) point code.
Note:
Refer to Chapter 2, Configuring Destination Tables in Database Administration - SS7 User's Guide for a definition of the point code types that are used on the EAGLE and for a definition of the different formats that can be used for ITU national point codes.:ssn – Subsystem number
– the subsystem address of the primary point code that is to receive the
message. The value for this parameter is 2 to 255.
:mssn – Mate subsystem
number – the subsystem address of the backup point code that is to receive the
message. The value for this parameter is 2 to 255.
:rc – The relative cost
value of the primary point code and subsystem, defined by the
pc/pca/pci/pcn/pcn24 and
ssn parameters. The
rc parameter has a range of values
from 0 to 99, with the default value being 10.
:materc – The relative
cost value of the backup point code and subsystem, defined by the
mpc/mpca/mpci/mpcn/mpcn24 and
mssn parameters. The
materc parameter has a range of values
from 0 to 99, with the default value being 50.
:grp – The name of the
concerned signaling point code group that contains the point codes that should
be notified of the subsystem status. This parameter applies to both RPCs/SSNs.
The value for this parameter is shown in the
rtrv-cspc output. If the desired value
is not shown in the
rtrv-cspc output, perform the
Adding a Concerned Signaling Point Code
procedure to add the desired group. If this parameter is not specified, then a
CSPC group name is not specified for the mated application.
:sso – Subsystem Status
Option – defines whether the subsystem status option is on or off. This
parameter allows the user the option to have the specified subsystem marked as
prohibited even though an MTP-RESUME message has been received by the
indicating that the specified point code is allowed. The value for this
parameter is
on or
off. The default value is
off.
:mapset – The MAP set
ID that the mated applications are assigned to. This parameter can be specified
only if the Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature is enabled. This parameter must
be specified if the Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature is enabled. If the
Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature is enabled, the point code and subsystem
specified for the global title translation must be assigned to the MAP set
specified by this parameter. The status of the Flexible GTT Load Sharing
feature is shown in the
rtrv-ctrl-feat output. To enable the
Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature, perform the
Activating the Flexible GTT Load Sharing Feature
procedure.
The
mapset parameter has three values.
dflt – to assign the
MAP to the default MAP set. This value can be specified with both the
ent-map and
chg-map commands.
new – to assign the
mated application to a new MAP set. This value can be specified only with the
ent-map command.
chg-map command.
Refer to the Provisioning a MAP Set section for information on provisioning MAP sets.
:wt – The weight value
assigned to the
pc/pca/pci/pcn/pcn24 parameter
value. The value of this parameter is from 1 - 99.
:mwt – The weight value
assigned to the
mpc/mpca/mpci/mpcn/mpcn24 parameter
value. The value of this parameter is from 1 - 99.
:thr – The in-service
threshold assigned to the MAP group or MAP set. The in-service threshold is the
minimum percentage (from 1 - 100) of weight that must be available for an RC
group (a group of entries in the MAP group or MAP set that have the same RC
value assigned) to be considered available to carry traffic. If the percentage
of the available weight is less than the in-service threshold, then the entire
RC group is considered unavailable for traffic. If the percentage of the
available weight is equal to or greater than the in-service threshold, then the
RC group is considered available, and traffic can be sent to any available
entity in the RC group. The value of the
thr parameter is assigned to all
entries that have the same RC (relative cost) value in the MAP group or MAP set
that contain the point code specified in the
ent-map or
chg-map command.
Refer to the Provisioning Weights and In-Service Thresholds for Mated Applications section for information on provisioning MAP groups or MAP sets with weight and in-service threshold values.
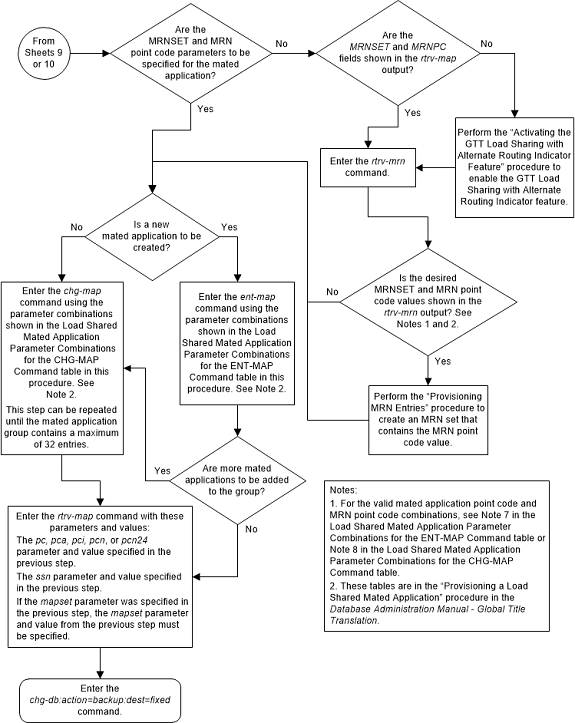
:mrnset – The MRN set
ID that is being assigned to the mated application. This is the MRN set from
which alternate routing indicator searches are performed.
