Creating and Reversing Interunit Expensed Issues
An interunit expensed issue is a stock request that issues material from an Inventory business unit to an internal department that is not reporting to the same GL unit as the inventory unit. If you are shipping stock from a centralized inventory location to various internal departments within the organization, then interunit expensed issues can create the proper accounting entries when multiple GL units are involved. The system creates an interunit expensed issue when you enter a stock request using the internal issue request type and then override the GL unit on the order. You can enter an interunit expense issue using the Material Stock Request or Express Issue pages in PeopleSoft Inventory. The system also processes interunit expense issues when demand is passed from a purchasing requisition and the GL unit on the requisition line is not the same as the inventory's GL unit. Use the Stock Request Maintenance page to add or change the destination GL unit. Use the Par Location Header page to define a destination GL unit for issues to a par location. When you override the GL unit, the system validates the destination ChartFields against the new GL unit.
Occasionally, the stock from an interunit expensed issue must be returned to inventory. Use the Expense Issue Return page to record the receipt of stock originally shipped as an interunit expensed issue. The stock can be received into the original sending inventory business unit or another inventory business unit. If the stock is received into a different inventory unit than the one from which it was initially shipped, then both inventory units must share the same set of items. You can enter the returned items on the Expense Issue Return page with or without the original interunit expensed issue stock request. To create an audit trail that goes back to the original shipment, you must retrieve and use the original interunit expensed issue transaction. You can return the full shipment or just part of the items or quantities shipped that you shipped.
Note: To run an interunit expensed issue, the currency and ChartFields must be the same for all the GL business units. For transactions with multiple currencies and accounting structures, enter an intercompany transaction (interunit sales approach) described in the "Managing Interunit Transfer Pricing and Additional Costs" topic.
See Understanding Interunit Transfers.
Costing and Accounting Interunit Expensed Issues
The system uses the transfer price to cost the material issue. Define the method for interunit transfer pricing in the sending inventory business unit using the Transfer Pricing Definition component and the transfer price default hierarchy.
See Applying Transfer Prices to a Material Stock Request.
See Using Transfer Pricing Definitions.
You can change the transfer price manually on any line of a material stock request. The sending inventory business unit reduces its inventory stock based on the deplete cost method that you selected on the Cost Profiles page. The system records any difference between the transfer price and the item's depletion cost as a gain or loss on transfer.
When you create an interunit expensed issue, the Accounting Line Creation process creates accounting entries that debit the interunit receivables of the sending GL unit and credit the interunit payables of the recipient's GL unit. The system identifies interunit expensed issues with the transaction group 036 (InterUnit Expensed Issue). Set up the accounting distribution for this transaction group in a different manner than the other transaction accounting rules. With this group, set up the debit for the destination GL unit and the ChartField validation against the destination GL unit. You cannot enter a cost element for the debit side of this entry. Set up the credit side for the inventory unit, if you are not using location accounting or if location accounting reports that it is using the function. Any difference between the transfer price and the item cost creates an additional entry using the transaction group 300 (Gain/Loss on Transfer Price).
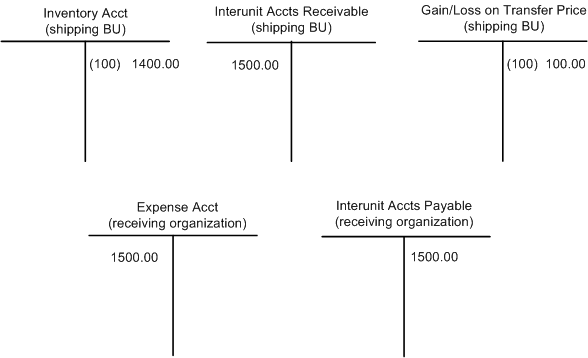
The following diagram illustrates an example of the accounting entries generated for an interunit expensed issue transaction. The cost of the item is removed from the shipping organization's inventory account using the deplete cost method of the item's cost profile. In this case the item cost is 1,400 stored in the cost element 100 (material- general). The transfer price for the item is used to record the interunit accounts receivable in the shipping organization and the interunit accounts payable and expense accounts in the receiving organization. In this case, the transfer price is 1,500 stored in the cost element 100 (material- general). The transfer price is computed by the Deplete On Hand Qty process and placed in the IN_DEMAND_TRPC table. In the shipping organization, any difference between the item cost and the item transfer price is recorded in a gain/loss account using the transaction group 300 (Gain/Loss on Transfer Price).
