 Understanding Batch Processing
Understanding Batch Processing
This chapter provides an overview of batch processing and discusses how to:
Verify model setup using Model Navigator.
Validate models.
Populate the Activity-Based Management Object table.
Process data using the Activity-Based Management engine.
Create multidimensional models using Data Manager.
Analyze profitability using Profit Manager.
 Understanding Batch Processing
Understanding Batch Processing
Once you complete the necessary setup, you can process your model using engines that validate metadata (or model setup) or that process data for single or multiple dimensions (or ensure that the model is configured correctly within the system).
This section provides overviews of:
Jobstreams and engines.
Activity-Based Management tables.
Batch processing process flow.

 Jobstreams and Engines
Jobstreams and Engines
Jobstreams let multiple users run their own jobs using instances of the same engines at the same time. By sharing temporary tables passed between jobs, jobstreams also speed up processing.
This section discusses:
Jobstreams.
Delivered engines.
Jobstreams
Instead of locking up the primary input (fact) tables in the operation warehouse - enriched (OWE), jobstreams use temporary tables for intermediate processing. A set of delivered temporary tables, which are called record suites, use only the relevant data from the main OWE fact tables to run the engines and process the data. This lets the engines in the jobstream run faster while keeping the fact tables open and accessible to other users so they can run the same engines simultaneously. The system assigns the record suites when the first engine runs and releases them when the last engine finishes.
Note. PeopleSoft Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) has predefined engines, engine metadata, jobs, job metadata, jobstreams, and record suites. You can also set up your own jobstreams. To do so, associate each engine with a job ID using the Job Metadata page, and then associate jobs with a jobstream using the Jobstream Setup page. A job must be unique across all jobstreams.
See Using Balancing and Reconciliation Features.
See Using the Reconciliation Engine and Job Total Metadata.
PeopleSoft EPM applications use engines to run processes. PeopleSoft delivers engine metadata with the system. This metadata stores information about the various PeopleSoft Application Engine programs used within an engine. The following table lists the delivered PeopleSoft engines and the associated job IDs that you use when processing Activity-Based Management:
|
Engine Name |
Job ID |
Description |
Usage |
|
RUN_PF_JOBSTREAM |
RUN_PF_JOBSTREAM |
Activity-Based Management Model and Activity-Based Management Ledger Mapper |
Generates the objects and drivers for a model and the ledger-to-resource mapping for a model. |
|
PF_EMP_SURV |
EMP |
Employee Profile |
Generates resources and drivers based on the employee profile information. |
|
AB_RTG |
RTG |
Routing Information engine |
Creates relationships (drivers) for activities and cost objects for manufacturing purposes as described in Appendix C of this PeopleBook. |
|
PF_Activity-Based Management_CUBE |
AB_CUBE |
Activity-Based Management Cube engine |
Creates online analytical processing cubes. |
|
AB_DRILLBACK |
AB_DRILL |
Activity-Based Management Drillback engine |
Processes data for multidimensional reporting using a third-party reporting tool. |
|
PF_ABPS |
ABPS |
ABPS engine |
Processes ABPS models. |
|
PF_OBJ_TBL |
OBJ_TBL |
Populate Activity-Based Management Object Table |
Combines the separate object tables into a single table for modeling and reporting. Run this engine any time that you make changes to any objects. |
|
AB_VALIDATE |
ABMD |
Activity-Based Management Model Validation |
Validates resources, activities, cost objects, business rules, and tree structures for the model. You can run it any time after creating the model. |
|
PF_ABC |
Activity-Based Management |
Activity-Based Management engine |
Calculates single dimensional costs for resources, activities, and cost objects. |
|
PF_MERGE |
MERGE |
Merge engine |
Moves engine output from the temporary processing tables to the appropriate final table. This engine is part of EPM Foundation and should be run after all other engines. |
|
ABM_RT_MAP |
ABM_RT_MAP |
Activity-Based Management mapping |
Assign costs and amounts to resources based on the resource-to-ledger mapping rules and saves the output in ABM_LEDMAP_F00. This engine is used when preparing the ledger to resource mapping/amounts from the Real-Time ABM model. |
Note. This list does not include any Data Manager activities discussed in the Enterprise Warehouse Tools and Administration PeopleBook.
This PeopleBook discusses the following engines:
Model Generator
Ledger Mapper Generator
Employee Profile
Routing Information
Activity-Based Management Cube
Activity-Based Management Drillback
Employee Profile
ABPS
You can only run the Activity-Based Management Objects engine in a jobstream. It does not have a separate run control page.
See Also
Running the Employee Profile Engine
Using the Reconciliation Engine and Job Total Metadata
Running Model Generator and Ledger Mapper Generator
Using Activity-Based Planning and Simulation (ABPS)
Generating and Maintaining Models