:mrnpc/mrnpca/mrnpci/mrnpcn/mrnpcn24 – The point code
assigned to the
mrnset that is being assigned to the
MAP set.
The current values of the
mrnset and
:mrnpc/mrnpca/mrnpci/mrnpcn/mrnpcn24
parameters are shown in the
rtrv-map output only if the Flexible
GTT Load Sharing and the GTT Load Sharing with Alternate Routing Indicator
features are enabled.
The new values for the
mrnset and
mrnpc/mrnpca/mrnpci/mrnpcn/mrnpcn24
parameters must be shown in the
rtrv-mrn output.
The network type of the
pc/pca/pci/pcn/pcn24 and
mrnpc/mrnpca/mrnpci/mrnpcn/mrnpcn24
parameter values must be compatible, as shown in
Table 2-45.
Table 2-45 MAP and MRN Point Code Parameter Combinations
| MAP Point Code Parameter | MRN Point Code Parameter |
|---|---|
| pc/pca | mrnpc/mrnpca |
| pci or pcn (See Notes 1 and 2) | mrnpci or mrnpcn (See Notes 1 and 2) |
| pcn24 | mrnpcn24 |
|
Notes: 1. If the network type of the MAP point code parameter is
ITU-I ( 2. If the network type of the MAP point code parameter is
ITU-N ( |
|
:mrc – Message routing
under congestion – specifies whether Class 0 messages are routed during
congestion conditions. The values for this parameter are
yes and
no. This parameter can be specified
for any type of mated application, but this parameter affects only the traffic
for a dominant mated application. The default value for ANSI load shared mated
applications is
yes. The default value for ITU load
shared mated applications is
no.
:srm – Subsystem
routing messages – defines whether subsystem routing messages (SBR, SNR) are
transmitted between the mated applications. The values for this parameter are
yes and
no. The
srm=yes parameter can be specified
only for ANSI mated applications. This parameter affects traffic only on
dominant and combined dominant/load shared mated applications. The default
value for ANSI load shared mated applications is
yes. The default value for ITU load
shared mated applications is
no.
A load shared mated application can contain up to 128
point codes and subsystems, a primary point code and subsystem, and up to 31
mated point codes and subsystems. When a new load shared mated application is
added to the database, the first two entries, the primary point code and
subsystem and a mate point code and subsystem are added using the
ent-map command. All other mated point
code and subsystem entries that are being assigned to the primary point code
and subsystem are added to the load shared mated application using the
chg-map command.
All the point codes and subsystems in a load shared mated application have the same relative cost value. Traffic is shared equally between the point codes and subsystems in this mated application.
If the Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature is not enabled, the primary point code and subsystem number or the mate point code and mate subsystem number combination can be in the database only once. If the Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature is enabled, the primary point code and subsystem number or mate point code and mate subsystem number combination can be in multiple MAP sets, but can be in the default MAP set only once.. Refer to the Provisioning a MAP Set section for information on provisioning MAP sets.
The point codes specified in the
ent-map or
chg-map commands (pc/pca,
pci,
pcn, or
pcn24, and
mpc/mpca,
mpci,
mpcn, or
mpcn24) must be either a full point
code in the routing point code table. Cluster point codes or network routing
point codes cannot be specified with this command. The
rtrv-rte command can be used to verify
the point codes in the routing table. The point codes in the routing table are
shown in the
DPCA,
DPCI,
DPCN, or
DPCN24 fields of the
rtrv-rte command output. The EAGLE’s
true point code, shown in the
PCA,
PCI,
PCN, or
PCN24 fields of the
rtrv-sid command output, cannot be
specified for a load shared mated application.
A load shared mated application can be provisioned with a point code that is assigned to other mated applications as long as the SSN is not assigned to other mated applications. A point code can be assigned to maximum of 12 different SSNs.
