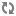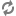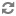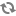dsp: lets you designate a target page in any J2EE Web application. You can do this in two ways:
Use the src attribute
To access a page in another Web application, set the src attribute to a full path that starts with a context path defined in web.xml. For example, this tag might appear in a JSP:
<dsp:include src="/QuincyFunds/en/guesthome.jsp">
where /QuincyFunds is a context path that is defined in web.xml.
You can configure the ATG platform to support multiple context paths. For example, the following fragment from web.xml defines two context paths delimited by colons: /QuincyFunds and /dyn:
<contextparam>
<paramname>atg.dynamo.contextPaths</paramname>
<paramvalue>/QuincyFunds:/dyn</paramvalue>
</contextparam>
Note: If you modify web.xml, you must reassemble, redeploy and restart the ATG platform application before changes take effect.
Use the src and otherContext attributes
Used together, the src and otherContext attributes let you access pages in other Web application by identifying a context path that is not specified in the application’s web.xml. For example:
<dsp:include otherContext="/QuincyFunds" src="/en/guesthome.jsp">
This tag should resolve correctly to the desired JSP whether or not the including application’s web.xml defines the context path /QuincyFunds.