ePerformance Business Processes
Image: ePerformance business process flow showing how a typical document moves through the system being evaluated, reviewed and approved by both managers and employees
This diagram illustrates the flow of ePerformance business processes — assuming that the document template implements the establish criteria, track progress, multi-participant, review, and approval processes.
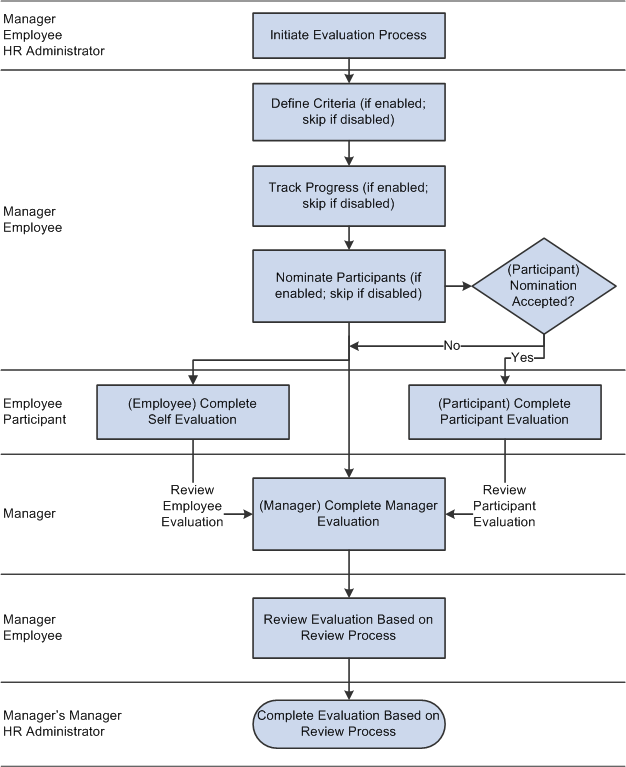
The ePerformance business process includes these steps:
Note: Depending on how you configure the business process, some of these steps are optional.
The manager, employee, or HR administrator initiates the process by creating documents.
Employees can only create documents for themselves; managers can create documents for employees and groups of employees that report to them; HR administrators can create documents for individual employees and groups of employees.
(Configurable) The employee or manager modifies the document's evaluation criteria and agree on the criteria that are established.
Criteria modifications include: adding free-form or predefined criteria, modifying the text of document criteria, or removing criteria. If integrating with Enterprise Learning Management, you can add learning activity.
(Configurable) The manager provides feedback on the employee's progress and completes the checkpoint. After that, employee and manager adjust and finalize the criteria before starting the evaluations.
(Configurable) The employee or manager nominates participants to provide additional feedback.
(Optional) After nominations are complete and the evaluation criteria are finalized, nominations are submitted to nominees by either the employee or manager.
When a nominee accepts a nomination, a participant evaluation is created for them.
Employees, managers, and (optionally) other participants complete their respective evaluations.
This step consists of rating evaluation items and entering comments.
The manager views average ratings and consolidates feedback into their evaluation.
During this step, the manager can optionally make use of several tools: notes that they entered pertaining to the evaluation; comments from other evaluators pertaining to the evaluation; development tips that are based upon competencies and sub-competencies; results writer statements that are based on competencies and sub-competencies; average consolidated ratings from other evaluators pertaining to the evaluation; and a language checker that checks language for objectionable terms.
See Understanding Feedback Consolidation.
Note: Depending on the document template definition, these tools are also available to employees and other participants. However, the manager makes primary use of these tools when completing an evaluation.
(Configurable) The manager sends the evaluation to the employee for review.
(Configurable) The manager submits the evaluation for approval.
See Understanding Review and Approval Processes.
Note: Depending on the review and approval process that is defined in the document template, the final two steps might occur in reverse order.
Administrative Processes
These administrative processes occur on an as-needed basis and are outside of the evaluation processes:
Transfer evaluations.
Change evaluation status.
Cancel evaluations.
Delete evaluations.
Enter preliminary ratings.
View evaluation contents.
Monitoring Evaluations
HR administrators can monitor the status of evaluations and view a summary of the results with various reports and tools, including the following:
Missing Documents report.
Late Documents report.
Status Summary chart.
Rating Distribution Summary chart.