3 Setting Up Tax Information
This chapter contains the following topics:
-
Section 3.8, "Setting Up Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Functionality (Release 9.1 Update),"
-
Section 3.9, "Assigning Tax Information to General Ledger Accounts,"
|
Note: Additional country-specific setup for tax processing exists for many countries. |
|
See Also: |
3.1 Common Fields Used in This Chapter
- Company
-
Enter a code that identifies a specific organization, fund, or other reporting entity. The company code must already exist in the F0010 table and must identify a reporting entity that has a complete balance sheet. At this level, you can have intercompany transactions.
Note:
You can use company 00000 for default values such as dates and automatic accounting instructions. You cannot use company 00000 for transaction entries. - Tax Rate/Area
-
Enter a code that identifies a tax or geographic area that has common tax rates and tax authorities. The system validates the code you enter against the F4008 table. The system uses the tax rate/area in conjunction with the tax explanation code and tax rules to calculate tax and GL distribution amounts when you create an invoice or voucher.
- Effective Date
-
Enter the date when a transaction, contract, obligation, preference, or policy rule becomes effective.
- Expiration Date
-
Enter the date when a transaction, contract, obligation, preference, or policy rule ceases to be in effect.
- Item Number
-
Enter a number that the system assigns to an item. It can be in short, long, or third item number format.
The number of the item or item grouping to which the tax applies.
Values for item groupings are 3 through 8. If you specify a value for an item grouping, you must ensure that the processing option to validate item numbers, which appears on the Edit tab, is set to 0 (off). If this processing option is not set correctly, the system attempts to validate the item grouping number as an actual item number.
- Document Type
-
Enter a user-defined code (00/DT) that identifies the origin and purpose of the transaction. The system reserves several prefixes for document types, such as vouchers, invoices, receipts, and time sheets.
3.2 Setting Up Tax Authorities
Tax authorities are government agencies that assess and collect taxes. For tracking and reporting purposes, the organization must set up an address book record for each tax authority to which it remits taxes. If you want, you can set up a user-defined code for a new search type, such as TAX, in UDC (01/ST) that you can assign to tax authority address book records to differentiate them from other address book records.
|
Note: Ensure that the self-service processing option is not activated for the Address Book program (P01012) using the Tax Authorities option on the Tax Processing and Reporting menu (G0021); otherwise, you cannot add new tax authorities (address book records). |
3.3 Setting Up Tax UDCs
Many fields throughout JD Edwards EnterpriseOne software accept only user-defined codes. You can customize the system by setting up user-defined codes that meet the specific needs of the business environment.
|
Note: The setup for many countries for which JD Edwards EnterpriseOne software processes taxes requires that you enter values for country-specific UDCs. Refer to the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Localizations implementation guide for each country for information about country-specific UDC tables. |
3.3.1 Tax ID Validation (70/TI)
To validate tax identification numbers that you set up in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Address Book system according to the country in which it is used, you must set up the country codes in UDC 70/TI.
This table displays examples of country codes set up in UDC 70/TI:
| Codes | Description 01 | Description 02 | Special Handling |
|---|---|---|---|
| . | Default Country | US | 1 |
| AU | Austria | AU | 1 |
| AUS | Austria | AU | 1 |
| BE | Belgium | BE | 1 |
| BEL | Belgium | BE | 1 |
| DE | Germany | DE | 1 |
| DEU | Germany | DE | 1 |
To activate tax ID validation for a specific country code, enter 1 in the Special Handling field for that country code. To disable tax ID validation for a specific country code, remove the 1 from the Special Handling field.
To activate tax ID validation for a country code that is not listed in UDC table (70/TI) or to change the meaning of an existing country code, complete the fields as:
-
Enter the country code in the Codes field.
The country code must also be set up in the Country Codes (00/CN) UDC table.
-
Enter the standard two-digit ISO code for that country in the Description 02 field.
The two-digit ISO code is required in the Description 02 field to cross-reference the new country code with the country code that is hard-coded in the system.
For example, if you use DE for Denmark, enter DN (the two-digit ISO code for Denmark) in the Description 02 field for the DE country code. The system then validates tax IDs that are entered with the country code DE according to Danish, not German, specifications.
-
Enter 1 in the Special Handling field.
To activate tax ID validation for the default (blank) country code, complete the fields as described, but leave the Codes field blank.