For transaction group 036 (InterUnit Expensed Issue), use these pages to derive the ChartField combinations for each accounting line. Use different pages based on the choice of interunit method (that you selected on the Installation Options - Overall/GL page) and location accounting (that you selected on the Inventory Options page):
|
InterUnit Method |
Location Accting |
Page for DR to Source BU |
Page for CR to Source BU |
Page for DR to Dest BU |
Page for CR to Dest BU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Direct |
Off |
InterUnit Template (defined on the source GL) |
Accounting Rules |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
InterUnit Template (defined on the destination GL) |
|
Direct |
On |
InterUnit Template (defined on the source GL) |
Storage Area Accounting |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
InterUnit Template (defined on the destination GL) |
|
Indirect |
Off |
InterUnit Template (defined on the destination GL) |
Accounting Rules |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
InterUnit Template (defined on the source GL) |
|
Indirect |
On |
InterUnit Template (defined on the destination GL) |
Storage Area Accounting |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
InterUnit Template (defined on the source GL) |
|
Pair |
Off |
InterUnit Pair |
Accounting Rules |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
InterUnit Pair |
|
Pair |
On |
InterUnit Pair |
Storage Area Accounting |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
InterUnit Pair |
Costing and Accounting InterUnit Expensed Issue Returns
Returns are completed using the Expense Issue Return page in PeopleSoft Inventory. To reverse the original interunit expensed issue transaction, the system uses the transfer price from the original stock request (if you have identified the interunit expensed issue transaction), or the value that you entered in the Transfer Price field on the Expense Issue Return page. The inventory business unit costs the receipt based on the receipt cost method that you selected on the Cost Profiles page. The system records any difference between the transfer price and the item's putaway cost as a gain or loss on transfer. For the GL unit that rejected the shipment, the system reverses the original entry by using the transfer price or you may override the price. When you use the original stock request (interunit expensed issue transaction), the system uses the transfer price stored in the IN_DEMAND_TRPC table where the transfer price is stored by cost elements. This granular detail is used to record the putaway. If you override the transfer price on the Expense Issue Return page, then the system uses the override transfer price and the Default Cost Element field defined on the Define Business Unit Item - General: Common page.
When you create an expensed issue return, the Accounting Line Creation process creates accounting entries that debit the interunit payables of the returning GL unit and credit the interunit receivables of the receiving inventory's GL unit, thereby reversing the original transaction. The system uses the transaction group 026 (Expensed Issue Return) to identify the ChartField combinations for the inventory account receiving the stock and the expense account to be reversed in the returning GL unit. Set up the accounting distribution for this transaction group in a different manner than the other transaction accounting rules. With this group, set up the credit to validate ChartFields against the returning GL unit. You cannot enter a cost element for the credit side of this entry. Set up the debit side for the inventory unit receiving the return, if you are not using location accounting or if location accounting reports that it is using the function. Any difference between the transfer price and the item's putaway cost creates an additional entry using the transaction group 300 (Gain/Loss on Transfer Price).
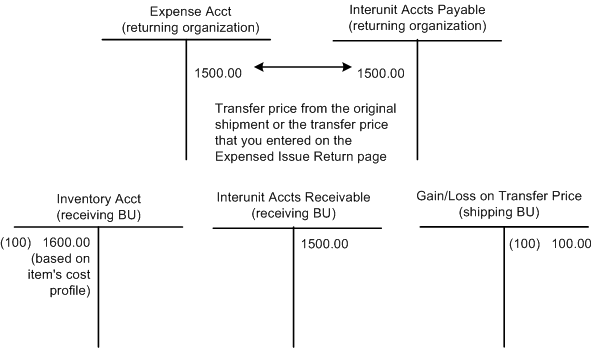
The following diagram illustrates an example of the accounting entries generated for an interunit expensed issue return transaction. The transfer price for the item is used to reverse the original entries in the returning organization's interunit accounts payable and expense accounts and the receiving organization's interunit accounts receivable account. In this case, the transfer price is 1,500 stored in the cost element 100 (material- general). The cost of the item is entered in the receiving organization's inventory account using the receipt cost method of the item's cost profile. In this case the item cost is 1,600. In the receiving organization, any difference between the item cost and the item transfer price is recorded in a gain/loss account using the transaction group 300 (Gain/Loss on Transfer Price).