For mated applications containing ANSI or 24-bit ITU-N
point codes, or the EAGLE's true point code, the format of the point codes
specified in the
ent-map command must be the same. For
example, if the primary point code is a 24-bit ITU-N point code (pcn24), the mate point code must be a 24-bit ITU-N
point code (mpcn24). The mate point codes of
mated applications containing either ITU-I, ITU-I spare, 14-bit ITU-N, or
14-bit ITU-N spare primary point codes do not have to be the same format as the
primary point code. The mate point codes of these mated applications can be a
mixture of ITU-I, ITU-I spare, 14-bit ITU-N, or 14-bit ITU-N spare point codes.
The format of the point codes in the CSPC group
specified with the
grp parameter must be the same as the
primary point code specified with the
ent-map command only if the ANSI/ITU
SCCP Conversion feature is not enabled. If the ANSI/ITU SCCP Conversion feature
is enabled, the CSPC group may contain a mixture of point code types (refer to
the
Adding a Concerned Signaling Point Code
procedure), and the network type of the CSPC group can be different from the
network type of the primary point code of the mated application. The status of
the ANSI/ITU SCCP Conversion feature can be verified with the
rtrv-ctrl-feat command.
The values for the primary point code and subsystem
combination (pc/ssn) cannot be the same as the mated point code and
subsystem combination (mpc/mssn). However, the primary and mated point codes can
be the same as long as the subsystem numbers are different.
If a mate point code (mpc/mpca/mpci/mpcn/mpcn24) is specified, the
mssn parameter must be specified.
If the
mssn parameter is specified, the mate
point code (mpc/mpca/mpci/mpcn/mpcn24) must be
specified.
If the
grp,
srm,
mrc, and
sso parameter values are specified,
and the specified point code and SSN is assigned to multiple mated
applications, the
grp,
srm,
mrc, and
sso values for all mated applications
containing the specified point code and SSN will be changed to the values
specified in this procedure.
The EAGLE can contain 1024, 2000, or 3000 mated applications. The EAGLE default is 1024 mated applications. This quantity can be increased to 2000 by enabling the feature access key for part number 893-0077-01, or to 3000 by enabling the feature access key for part number 893-0077-10. For more information on enabling these feature access keys, refer to the Enabling the XMAP Table Expansion Feature procedure.
Provisioning a MAP Set
The Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature provides the ability to define multiple load sharing sets in the MAP table where the same point code and subsystem can be assigned to different load sharing sets.
The MAP table contains specific load sharing sets, designated by numbers, and a default MAP set.
Flexible Final GTT Load Sharing provides flexible load sharing for global title translations defined in the GTT table and not for the MPS-based features. The MPS-based features do not support the MAP set ID parameter. The MPS-based features perform lookups for load sharing in the default MAP set and the GTT table. The entries in the GTT table can be linked to a MAP set ID, allowing lookups in a specific MAP set other than the default MAP set.
Any MAP entries that were provisioned in the database before the Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature is enabled are placed in the default MAP set when the Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature is enabled.
To provision entries in the default MAP set, the
mapset=dflt parameter must be
specified with the
ent-map or
chg-map commands.
To provision entries in an existing MAP set other than
the default MAP set, the
mapset=<MAP set ID> parameter
must be specified with the
chg-map command. Provisioning entries
in an existing MAP set can be performed only with the
chg-map command.
To provision entries in a new MAP set, the
mapset=new parameter must be specified
with the
ent-map command. The
mapset=new parameter can be specified
only with the
ent-map command. When the
ent-map command is executed with the
mapset=new parameter, the new MAP set
ID is automatically generated and displayed in the output of the
ent-map command as follows.
New MAPSET Created : MAPSETID = <new MAP set ID>
A MAP set, other than the default MAP set, is a MAP group provisioned with the MAP set ID and can contain a maximum of 128 point codes.
The default MAP set can contain multiple MAP groups. The point code and subsystem number combination can appear only once in the default MAP set. The point code can appear in multiple MAP groups in the default MAP set with different subsystem numbers.
The point code and subsystem number combination provisioned in a MAP set can be provisioned in multiple MAP sets. All the point codes in a MAP set must be different.
Provisioning Weights and In-Service Thresholds for Mated Applications
Weighted GTT Load Sharing allows unequal traffic loads to be provisioned in MAP load sharing groups or MAP load sharing sets. This feature also allows provisioning control over load sharing groups or sets so that if insufficient capacity within the load sharing group or set is available, the load sharing group or set is not used.
To provision the weight values and in-service threshold
values for MAP groups or MAP sets in this procedure, the
wt,
mwt, and
thr parameters are used.