For example, if you use a blank country code to mean Denmark, enter DN (the two (2) digit ISO code for Denmark) in the Description 02 field for the blank country code.
3.3.2 Setting Up UDCs for Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment (Release 9.1 Update)
Set up or verify these UDCs to work with the alternate tax rate/area assignment functionality:
-
Countries Alternate Tax Rate/Area (00/EC)
-
Edit Flag (00/EE)
-
Transaction Source (00/ES)
3.3.2.1 Countries Alternate Tax Rate/Area (00/EC)
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne provides values for this UDC table. However, you must review and maintain this UDC to ensure it contains all countries you will need to use this functionality for. You must set up country code values to specify the countries eligible for the alternate tax rate/area assignment.
This table shows examples of country codes:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| BE | Belgium |
| FR | France |
| GB | Great Britain |
3.3.2.2 Edit Flag (00/EE)
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne provides hard-coded values for this UDC table. You use these values to specify the error handling type for each company that uses the alternate tax rate/area assignment functionality. You enter the code when you define the alternate tax rate/area assignment constants. The system saves this value to the Company Constants Tag table (F0010T).
Values are:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| Blank | Do not set Error or Warning |
| 1 | Set a Warning |
| 2 | Set an Error |
3.4 Setting Up Tax Rules by Company
This section provides an overview of tax rules and discusses how to set up tax rules by company.
3.4.1 Understanding Tax Rules by Company
You set up tax rules so that the system can calculate any applicable taxes when you enter transactions with taxes. Use the Tax Rules (P0022) program to define tax rules differently by company and by system. The system uses these rules to:
-
Establish tolerance limits on changes that you make to the tax amount when you use VAT tax explanation codes (V, C, and B).
-
Display a warning message (or reject a transaction) whenever you enter a tax amount that differs from the system-calculated tax.
-
Determine whether transaction amounts should be calculated on the gross amount or the gross amount less the discount amount.
-
Determine whether discount amounts should be calculated on the gross amount (including tax) or the net amount (excluding tax).
-
Determine whether taxes are calculated for sales orders at the order or detail level.
-
Allow taxes to be understated.
-
(Release 9.1 Update) Determine whether the system should perform soft rounding of taxes for voucher match at either the tax explanation, tax area, and tax rate level or the tax explanation and tax area level.
|
Note: If you do not set up rules for a specific company, the system uses the rules that you define for company 00000. If you do not set up rules for company 00000, the system uses only these default rules:Tolerance limits are set to zero. The system calculates tax on gross including discount. The system performs soft rounding of taxes at the tax explanation and tax area level. |
When you set up tax rules for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable system, you also set up rules for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement system. When you set up tax rules for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system, you also set up rules for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management system.
The tax rules that you set up for the system consist of tolerance ranges and calculation rules. Not all of the tax rules apply to all systems.
3.4.1.1 Tolerance Rules
Tolerance rules specify the amount of variance that can exist between the amount of tax that you enter for a transaction and the tax amount that the system calculates. When you enter a tax amount that differs from the system-calculated tax amount, the system automatically issues a warning message for all tax types except VAT.
For VAT taxes, the system uses the tolerance rules that you set up to determine when to issue a warning or error message. The system does not issue a warning message until the difference between the tax amount that you enter and the tax amount that they system calculates exceeds the tolerance limit established for a warning. By setting up tolerance information, you control the type of message that the system issues.
Tolerance rules:
-
Apply to both understated and overstated amounts.
-
Apply only to VAT taxes and can be defined as either a percentage or amount.
For accounts receivable, the tolerance rules that you define do not apply to VAT taxes unless you also activate the option to understate taxes.
For example, you might specify a tax rule with a tolerance range by amounts as:
-
Tolerance amount for warning is 2.
-
Tolerance amount for error is 10.
To determine the tax amount, the system multiplies the taxable amount by the tax rate. If the taxable amount for a transaction is 1000 and the tax rate is 10 percent, the system calculates a tax amount of 100. Based on the tolerance range, the system determines the range for warning or error as:
| Tolerance Range | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Range for warning | Tolerance amount for warning is 2:
The system issues a warning message if the tax amount that you enter is greater than 102 or less than 98 (that is, outside of the tolerance range of 98 to 102). Note: If you enter a tax amount of 98.01 or 101.99, the system does not issue a warning message. The amount is within the acceptable tolerance range. |
| Range for error | Tolerance amount for error is 10:
The system issues an error message if the tax amount that you enter is greater than 110 or less than 90 (that is, outside of the tolerance range of 90 to 110). Note: If you enter a tax amount of 109.99 or 90.01, the system does not issue an error message. |
3.4.1.2 Calculation Rules for Discount and Tax Amounts
When you enter transactions with discounts and taxes, you must specify how you want the system to calculate the discount and tax amounts. Calculation rules specify which method to use for calculating discount and tax amounts when both are specified. The rules control how the system validates the correct tax amount, based on the total amount transaction.
