6 JavaScriptからJavaFXへのアップコール
ここでは、JavaFXからJavaScriptを起動する方法について説明します。 この章では、WebコンテンツからのJavaFXのコールという反対の機能を確認できます。
一般的な概念は、JavaFXアプリケーションでインタフェース・オブジェクトを作成し、JSObject.setMember()メソッドをコールしてJavaScriptに認識されるようにすることです。 その後、JavaScriptからpublicメソッドをコールし、このオブジェクトのpublicフィールドにアクセスできます。
JavaScriptコマンドを使用したJavaFXアプリケーションの終了
まず、help.htmlファイルに<p><a href="about:blank" onclick="app.exit()">Exit the Application</a></p>という1行を追加します。 help.htmlファイルでユーザーが「Exit the Application」リンクをクリックすると、WebViewSampleアプリケーションが終了します。 この機能を実装するには、例6-1に示すようにアプリケーションを変更します。
例6-1 JavaScriptを使用したJavaFXアプリケーションの終了
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.application.Platform;
import javafx.beans.value.ObservableValue;
import javafx.concurrent.Worker.State;
import javafx.event.ActionEvent;
import javafx.geometry.HPos;
import javafx.geometry.Pos;
import javafx.geometry.VPos;
import javafx.scene.Node;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.Hyperlink;
import javafx.scene.image.Image;
import javafx.scene.image.ImageView;
import javafx.scene.layout.HBox;
import javafx.scene.layout.Priority;
import javafx.scene.layout.Region;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.web.WebEngine;
import javafx.scene.web.WebView;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import netscape.javascript.JSObject;
public class WebViewSample extends Application {
private Scene scene;
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
// create scene
stage.setTitle("Web View Sample");
scene = new Scene(new Browser(stage), 900, 600, Color.web("#666970"));
stage.setScene(scene);
// apply CSS style
scene.getStylesheets().add("webviewsample/BrowserToolbar.css");
// show stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
}
class Browser extends Region {
private final HBox toolBar;
final private static String[] imageFiles = new String[]{
"product.png",
"blog.png",
"documentation.png",
"partners.png",
"help.png"
};
final private static String[] captions = new String[]{
"Products",
"Blogs",
"Documentation",
"Partners",
"Help"
};
final private static String[] urls = new String[]{
"http://www.oracle.com/products/index.html",
"http://blogs.oracle.com/",
"http://docs.oracle.com/javase/index.html",
"http://www.oracle.com/partners/index.html",
WebViewSample.class.getResource("help.html").toExternalForm()
};
final ImageView selectedImage = new ImageView();
final Hyperlink[] hpls = new Hyperlink[captions.length];
final Image[] images = new Image[imageFiles.length];
final WebView browser = new WebView();
final WebEngine webEngine = browser.getEngine();
final Button toggleHelpTopics = new Button("Toggle Help Topics");
private boolean needDocumentationButton = false;
public Browser(final Stage stage) {
//apply the styles
getStyleClass().add("browser");
for (int i = 0; i < captions.length; i++) {
// create hyperlinks
Hyperlink hpl = hpls[i] = new Hyperlink(captions[i]);
Image image = images[i]
= new Image(getClass().getResourceAsStream(imageFiles[i]));
hpl.setGraphic(new ImageView(image));
final String url = urls[i];
final boolean addButton = (hpl.getText().equals("Help"));
// process event
hpl.setOnAction((ActionEvent e) -> {
needDocumentationButton = addButton;
webEngine.load(url);
});
}
// create the toolbar
toolBar = new HBox();
toolBar.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER);
toolBar.getStyleClass().add("browser-toolbar");
toolBar.getChildren().addAll(hpls);
toolBar.getChildren().add(createSpacer());
//set action for the button
toggleHelpTopics.setOnAction((ActionEvent t) -> {
webEngine.executeScript("toggle_visibility('help_topics')");
});
// process page loading
webEngine.getLoadWorker().stateProperty().addListener(
(ObservableValue<? extends State> ov, State oldState,
State newState) -> {
toolBar.getChildren().remove(toggleHelpTopics);
if (newState == State.SUCCEEDED) {
JSObject win
= (JSObject) webEngine.executeScript("window");
win.setMember("app", new JavaApp());
if (needDocumentationButton) {
toolBar.getChildren().add(toggleHelpTopics);
}
}
});
// load the home page
webEngine.load("http://www.oracle.com/products/index.html");
//add components
getChildren().add(toolBar);
getChildren().add(browser);
}
// JavaScript interface object
public class JavaApp {
public void exit() {
Platform.exit();
}
}
private Node createSpacer() {
Region spacer = new Region();
HBox.setHgrow(spacer, Priority.ALWAYS);
return spacer;
}
@Override
protected void layoutChildren() {
double w = getWidth();
double h = getHeight();
double tbHeight = toolBar.prefHeight(w);
layoutInArea(browser,0,0,w,h-tbHeight,0,HPos.CENTER,VPos.CENTER);
layoutInArea(toolBar,0,h-tbHeight,w,tbHeight,0,HPos.CENTER,VPos.CENTER);
}
@Override
protected double computePrefWidth(double height) {
return 900;
}
@Override
protected double computePrefHeight(double width) {
return 600;
}
}
例6-1で、太字の行をよく確認してください。 JavaAppインタフェースのexit()メソッドはpublicであるため、外部からアクセスできます。 このメソッドがコールされると、JavaFXアプリケーションが終了します。
例6-1のJavaAppインタフェースがJSObjectインスタンスのメンバーとして設定され、これによりこのインタフェースはJavaScriptで認識されるようになります。 window.app (または単にapp)という名前でJavaScriptに認識され、その唯一のメソッドはapp.exit()としてJavaScriptからコールできます。
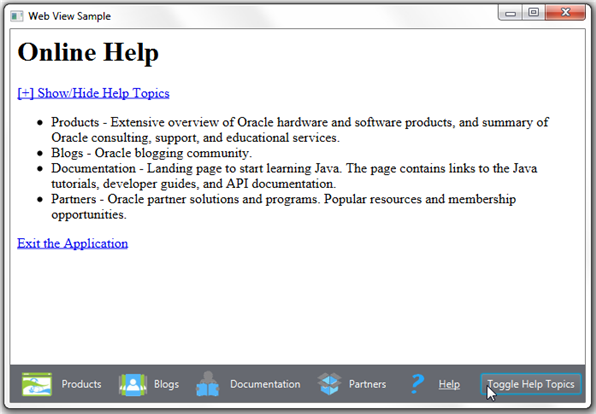
WebViewSampleアプリケーションをコンパイルして実行し、「Help」アイコンをクリックすると、図6-1に示すように「Exit Application」リンクが表示されます。
ファイルの内容をよく確認してから、図6-1に示すような「Exit the Application」リンクをクリックして、WebViewSampleアプリケーションを閉じます。