The
wt,
mwt, and
thr parameters can be used only:
The status of the Weighted GTT Load Sharing feature can
be verified by entering the
rtrv-ctrl-feat command. If the
Weighted GTT Load Sharing feature is not enabled or not turned on, perform the
Activating the Weighted GTT Load Sharing Feature
procedure to enable and turn on the Weighted GTT Load Sharing feature.
If either the
wt or
mwt parameters are specified with the
ent-map command, both parameters must
be specified with the
ent-map command.
To assign an in-service threshold value to the entries
of a MAP group or MAP set that contains the point code value specified in the
ent-map command, use the
thr parameter with the
wt and
mwt parameters. When the
thr parameter is specified with the
ent-map command, the in-service
threshold value is assigned to both entries specified in the
ent-map command. The
thr parameter cannot be specified with
the
chg-map command when adding additional
entries to the MAP group or MAP set. When additional entries are added to the
MAP group or MAP set with the
chg-map command, the
thr value that was specified in the
ent-map command is assigned to the
additional entries. For information on using the
thr parameter with the
chg-map command, refer to the
Changing the Weight and In-Service Threshold Values of a Mated Application
procedure.
The
thr parameter does not have to be
specified with the
ent-map command. If the
thr parameter is not specified with
the
ent-map command, the
THR parameter value for the MAP group
or MAP set is set to 1.
Specifying the
wt and
mwt parameters assigns a weight value
to the point codes specified in the
ent-map command. The
wt parameter value is assigned to the
mpc/mpca/mpci/mpcn/mpcn24 parameter
value and the
mwt parameter value is assigned to the
mpc/mpca/mpci/mpcn/mpcn24 parameter
value.
When additional entries are added to the MAP group or
MAP set with the
chg-map command, and the MAP group or
MAP set entries have weight and in-service threshold values assigned, a weight
value must be assigned to the
mpc/mpca/mpci/mpcn/mpcn24 parameter
value using the
mwt parameter.
The
wt parameter does not have to be
specified with the
chg-map command. If the
wt parameter is specified with the
chg-map command, the weight value for
the
pc/pca/pci/pcn/pcn24 parameter is
not changed.
If the
wt parameter is specified with the
chg-map command and the
wt value is the same as the value
currently assigned to the
pc/pca/pci/pcn/pcn24 parameter,
the weight value for the
pc/pca/pci/pcn/pcn24 parameter is
not changed.
If the
wt parameter is specified with the
chg-map command and the
wt value is different from the value
currently assigned to the
pc/pca/pci/pcn/pcn24 parameter,
the weight value for the
pc/pca/pci/pcn/pcn24 parameter is
changed to the new
wt value.
The weight values assigned to the entires in the MAP
group or MAP set are shown in the
WT column in the
rtrv-map output.
The in-service threshold values assigned to the entires
in the MAP group or MAP set are shown in the
THR column in the
rtrv-map output.
The
%WT column in the
rtrv-map output shows the percentage
of the traffic the particular entry in the MAP group or MAP set will handle.
The
WT,
%WT, and
THR columns are shown in the
rtrv-map output only if the Weighted
GTT Load Sharing feature is enabled and turned on.
For more information on the Weighted GTT Load Sharing feature, refer to the Weighted GTT Load Sharing section.
Canceling the
RTRV-MAP Command
Because the
rtrv-map command used in this
procedure can output information for a long period of time, the
rtrv-map command can be canceled and
the output to the terminal stopped. There are three ways that the
rtrv-map command can be canceled.
F9 function key on the keyboard at
the terminal where the
rtrv-map command was entered.
canc-cmd without the
trm parameter at the terminal where
the
rtrv-map command was entered.
canc-cmd:trm=<xx>, where
<xx> is the terminal where the
rtrv-map command was entered, from
another terminal other that the terminal where the
rtrv-map command was entered. To
enter the
canc-cmd:trm=<xx> command, the
terminal must allow Security Administration commands to be entered from it and
the user must be allowed to enter Security Administration commands. The
terminal’s permissions can be verified with the
rtrv-secu-trm command. The user’s
permissions can be verified with the
rtrv-user or
rtrv-secu-user commands.
For more information about the
canc-cmd command, refer to
Commands User's Guide.
