| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Oracle Java CAPS Worklist Manager Service Engine User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
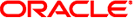
|
Oracle Java CAPS Worklist Manager Service Engine User's Guide Java CAPS Documentation |
Using the Worklist Manager Service Engine
Worklist Manager Service Engine Overview
Worklist Manager Service Engine Features
Worklist Manager Service Engine Architecture
About the Worklist Manager Console
The Composite Application Project
XPath Expressions in Task Definitions
Worklist Manager Task Validation
Steps to Implement a Worklist Manager Task
Defining Worklist Manager Tasks
(Optional) Connecting to the LDAP Server
(Optional) Installing the Sample Worklist Manager Console Projects
To Install the Sample Worklist Manager Console
Creating the Worklist Module Project
Creating the XML Schema Definition (XSD)
To Create the XML Schema Definition
Creating the Worklist Manager Task Definition
To Create the Worklist Manager Task Definition
Assigning Users and User Groups to a Task
To Assign File Realm Users and Groups to a Task
To Assign LDAP Users and Groups to a Task
Configuring Advanced Task Options
Defining Time Limits and Deadlines for a Task
Defining Automatic Task Escalations
To Define Automatic Escalations
Defining Automatic Task Notifications
To Define Automatic Notifications
To Associate a Notification With a Task Status Change or Escalation
To Configure the Email BC for Task Notification
To Define a Custom Notification
Defining Trigger Actions Using the Mapper
To Define Trigger Actions Using the Mapper
Initializing Variables Using the Mapper
To Initialize Variables Using the Mapper
Creating the Worklist Manager Database
Creating the Worklist Manager Database
Creating the Database for JavaDB (Derby)
Creating the Database for MySQL
Creating the Database for Oracle
Setting the GlassFish JVM Classpath to the Database Drivers
To set the GlassFish JVM Classpath settings
Creating the JDBC Connection Pool and JDBC Resource
To Create the JDBC Connection Pool
Configuring the Service Engine to Use the Worklist Manager Database
To Configure the Service Engine for the Database
Configuring Worklist Manager Service Engine Runtime Properties
To Configure WLM SE Runtime Properties
Worklist Manager Service Engine Runtime Property Descriptions
Defining Worklist Manager Console Security
Defining Worklist Manager Console Security Using a File Realm
To Create a User Login Profile in the File Realm
To Define Security Roles for the Worklist Manager Console
To Map Groups to Security Roles for the Worklist Manager Console
Defining Worklist Manager Console Security Using LDAP
To Create an LDAP Realm in the GlassFish Server
To Update web.xml for the Worklist Manager Console (for LDAP)
To Map User Groups to Security Roles for the Worklist Manager Console (for LDAP)
To Configure the Worklist Manager Service Engine for LDAP
Including the Worklist Manager Task in a BPEL Process
To Include the Worklist Manager Task in a BPEL Process
Creating and Deploying the Composite Application
To Create and Deploy the Composite Application
Testing the Worklist Manager Composite Application
To Run All Test Cases in a Project
Using the Default Worklist Manager Console
Installing and Deploying the Worklist Manager Console Sample
To Install and Deploy the Worklist Manager Console Sample
Logging In to the Worklist Manager Console
To Launch the Worklist Manager Console From a Browser
To Launch the Worklist Manager Console From the GlassFish Admin Console
Using XPath Expressions and Functions in Task Definitions
wlmfn:get-task-owner as xs:string
wlmfn:get-email() as xs:string
wlmfn:get-email($arg as xs:string) as xs:string
wlmfn:get-manager-email() as xs:string
wlmfn:get-manager-email($arg as xs:string) as xs:string
wlmfn:get-manager-uid() as xs:string
Creating Worklist Manager Task Mappings
To Create a Mapping Without Using any Functions
To Use a Function in a Mapping
To Delete a Link or Function From a Mapping
Customizing the Worklist Manager Console
About the Worklist Manager Console
Functionality and UI Semantics Specification
Customizing the Worklist Manager Console
Correcting the Task Input Data Display
Correcting the Task Output Data Display
Creating a Custom Worklist Manager Console
Creating the Web Application and Composite Application
To Configure the Web Application
You can use XPath expressions to dynamically derive the values for user names, notifications, escalations, and other properties of a task definition. Two internal variables are provided: TaskInput and TaskOutput. TaskInput is read-only and holds a single element of the input message from the workflow process that triggers the task instance. These are the values that are used to populate the task definition properties. TaskOutput holds the output message that is returned to the workflow process when the task completes. Initially it is an empty element.
TaskInput and TaskOutput are single-part variables. The Task Definition Editor provides a mapper that allows you to graphically define XPath expressions for initialization and changing these variables on the Actions tab. For the General, Escalations, and Notification tab, you can type the expressions manually. An XPath expression in the Task Definition Editor begins with an equals sign (=), which is stripped out in the actual source code.
The WLM SE provides functions to retrieve information from the Worklist Manager database about task owners, email addresses, and LDAP UIDs. You can enter the functions directly into the task definition file using the syntax described below, or you can use the task mapper to graphically add the functions to the file. The mapper is described in Using the Task Mapper.
Currently the WLM SE provides one function that retrieves the owner of a particular task.
This function returns the user who claims the task. If the task is not claimed, it returns null.TaskInstance.Owner is automatically assigned by the WLM SE when a user claims the task.
LDAP functions are only available when LDAP is used for task assignment and authorization. The namespace for these functions is http://jbi.com.sun/wfse/xpath-functions.
This function retrieves the email address for the user who claimed the task.
This function retrieves the email address for the user specified in the argument passed to the function.
This function retrieves the email address for the manager of the user who claimed the task.
This function retrieves the email address for the manager of the user specified in the argument passed to the function.
This function retrieves the LDAP UID for the manager of the user who claimed the task.
This function retrieves the LDAP UID for the manager of the user specified in the argument passed to the function.
Initializing a variable allows you to define some default value for the task output when a user views the task on the Worklist Manager Console. Variables are initialized using the init element of the task definition file. This is not a required section for the file. Variable initialization occurs before the task is created, and once the variable is assigned it cannot be changed. If you define the initialization using the Task Definition Editor Mapper, it automatically writes this section for you.
The format of the init element is as follows:
<init>
<variables>
...
</variables>
<variable-init>
<copy>
<from>XPath_or_literal</from>
<to>XPath_variable</to>
</copy>
</variable-init>
For example, this excerpt from the sample project maps the literal value “Approved” to the approveResult:
<variable-init>
<copy>
<from>'Approved'</from>
<to>$TaskOutput.part1/ns:approveResult</to>
</copy>
</variable-init>
For an example of how this is implemented in the Mapper, see Initializing Variables Using the Mapper.
When you enter XPath expressions directly into the graphical Design view of the Task Definition Editor, you begin the expression with an equals sign (=) to let the editor know that the value is a variable and not a literal value. The equals sign is not part of the generated XPath in the source code.
For example, the variables in the figure below translate into the following source code in the task definition file:
Title
<title>concat($TaskInput.order/po:purchaserName, concat(' Purchase Order for ', $TaskInput.order/po:productId))</title>
Priority
<priority>$TaskInput.order/po:priority</priority>
Group
<group>$TaskInput.order/po:users</group>