Calculation rules are not displayed if you select the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting system.
3.4.1.3 Examples: Calculation Rules for Taxes
The system calculates gross and discount amounts using the tax rules that you set up. Each of these examples uses a different combination of rules to calculate:
-
Tax on gross including or excluding the discount amount
-
Discount on gross including or excluding the tax amount
The examples use these amounts:
-
Taxable amount: 1,000
-
Gross amount: Varies
-
Tax rate: 10 percent
-
Tax amount: 100
-
Discount: 1 percent
3.4.1.4 Example 1
This table displays how the system calculates the discount, gross, and taxable amounts when the options Calculate Tax on Gross (Including Discount) and Calculate Discount on Gross (Including Tax) are activated.
| Formula | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Discount Formula | (Taxable Amount + Tax Amount) x Discount Percent = Discount Available
(1,000 + 100) x.01 = 11.00 |
| Gross Formula | Taxable Amount + Tax Amount = Gross Amount
1,000 + 100 = 1,100 |
| Taxable Formula | Gross Amount / (1 + Tax Rate) = Taxable Amount
1,100 / 1.1 = 1,000 |
3.4.1.5 Example 2
This table displays how the system calculates the discount, gross, and taxable amounts when the options Calculate Tax on Gross (Including Discount) and Calculate Discount on Gross (Excluding Tax) are activated.
| Formula | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Discount Formula | Taxable Amount x Discount Percent = Discount Available
1,000 x.01 = 10.00 |
| Gross Formula | Taxable Amount + Tax Amount = Gross Amount
1,000 + 100 = 1,100 |
| Taxable Formula | Gross Amount / (1 + Tax Rate) = Taxable Amount
1,100 / 1.1 = 1,000 |
3.4.1.6 Example 3
This table displays how the system calculates the discount, gross, and taxable amounts when the options Calculate Tax on Gross (Excluding Discount) and Calculate Discount on Gross (Including Tax) are activated.
| Formula | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Discount Formula | (Tax Amount / [(1 - Discount Percent) x Tax Rate)] + Tax Amount) x Discount Percent = Discount Available
(100 / [(1 -.01) x.1] + 100) x.01 = 11.10 |
| Gross Formula | Taxable Amount + Tax Amount + Discount Amount = Gross Amount
1,000 + 100 + 11.10 = 1,111.10 |
| Taxable Formula | Gross Amount - Tax Amount - Discount Amount = Taxable Amount
1,111.10 - 100 - 11.10 = 1,000 |
3.4.1.7 Example 4
This table displays how the system calculates the discount, gross, and taxable amounts when the options Calculate Tax on Gross (Excluding Discount) and Calculate Discount on Gross (Excluding Tax) are activated.
| Formula | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Discount Formula | (Taxable Amount x Discount Percent) / (1 - Discount Percent) = Discount Available
(1,000 x.01) / (1 -.01) = 10.10 |
| Gross Formula | Taxable Amount + Tax Amount + Discount Amount = Gross Amount
1,000 + 100 + 10.10 = 1,110.10 |
| Taxable Formula | Gross Amount - Tax Amount - Discount Amount = Taxable Amount
1,110.10 - 100 - 10.10 = 1,000 |
3.4.1.8 (GBR) Example 5
In Great Britain, you must set the options for the calculation rules as:
-
Tax on Gross (Including Discount) - Off
-
Discount on Gross (Including Tax) - Off
The system calculates the discount and gross amounts as:
| Formula | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Discount Formula | (Taxable Amount x Discount Rate Percent) / ((1 - Discount Rate Percent) x Tax Rate)
(1,000 x.01) / ((1 -.01) x.10) = 10.10 |
| Gross Formula | Taxable Amount + Tax + Discount
1,000 + 100 + 10.10 = 1,110.10 |
3.4.1.9 (DEU) Example 6
In Germany, you must set the options for the calculation rules as:
-
Tax on Gross (Including Discount) - On
-
Discount on Gross (Including Tax) - On
The system calculates the discount and gross amounts as:
| Formula | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Discount Formula | (Taxable Amount + Tax Amount) x (Discount Rate Percent) = Discount Available
(1,000 + 100) x.01 = 11.00 |
| Gross Formula | Taxable Amount + Tax = 1,000 + 100 = 1,100 |
3.4.1.10 Edit Rules
You have only the option to understate tax amounts when you select the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system.