 Activity-Based Management Tables
Activity-Based Management Tables
Activity-Based Management has input tables that enable you to enter information into the system for processing and output tables that store processing results.
The following flow chart illustrates key tables that the system uses during Activity-Based Management, Data Manager, and Profit Manager processing:
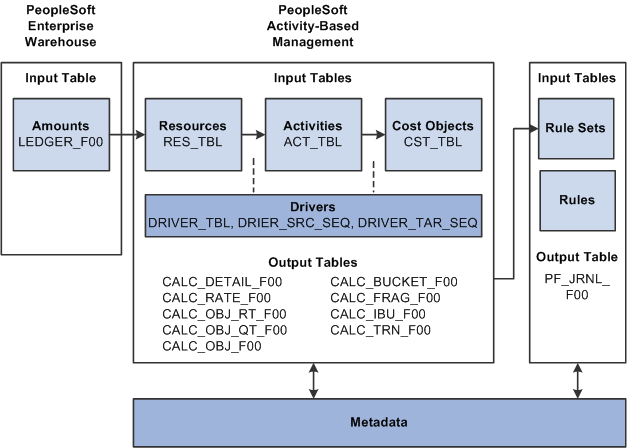
Key Activity-Based Management tables
You can select any of the following input tables for ledger mapping information; however, you may choose to use the first two tables more frequently:
Optional Budget Amounts (LEDGER_BUDG)
The output tables contain calculation tables. Metadata defines the types of data that the calculation tables store, which affects the calculation tables' output and how Data Manager uses the output for processing. The calculation tables store the output of the Activity-Based Management engine until it is used by other system processes. The system performs calculations in stages, and then stores these calculations in temporary tables; however, the system copies all of the results to the final tables.
The following table lists Activity-Based Management calculation tables:
|
Table Name |
Object ID |
Contents |
|
CALC_OBJ_F00 |
Contains calculated cost values for resource, activity, and cost object amount information as processed by the Activity-Based Management engine. Use this table to query amount results for an object. |
|
|
CALC_DETAIL_F00 |
Contains drillback or direct assignment information. The Drill Level field within the table denotes the type of calculation assignment. Use this table to drill back to the previous object (direct calculation) and obtain information for drilling back to all objects that contribute indirectly to the object (drillback calculation). |
|
|
CALC_BUCKET_F00 |
Contains temporary calculation results for resources, activities, and cost objects; therefore, it contains the most amount of detail. The system stores all finalized values in the Calculation Detail table (to be used for other processes). |
|
|
CALC_RATE_F00 |
Contains driver rates. |
|
|
CALC_OBJ_RATE_F00 |
Contains object rates such as object costs or object-calculated amounts. |
|
|
CALC_OBJ_QTY_F00 |
Contains object volume and quantity. |
|
|
CALC_FRAG_F00 |
Contains activity fragmentation data for employee resources. |
|
|
CALC_IBU_F00 |
Contains cost data from inter-unit drivers. |
|
|
CALC_TRN_F00 |
Contains transaction rates. |
|
|
BU_RATE_F00 |
Contains inter-business unit driver rates. |
See Also
Setting Up and Using Profit Manager
 Verifying Model Setup Using Model Navigator
Verifying Model Setup Using Model Navigator
This section provides an overview of model setup verification using Model Navigator and discusses how to:
Drill back through model data.
Review resource attributes.
Review activity attributes.
Review cost-object attributes.