Figure 2-79 Provision a Load Shared Mated Application - Sheet 1 of 11
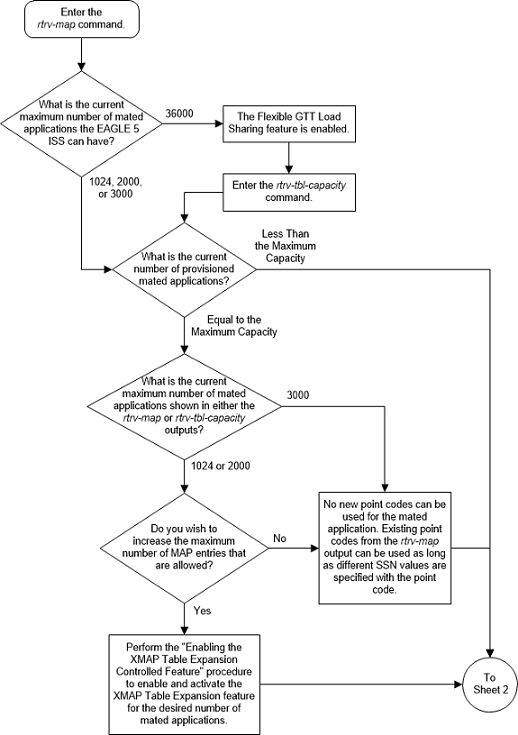
Figure 2-80 Provision a Load Shared Mated Application - Sheet 2 of 11

Figure 2-81 Provision a Load Shared Mated Application - Sheet 3 of 11

Figure 2-82 Provision a Load Shared Mated Application - Sheet 4 of 11
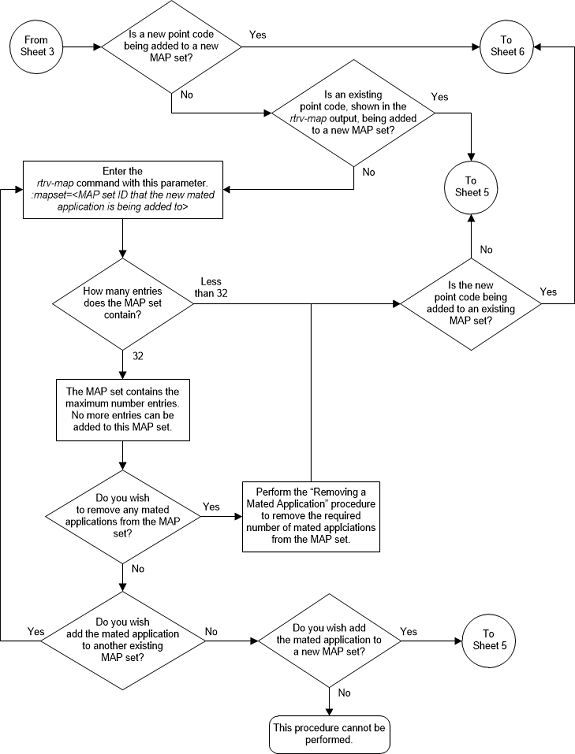
Figure 2-83 Provision a Load Shared Mated Application - Sheet 5 of 11
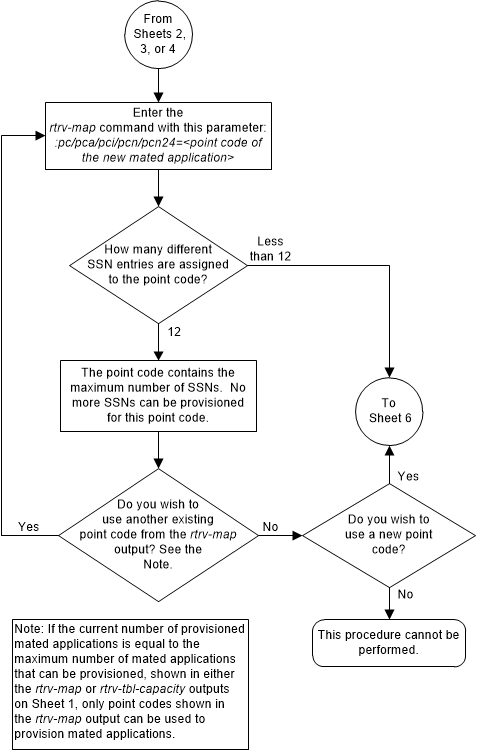