The edit rules activate the tolerance rules for VAT for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable system only. If you do not allow taxes to be understated, the tolerance rules that you set up apply to sales taxes only.
3.4.2 Forms Used to Set Up Tax Rules
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With Tax Rules | W0022A | Tax Setup (G00218), Tax Rules | Review and select tax rules by company. |
| Tax Rules Revisions | W0022B | Click Add on the Work With Tax Rules form. | Set up tax rules. |
3.4.3 Setting Up Tax Rules
Access the Tax Rules Revisions form.
- Company
-
Enter the company for which you define the tax rules. If you do not define rules for a specific company, the system uses the rules that you define for company 00000.
- Tolerance Rate - Warn
-
Enter a number that specifies the maximum percent of change that you can make to the tax amount on an invoice, voucher, or journal entry before the system issues a warning message. For example, if you specify 5.00, the system allows you to change the tax amount for a transaction by up to 5 percent without issuing a warning message. The system issues a warning message for changes to the tax amount when the percent of the change is between the percent specified in the Warning field and the percent specified in the Error field.
This system uses the tolerance limits only for tax explanation codes V, B, and C. For all other tax explanation codes, the system issues a warning regardless of the change.
You must select the option Allow Understatement of Tax Amt before the system allows you to understate the tax amounts on AR invoices by up to the percent specified.
Enter the percent as a whole number. For example, to specify 5 percent, enter 5.00 instead of .05.
(COL) Enter 1 for Colombian companies.
- Tolerance Rate - Error
-
Enter a number that specifies the maximum percent of change that you can make to the tax amount on an invoice, voucher, or journal entry before the system issues an error message. For example, if you specify 10.00, the system allows you to change the tax amount for a transaction by up to 10 percent. If the percent of the change exceeds the tolerance limit that you specified, the system does not allow the change. The system issues a warning message for changes to the tax amount when the percent of the change is between the percent specified in the Warning field and the percent specified in the Error field.
The system uses the tolerance limits only for tax explanation codes V, B, and C. For all other tax explanation codes, the system issues a warning regardless of the change.
You must select the option Allow Understatement of Tax Amt before the system allows you to understate the tax amounts on AR invoices up to the percent specified.
Enter the percent as a whole number. For example, to specify 10 percent, enter 10.00 instead of .1.
(COL) Enter 0 for Colombian companies.
- Amt (amount)
-
Specify whether the tolerance that you use to generate warning or error messages is based on a percent or an amount.
- % (percent)
-
Specify whether the tolerance that you use to generate warning or error messages is based on a percent or an amount.
- Tax on Gross Including Discount and Tax on Gross Excluding Discount
-
Select this option to calculate the tax amount based on the gross amount, including the discount.
(COL) Select the Tax on Gross Including Discount option.
- Discount on Gross Including Tax
-
Select this option to specify whether the system calculates the discount based on the gross amount, including the tax amount.
- Sales Order Taxes at Order Level
-
Select this option to specify whether the system calculates taxes and performs rounding for sales orders at the detail level or the order level.
The system calculates taxes at the detail level. The system calculates the tax on each detail line item, and then sums the detail line items for the order.
The system displays this field only when you select the option for AR.
- Allow Understatement of Tax Amt
-
Select this option to specify whether you can override the tax amount on an AR invoice to be less than the system-calculated tax amount. The system displays this field only when you select the option for AR. This option applies to tax explanation codes V and B only, and the amount of the understatement must be within the defined tolerance limits.
The system does not allow you to understate the tax amount. The system generates an error.
Note:
If you use tax explanation code S, the system allows you to understate the tax amount if it is within the defined tolerance limits, regardless of the setting of this option. - (Release 9.1 Update) Voucher Match Tax Rounding
-
Select this option to perform soft rounding of taxes for voucher match at the tax explanation, tax area, and tax rate level. If you do not select this option, the system performs soft rounding of taxes at the tax explanation and tax area level.