 Understanding How to Verify Model Setup Using Model Navigator
Understanding How to Verify Model Setup Using Model NavigatorUse Model Navigator to verify your model setup before running the Activity-Based Management Model Validation engine and Activity-Based Management engines. Model Navigator lets you drill back through resources, activities, and cost objects based on how the you set up the drivers. It uses information from the sources and targets to drill down to the next level.
Note. The Model Navigator - Resources, Model Navigator - Activities, and Model Navigator - Cost Objects pages display only the attributes for the Activity-Based Management objects, not the monetary amounts. (To determine how the system assigns costs throughout the model, use Object Navigator.) You can also use Model Navigator to drill through implicit drivers; however, to use this functionality, first run the Model Validation engine.
See Also
Using Object Navigator and Model Analyzer

 Pages Used to Verify Your Model Setup
Pages Used to Verify Your Model Setup
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|
ABC_DRILL_MODEL1 |
Activity Based Management, Setup, Model, Model Navigator, Model Navigator |
Review your model setup. |
|
|
ABC_DRILL_RES |
Activity Based Management, Setup, Model, Model Navigator, Resources |
Review the attributes of the resources used in your models. |
|
|
ABC_DRILL_ACT |
Activity Based Management, Setup, Model, Model Navigator, Activities |
Review the attributes of the activities used in the model. |
|
|
ABC_DRILL_CST |
Activity Based Management, Setup, Model, Model Navigator, Cost Objects |
Review the attributes of the cost objects used in the model. |

 Drilling Back Through Model Data
Drilling Back Through Model Data
Access the Model Navigator page (Activity Based Management, Setup, Model, Model Navigator, Model Navigator).
|
Object Type |
Select Activity, Cost Obj. (cost object), or Resource. |
|
Object ID |
Enter the unique identifier of the object. |
|
Get Source(s) |
Click to populate the grid with a list of sources for the associated object ID. |
|
Get Target(s) |
Click to populate the grid with a list of targets for the associated object ID. |
|
|
Click the Drill Down button to navigate through the model. |
|
|
Click the Get Object Data button to navigate to the appropriate setup page for that object. For example, if you click this button while viewing an activity, the Define Activities page displays. |
|
|
Click the Get Driver Data button to view the driver setup in the Drivers component. |

 Reviewing Resource Attributes
Reviewing Resource Attributes
Access the Model Navigator - Resources page (Activity Based Management, Setup, Model, Model Navigator, Resources).
|
All Resources |
Select All Resources to search for all possible resources that you want to review. |
|
All Res Use (all resource use), All Res Group (all resource groups), All Res Supply As (all resource supply as), and All Accounting Class |
Select any combination of check boxes to search for those types of resources that you want to review, and then refine your search further by selecting a value from the associated drop-down lists that display. For example, selecting the All Res Group check box displays the corresponding Resource Use drop-down list where you can select a specific resource use. The more check boxes that you select, the more detailed your search. |
|
Get Resources |
Click to display your search results. |
See Also

 Reviewing Activity Attributes
Reviewing Activity Attributes
Access the Model Navigator - Activities page (Activity Based Management, Setup, Model, Model Navigator, Activities).
This page functions the same as the Model Navigator - Resources page. In the Search Criteria group box, specify the detail of your search by selecting the desired check boxes, and then selecting items for the corresponding drop-down lists. Click Get Activities to display your search results. The Defining Activities section describes the grid columns.
See Also

