Managing Your Enterprise Profitability and Cost Management Implementation
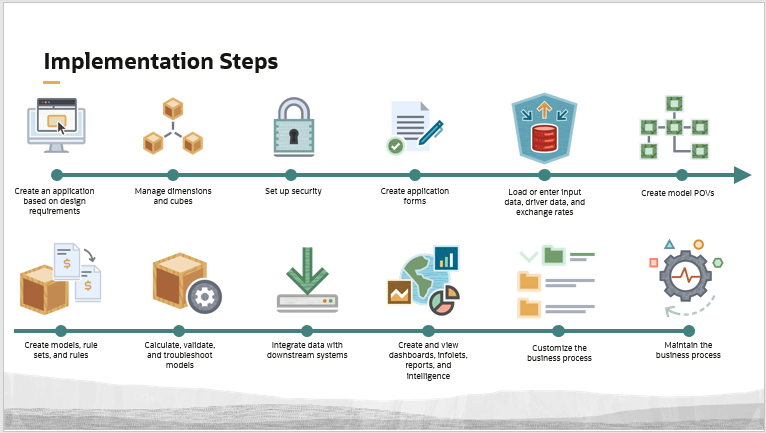
Though the order of steps may vary based on how you manage your implementation, a typical implementation process for a new Enterprise Profitability and Cost Management application includes these steps:
-
Create an application based on design requirements: Start by designing the structure of the business process. This includes planning which custom dimensions and attribute dimensions you will need for the default and custom cubes in your application. You also make decisions on items such as naming conventions, the calendar structure, and currency specifications. See Creating an Enterprise Profitability and Cost Management Application.
-
Manage dimensions and cubes: After the business process is created, you set up any custom dimensions and attribute dimensions, and then load metadata to build out all your dimensions. You can also add member formulas, attributes, user-defined attributes and smart lists to your dimension members. After creating your dimensions you can optionally add any custom cubes you require. See Managing Dimensions and Managing Cubes.
-
Set up security: Set up role-based, metadata, data, and artifact security. See Setting Up Access Permissions and Data Security.
-
Create application forms: Create forms needed for data entry, data validation, and Rule Balancing. See Administering Forms and Designing Data Forms for Rule Balancing.
-
Load or enter input data, driver data, and exchange rates: Enter data in forms and load data using native import or data integrations. See About Entering Data, Importing Data, and Creating File-Based Integrations.
-
Create model POVs: Create and manage model POVs for running model calculations. See Understanding Points of View, Creating a Point of View, and Using the Calculation Control Page.
-
Create models, rule sets, and rules: Create models, rule sets, and rules based on your business requirements. See Creating and Managing Models and Creating and Managing Rules.
-
Calculate, validate, and troubleshoot models: After loading data and creating models, you validate your rules, calculate models, and manage calculations. See Running Model Validation, Calculating Models, Analyzing Calculations, and Viewing Rule Balancing Reports.
-
Integrate data with downstream systems: After finalizing your calculated data, you can export it to a file, or to external systems such as Oracle Financials Cloud, Oracle General Ledger, and Planning. You can also export data from your calculation cube to your reporting cube. See Administering Data Integration.
-
Create and view dashboards, infolets, reports, and intelligence: Use dashboards, infolets, reports, and intelligence to analyze and report on your data. See Designing and Working with Dashboards, Viewing Key Information with Infolets, and Working with Reports for information on how to interact with existing dashboards, infolets, and reports. See Designing Data Forms for Profit Curves and Designing Data Forms for Trace to learn how to design forms for and build Profit Curves and Allocation Traces, which are unique toEnterprise Profitability and Cost Management.
-
Customize the business process: You customize your business process by designing custom navigation flows to customize the look and feel of the user interface for specific roles or groups, definng valid intersections, and creating custom action menus for forms. See Designing Custom Naviation Flows and Defining Valid Intersections.
-
Maintain the business process: You maintain your business process by scheduling backups, analyzing system diagnostics, and cloning environments.