Figure 2-84 Provision a Load Shared Mated Application - Sheet 6 of 11

Figure 2-85 Provision a Load Shared Mated Application - Sheet 7 of 11
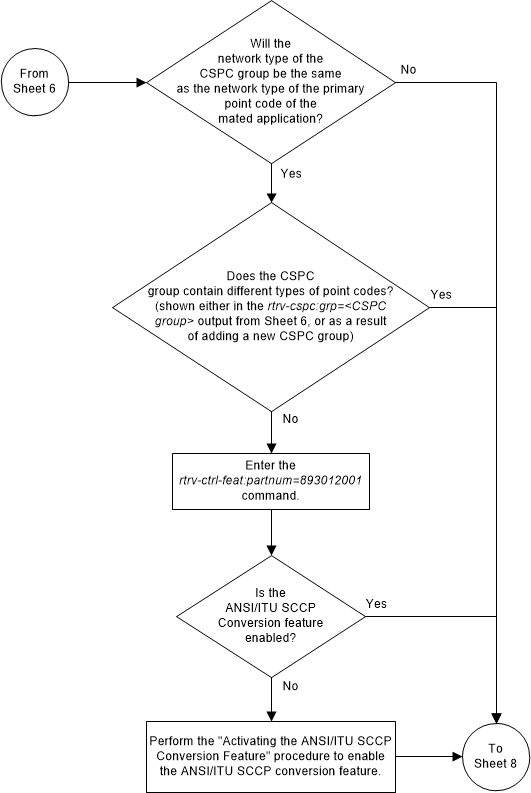
Figure 2-86 Provision a Load Shared Mated Application - Sheet 8 of 11

Figure 2-87 Provision a Load Shared Mated Application - Sheet 9 of 11
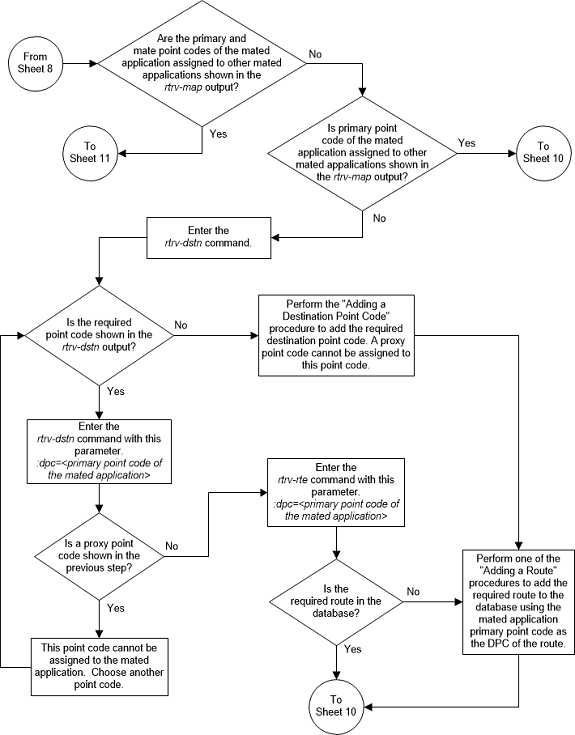
Figure 2-88 Provision a Load Shared Mated Application - Sheet 10 of 11
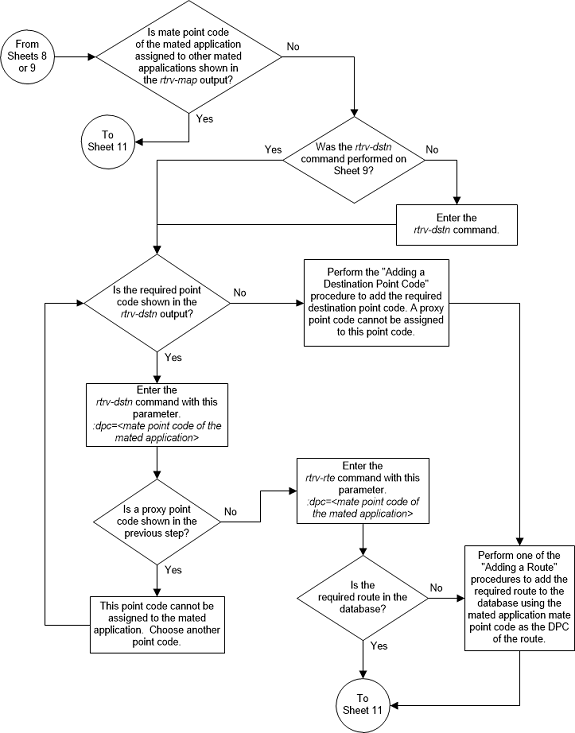
Figure 2-89 Provision a Load Shared Mated Application - Sheet 11 of 11