The system displays this field only if you select the A/P option.
3.5 Setting Up AAIs for Taxes
This section provides overviews of setting up AAIs for taxes, including financial AAIs and distribution AAIs.
3.5.1 Understanding AAIs for Taxes
If you are required to collect or pay taxes, you must set up the system so that the tax amounts are applied to the correct general ledger accounts. The system applies tax amounts automatically to the account that you specify in an Automatic Accounting Instruction (AAI).
When you set up AAIs for a specific type of tax, such as VAT, specify which accounts you want the system to debit and credit for the tax amount. If you pay taxes in multiple currencies, you need to set up tax AAIs for each company.
The financial systems within JD Edwards EnterpriseOne software (JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable, JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable, and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting) use different AAIs than the distribution systems within JD Edwards EnterpriseOne software (JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement).
3.5.2 Understanding Financial AAIs for Taxes
You can enter taxes on invoices, vouchers, journal entries, purchase orders, and sales orders. If you enter VAT or Use taxes, you must set up an AAI to debit or credit the appropriate tax account for each of these systems:
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement
-
JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management
You use the Automatic Accounting Instructions (P0012) program to set up AAIs.
Country-specific setup for AAIs for taxes exists for Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Peru, and Russia.
3.5.2.1 AAI Hierarchy
You can set up the AAI for each company or for company 00000 only. If you do not set up company-specific AAIs, the system uses the AAI that is set up for company 00000. If you do not use a GL offset, the system uses the account associated with the AAI item (PT, RT, GT) only.
If a tax rate area has a GL offset specified, you must set up an AAI with the same GL offset. If the system does not find the PTxxxx, RTxxxx, or GTxxxx, where xxxx is the GL offset specified in the tax rate area, the system returns an error message when you attempt to process the transactions.
You must specify a business unit and object account when you set up tax AAIs for the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable systems. The subsidiary field is optional. For the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting system, if you do not specify a business unit for the tax AAI, the system uses the business unit from the account entered on the journal entry.
This table displays the hierarchy that the system uses to determine the account to which tax amounts are posted.
| Hierarchy | Company | JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable | JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable | JD Edwards EnterpriseOne General Accounting |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Company specific | PT + GL Offset | RT + GL Offset | GT + GL Offset |
| 2 | Company 00000 | PT + GL Offset | RT + GL Offset | GT + GL Offset |
3.5.2.2 VAT Tax AAIs for the Accounts Payable, Accounts Receivable, and General Accounting Systems (PTxxxx, RTxxxxx, GTxxxx)
When you post a transaction that has VAT taxes, the system uses an AAI to locate the general ledger account to use to post the tax amount. Because you might require different accounts for different tax authorities, you can specify a GL offset value for each tax authority that you set up in the tax rate/area, and then set up a corresponding AAI that includes that value. The GL offset can be up to four characters in length and it follows the AAI item. Examples are PTVATA, RTVATB, and GTTXTX. Specifying a value in the GL Offset field enables you to direct VAT tax amounts to different accounts by offset (or tax authority) for each company and differentiates VAT tax accounts from use tax accounts in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable system.
|
Note: The system uses the GTxxxx AAIs when the journal entry with VAT transaction is entered, not when it is posted. |
3.5.2.3 VAT Tax AAIs for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement (PTVATD)
The JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement system uses the same AAI item as the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable system (PT), except when you have a purchase order with retainage and you defer VAT. In this case, when you match the voucher to the receipt using the Voucher Match program (P4314), the system uses the AAI item PTVATD to locate the account for the deferred VAT. The system uses this AAI only when:
-
The processing option (Retainage tab) for the Voucher Match program (P4314) is set to apply tax to the retained amount.
-
You use a tax type of C or V.
When you release retainage, this AAI reverses debits and credits with the VAT Payables (PCVATP) AAI.
If you do not set up this AAI, the system returns an error.
3.5.2.4 Tax AAI (PT) in the Accounts Payable and Procurement Systems
Use taxes (tax explanation code U and B) do not use a GL offset to specify a tax account; the system always uses PT (blank). You can set up the AAI for each company or for company 00000 only. If you do not set up company-specific AAIs, the system uses the AAI set up for company 00000.
