Oracle Solaris 10 Networking Overview
The following diagram shows that a guest domain that runs the Oracle Solaris 11 OS is fully compatible with an Oracle Solaris 10 service domain. The only differences are features added or enhanced in the Oracle Solaris 11 OS.
Figure 11 Oracle VM Server for SPARC Network Overview for the Oracle Solaris 10 OS
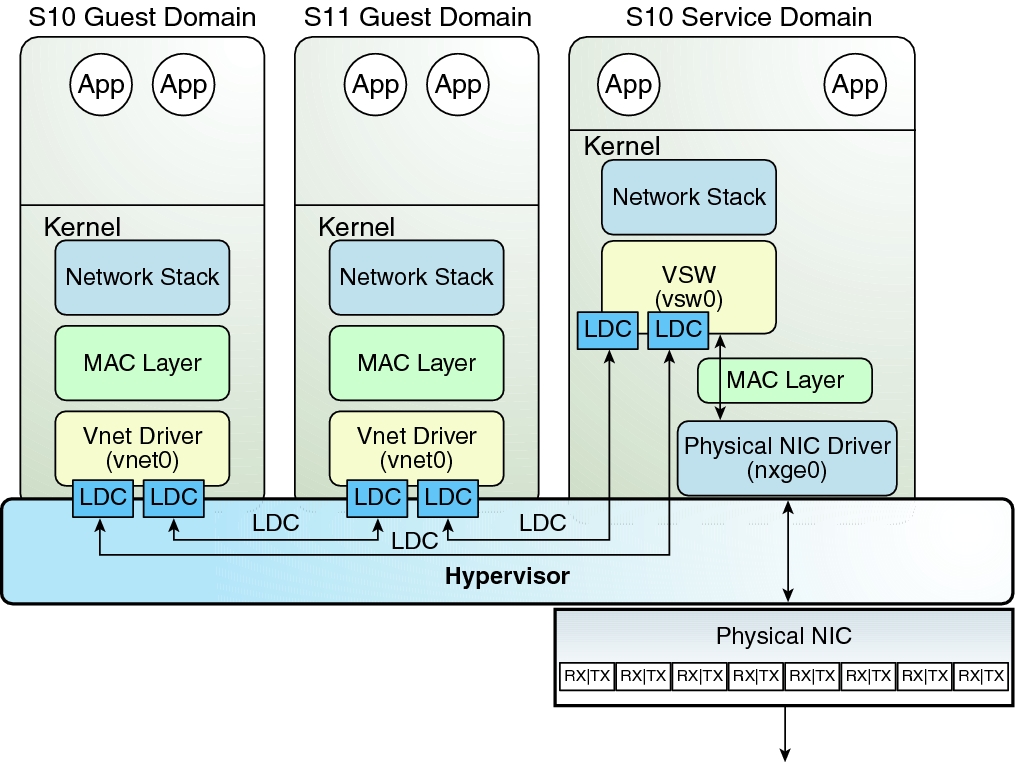
The virtual switch in the service domain is connected to the guest domains, which enables guest domains to communicate with each other.
The virtual switch is also connected to the physical network interface nxge0, which enables guest domains to communicate with the physical network.
The virtual switch network interface vsw0 is created in the service domain, which enables the two guest domains to communicate with the service domain.
The virtual switch network interface vsw0 in the service domain can be configured by using the Oracle Solaris 10 ifconfig command.
The virtual network device vnet0 in an Oracle Solaris 10 guest domain can be configured as a network interface by using the ifconfig command.
The virtual network device vnet0 in an Oracle Solaris 11 guest domain might appear with a generic link name, such as net0. It can be configured as a network interface by using the ipadm command.
The previous diagram shows interface names such as nxge0, vsw0, and vnet0 which apply to the Oracle Solaris 10 OS only. Also note the following:
The virtual switch behaves like a regular physical network switch and switches network packets between the different systems, such as guest domains, the service domain, and the physical network, to which it is connected. The vsw driver provides the network device functionality that enables the virtual switch to be configured as a network interface.