For the transaction group 026 (Expensed Issue Return), use these pages to derive the ChartField combinations for each accounting line. Use different pages based on the choice of interunit method (that you selected on the Installation Options - Overall/GL page) and location accounting (that you selected on the Inventory Options page). In this table, the receiving GL refers to the GL unit tied to the inventory unit that originally issued the stock. The returning GL refers to the GL unit returning the stock.
|
InterUnit Method |
Location Accting |
Page for DR Receiving Inv BU |
Page for CR Receiving Inv BU |
Page for DR Returning GL BU |
Page for CR Returning GL BU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Direct |
Off |
Accounting Rules |
InterUnit Template (defined on the receiving GL) |
InterUnit Template (defined on the returning GL) |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
|
Direct |
On |
Storage Area Accounting |
InterUnit Template (defined on the receiving GL) |
InterUnit Template (defined on the returning GL) |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
|
Indirect |
Off |
Accounting Rules |
InterUnit Template (defined on the returning GL) |
InterUnit Template (defined on the receiving GL) |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
|
Indirect |
On |
Storage Area Accounting |
InterUnit Template (defined on the returning GL) |
InterUnit Template (defined on the receiving GL) |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
|
Pair |
Off |
Accounting Rules |
InterUnit Pair |
InterUnit Pair |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
|
Pair |
On |
Storage Area Accounting |
InterUnit Pair |
InterUnit Pair |
Accounting Rules (no cost element) |
Setting Up Interunit Expensed Issues
To enable Interunit Expensed Issues:
Enable interunit expense issues for PeopleSoft Inventory by selecting the Display GL BU Override check box on the Inventory Display Options page.
This option displays the GL BU Override field on the Material Stock Request, Express Issue and Stock Request Inquiry pages. On the Stock Request Maintenance page, the GL BU override is visible, but you cannot enter values if this option is not selected.
Define the interunit receivables and payables accounts.
Where you define these accounts depends on the value that you selected in the InterUnit Method field on the Installation Options - Overall page. If the value is:
Direct: the interunit receivables or payables accounts are entered on the InterUnit Template page defined for both GL business units.
Indirect: the interunit receivables or payables accounts are entered on the InterUnit Template page defined for both GL business units.
Pairs: the interunit receivables or payables accounts are entered on the InterUnit Pair page. The sending GL unit must be entered in the From GL Unit field and the receiving unit must be defined in the To GL Unit field. A separate pair is defined for every combination of GL units using the interunit expensed issues feature.
Enter the interunit template ID on the General Ledger Definition - Inter/IntraUnit page, if you use direct or indirect methods.
Define the interunit transfer pricing using the Transfer Pricing Definition page.
InterUnit expensed issues are costed using the sending inventory business unit's transfer pricing structure.
Use the Accounting Rules page to define the expense account (or accrued liability) to debit and the inventory account to credit using the transaction group 036 (InterUnit Expensed Issue).
If you are using location accounting, the inventory account (credit side) is derived from the Storage Area Accounting page. With this transaction group, the debit is set up for the returning GL business unit; you cannot enter a cost element for the debit side of this entry.
Use the Accounting Rules page to record the gain or loss account to debit or credit when the item's cost differs from the transfer price using the transaction group 300 (Gain/Loss on Transfer Price).
Use the Accounting Rules page to define the expense account (or accrued liability) to credit and the inventory account to debit using the transaction group 036 (Expensed Issue Return).
If you are using location accounting, the inventory account (debit side) is derived from the Storage Area Accounting page. With this transaction group, the credit is set up for the GL business unit returning the stock; you cannot enter a cost element for the credit side of this entry.
Add reason codes for return.
On the Reason Codes page, define reason codes to describe the reason that the stock was returned, such as over stocked, damaged in shipment, and so on. When defining the reason codes, use the Return Type of Expense Issue Return. This allows you to select the reason code on the Expense Issue Return page.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
EZ_ISSUE_INV |
Enter an interunit expensed issue by using the internal issue request type and then override the GL unit on the order. |
|
|
EXPRESS_ISSUE1_INV |
Enter an interunit expensed issue by using the internal issue request type and then override the GL unit on the order. |
|
|
PUTAWAY_EXP_INV |
Enter a return of stock originally issued as an interunit expensed issue transaction. |
|
|
Inventory Display Options Page |
BUS_UNIT_DSP_IN |
Select the Display GL BU Override check box to enable interunit expense issues for the inventory business unit. |
|
CM_ACCTG_DIST |
Create the debit and credit lines for accounting entries based on the business unit, transaction group, distribution type, item or item group, and cost element. |
|
|
CM_TRAN_PRICE_DEFN |
Define the transfer prices to be used for a shipping business unit. |
|
|
Installation Options - Overall/GL Page |
INSTALLATION_FS1 |
Select an interunit method. |
|
BUS_UNIT_TBL_GL1 |
If using interunit templates, define the template for both receiving and sending GL units. |
|
|
IU_INTER_TMPLT |
If you selected the direct or indirect method on the Installation Options - Overall/GL page, then enter the interunit receivables and payables. |
|
|
IU_INTER_PR_BASIC |
If you selected the pairs method on the Installation Options - Overall/GL page, then enter the interunit receivables and payables for the GL pair. |
|
|
Reason Code Page |
REASON_CD |
Enter reason codes to describe the various reasons that stock was returned. Use the Reason Type of Expense Issue Return. |