 Reviewing Cost Object Attributes
Reviewing Cost Object Attributes
Access the Model Navigator - Cost Objects page (Activity Based Management, Setup, Model, Model Navigator, Cost Objects).
This page functions the same as the Model Navigator - Resources page. In the Search Criteria group box, specify the detail of your search by selecting the desired check boxes, and then selecting items for the corresponding drop-down lists. Click Get Cost Objects to display your search results.
See Pages Used to Verify Your Model Setup.
See Also
 Validating Models
Validating Models
To enhance data integrity, run the Activity-Based Management Model Validation engine to find most of the setup problems, data integrity errors, business rule errors, tree errors, and other audit errors. The Model Validation engine lets you display all errors online according to type, severity, and related parameters that identify the cause of the error so that you can correct errors without substantial additional investigation.
See Activity-Based Management Validation Engine Messages.
When you run this engine, the system creates a temporary table for error message details. Because you need to merge these details into the final tables, run a single jobstream that runs this engine with the Merge engine to ensure that the system populates the final tables.
When you set up your models using the Models component (MODEL_TBL1), click the Run Control Information tab (MODEL_TBL3) to define the Activity-Based Management Model Validation Profile that you want to use.
|
Audit Validation |
Select to check your model metadata setup. |
|
Complete Validation |
Select to run a complete validation for the model including audit, data integrity, and setup. |
|
Data Integrity Validation |
Select to ensure that the information that you want to use in the model is available and accurate. |
|
Setup Validation |
Select to search for errors that cause the Activity-Based Management engine to stop processing. |
Note. You can also audit your metadata before running these engines by running the Audit Utility in the PeopleSoft EPM.
See Also
Activity-Based Management Validation Engine Messages
Defining Run Control Information
 Populating the Activity-Based Management Object Table
Populating the Activity-Based Management Object Table
The Preprocess Activity-Based Management Objects engine (OBJ_TBL) takes the separate object tables and combines them into one table for reporting and modeling. Run this engine as soon as you set up your objects. Thereafter, run it whenever you make any changes to any of the resources, activities, or cost objects. In addition, run this process before running any reports; otherwise, your reports do not reflect meaningful information.
Run this engine in a jobstream by itself. You cannot combine it with other engines; it must be run separately.
See Streamlining Processing with Jobstreams.
 Processing Data Using the Activity-Based Management Engine
Processing Data Using the Activity-Based Management Engine
To process single dimensional models, run the Activity-Based Management engine. This engine stores the final output in the calculation tables.
Before running this engine, complete model setup including its resources, activities, cost objects, pointers, drivers, and ledger mappers.
After running this engine, reconcile your model (as discussed later in this PeopleBook).
See Understanding Batch Processing.
See Also
Reconciling Your Model and Analyzing Engine Output
 Creating Multidimensional Models Using Data Manager
Creating Multidimensional Models Using Data Manager
This section provides an overview of creating multidimensional models using Data Manager and lists the page to run Data Manager.

