I/O Communication Between Oracle Solaris Storage Stack Components
Oracle Solaris I/O multipathing is an integral part of the Oracle Solaris storage stack, which supports most of the storage devices. Oracle Solaris I/O multipathing feature provides high availability, reliability, and persistent names for the Oracle Solaris operating system (OS). For high availability, the storage stack devices use the I/O multipathing feature to ensure that the secondary path is online when the primary path of the device goes offline.
Figure 1 I/O Communication Between Oracle Solaris Storage Stack Components
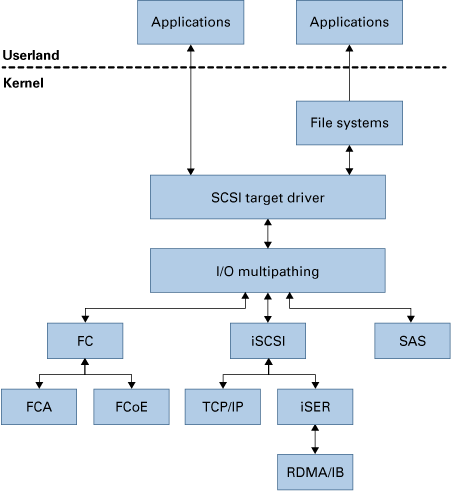
The storage I/O communicates with processes, applications, and other components in the storage stack such as disks, tape devices, and target device drivers, by using a multiplexer through the Signal Computing System Architecture (SCSA) layer. Each device in the storage stack has its driver, which helps in I/O communication. The SCSI target driver includes drivers such as sd, ssd, st, ses, and sgen. These device drivers include specific device codes to communicate with the specific storage device available in the network. Target drivers can either be character or block device drivers, depending on the device. For example, tape devices have character device drivers, and disks have block device drivers.
The multiplexer manages multiple I/O operations between the software and the hardware interfaces in a storage setup. In Oracle Solaris, the I/O multipathing feature is implemented by the scsi_vhci driver. This driver is SCSA compliant and supports FC, iSCSI, and SAS transport protocols in Oracle Solaris. These transport protocols enable you to access data from the storage devices for read or write operations. The Oracle Solaris storage stack uses file systems or applications, which can directly access block or collector devices. Oracle Solaris also supports FC switched, point-to-point, and FC-AL topologies.
In Oracle Solaris, the FC transport protocol support different types of Fibre Channel Adapters (FCAs) and Fibre Channel over Ethernet (FCoE) cards. The FCA cards have qlc or emulex drivers are integrated on the adapter, which enables automatic configuration. You can use an FCoE card either as an Ethernet NIC, FCoE card, or FC card. Oracle Solaris also provides software implementation for these FCoE cards. For more information about Fibre Channel devices in Oracle Solaris, see Configuring Fibre Channel Devices.
The iSCSI transport protocol supports the regular TCP/IP protocol and the iSCSI Extension for RDMA (iSER). iSER also supports InfiniBand remote direct memory access (RDMA). You can map multiple targets to a single initiator and access targets by using Oracle Solaris I/O multipathing. For more information about administering iSCSI devices, see Configuring an Oracle Solaris iSCSI Initiator.
Oracle Solaris supports SAS devices, expanders, and controllers. These SAS devices have drivers that enable you to access data from storage devices that are connected to an Oracle Solaris host that supports automatic configuration. For more information, see Configuring SAS Devices.