 Understanding Multidimensional Models Using Data Manager
Understanding Multidimensional Models Using Data ManagerAlthough you may have used single-dimensional assignments in your model to preserve cause-and-effect relationships, the Data Manager engine can help you enrich and convert data into a multidimensional format for further analysis. It takes direct costs, indirect costs, and revenue, and calculates data across multiple dimensions—product, customer, channel, and department.
Determining whether to use single-dimensional costing or multidimensional costing requires a precise definition of the business case that you want to address. You must know what questions you want answered. For example, if your organization manufactures beverages, such as coffee and tea, you can use Activity-Based Management to calculate a model based on single-dimensional costing. The output of Activity-Based Management single-dimensional analysis might look something like this:
|
Cost Object |
Type |
Cost in USD |
Units |
Cost per Unit in USD |
|
Southwest Company |
Customer |
400 |
n/a |
n/a |
|
Central Company |
Customer |
600 |
n/a |
n/a |
|
New Northern Company |
Customer |
400 |
n/a |
n/a |
|
Tea |
Product |
600 |
60 |
10/case |
|
Coffee |
Product |
900 |
120 |
7.50/case |
With single-dimensional output and information, answers to these questions come easily:
How much does it cost to make four cases of tea?
How much is the unit cost of a case of coffee?
How much does it cost to serve all of our customers?
How much money could be saved by not doing business with the Central Company?
However, these types of questions are impossible to answer using this single-dimensional output:
Which customer is the most or least profitable?
Which product is the most or least profitable?
Which mix of products is the most or least profitable?
Clearly, more information is required to answer these questions. You need information regarding the revenue from each of the products as well as information regarding the products that each of the customers purchased. Such information could be obtained from your billing system as the following table represents:
|
Customer |
Product |
Quantity |
Revenue in USD per Case |
Total Revenue in USD |
|
Southwest Company |
Coffee |
50 |
10 |
500 |
|
Central Company |
Coffee |
30 |
10 |
300 |
|
New Northern Company |
Coffee |
40 |
10 |
400 |
|
Southwest Company |
Tea |
10 |
15 |
150 |
|
Central Company |
Tea |
20 |
15 |
300 |
|
New Northern Company |
Tea |
30 |
15 |
450 |
The data in this example provides information regarding the number of product cases purchased by a customer and the revenues associated with these product cases. You can use the quantities purchased as the basis for assigning the single-dimensional costs.
After you obtain billing information, use that information in conjunction with the single-dimensional information and use both as input for Data Manager. Data Manager lets you integrate the product and customer dimensions effectively. The following table lists an example of possible Data Manager output with all amounts in USD:
|
Revenues |
Product |
Southwest Company |
Central Company |
New Northern Company |
Total |
|
Coffee |
500 |
300 |
400 |
1,200 |
|
|
Tea |
150 |
300 |
450 |
900 |
|
|
Total |
650 |
600 |
850 |
2,100 |
|
|
Cost of Sales |
|||||
|
Coffee |
375 |
225 |
300 |
900 |
|
|
Tea |
100 |
200 |
300 |
600 |
|
|
Total |
475 |
425 |
600 |
1,500 |
|
|
Gross Profit |
175 |
175 |
250 |
600 |
|
|
Customer Costs |
400 |
600 |
400 |
1,400 |
|
|
Net income (or loss) |
(225) |
(425) |
(250) |
(800) |
The results of this analysis show that the Central Company is the least profitable customer.
The following flow chart illustrates how Activity-Based Management and Data Manager use direct and indirect costs and revenue:
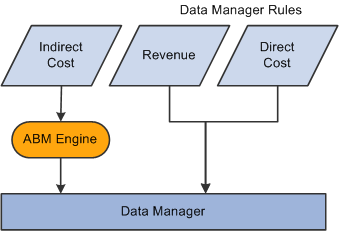
Data flow to Data Manager
After the system processes data through Data Manager, it is stored in the PF Journal table (PF_JOURNAL_F00).
Note. The Calculation Detail fact table (CALC_DETAIL_F00) and the Calculation Objects fact table (CALC_OBJ_F00) describe the same set of data in different ways. Be careful not to process data redundantly using Data Manager. You should take an either-or approach when determining which tables to use when you are assigning costs using Data Manager.
See Also
 Analyzing Profitability Using Profit Manager
Analyzing Profitability Using Profit Manager
After your model is set up and processed, you can generate profitability reports. To report on profitability, ensure that your data is in the PF Ledger table (PF_LEDGER_F00) where the reporting tools access information. Your data may still be in the PF Journal table, particularly if you ran Data Manager (which stores data in the journal). To get data from the PF Journal table to the PF Ledger table, run Profit Manager, which is the PF Post process.
Note. PeopleSoft EPM considers model ID to be the same as ledger for reporting purposes. It is important that the engines use the same model ID in those instances when you want the engine results to be reflected in the same profitability report.