Unlike VAT taxes, you can specify use tax accounts by tax rate/area. Instead of using multiple AAIs to specify different tax accounts, you set up different tax accounts for each tax rate/area by defining the subsidiary portion of the account as the tax rate/area. For example, if the tax account were 1.4433 and the tax rate/area were ONT (for Ontario), you would set up 1.4433.ONT in the F0901 table. Thus, you would have a unique account number for each tax rate/area.
When you set up the AAI for PT, you do not specify a subsidiary account; you specify the business unit and object account only. The system ignores the subsidiary account if one exists. When you post the voucher, the system looks for the account number specified in the AAI in conjunction with the tax rate/area specified on the voucher. If the account number exists, the system uses it. If the account number, including the tax rate/area, does not exist, the system uses the account number. For example, if you set up PT for 1.4433 and enter tax rate/area DEN on the voucher, the system searches for 1.4433.DEN. If the system cannot locate this account number, it uses 1.4433.
3.5.3 Understanding Distribution AAIs for Taxes
Transactions in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement systems use both distribution and financial AAIs. The distribution AAIs are set up in multiple tables, each of which applies to a certain type of transaction. Not all transactions with taxes use the distribution AAIs. you use the Distribution AAIs (P40950) program to set up AAIs for the distribution systems.
This table displays the distribution AAI tables that you must set up to enter purchase orders and sales orders with taxes for the specified tax explanation code. Any other tax explanation codes that you enter on the order revert to the financial AAIs (RT, PT, GT).
| System | AAI Table | Description | Tax Explanation Code | Transaction Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management | 4250 | Tax liability | S | . |
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement | 4350 | Purchase tax accrual | S | 3-Way Match (Inventory) |
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement | 4350 | Purchase tax accrual | U | 3-Way Match (Inventory) |
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement | 4355 | Received not vouchered tax | S | 3-Way Match (Inventory)
3-Way Match (Non- Inventory) |
| JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement | 4355 | Received not vouchered tax | U | 3-Way Match (Inventory)
3-Way Match (Non- Inventory) |
|
Note: The system also uses the distribution AAIs for tax explanation codes B and C for the sales and use portion of the tax amount. |
Each AAI table enables you to set up different general ledger accounts based on the company, document type, and GL category code (offset) that you enter. You enter the same value in the GL Cat field (data item GLPT) for the AAI that you have set up in the GL Offset field in the tax rate/areas. For example, if you had a tax rate/area set up for CO that includes a GL offset TXTX, and you had another tax rate/area ONT that includes a GL offset TXTY, you would set up two distribution AAIs. This example illustrates how the distribution AAIs correlate to the tax rate/area.
3.5.3.1 Tax Rate Area Setup
This table describes the Tax Rate Area, GL Offset, and Tax Rate.
| Tax Rate Area | GL Offset | Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|
| CO | TXTX | 7.3 |
| ONT | TXTY | 5.0 |
3.5.3.2 Distribution AAI Set Up
This table describes the Distribution AAI Set Up for AAI Table 4250.
| Company | Document Type | GL Cat | Branch/Plant | Object | Subsidiary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00001 | SD | TXTX | 1 | 4551 | . |
| 00001 | SD | TXTY | 1 | 4552 | . |
| 00002 | SO | TXTX | 1 | 4553 | . |
| 00002 | SO | TXTY | 1 | 4554 | . |
|
Note: You can define a flexible account number for the AAI table 4250. The system searches for the account number in the F4096 based on the AAI table. If the AAI table is not defined to use flexible accounts, the system uses the account number that is set up in the 4095. |
3.6 Setting Up Tax Rate Areas
This section provides overviews of tax rate areas and nonrecoverable VAT, lists prerequisites, and discusses how to:
-
Set processing options for Tax Rate/Areas (P4008).
-
Set up tax rate/areas.
3.6.1 Understanding Tax Rate Areas
To calculate and track the different taxes that you pay to suppliers or for customers, you must set up tax rate areas. Each tax area is a physical, geographic area, such as a state, province, or county. Different tax authorities assess a variety of taxes for each geographic area. Additionally, each authority within a tax area can have a different tax rate.
When you set up tax rate areas, you must specify effective dates. The system does not check for duplicate tax rate and area information, which means that you can set up different tax rates and effective date ranges for the same tax rate and area. The system checks for overlapping effective date ranges. When an overlap exists, the system issues an error.
The Tax Rates/Areas (P4008) program also provides features for special situations. For example, you can specify whether tax is calculated as tax-on-tax, whether a portion of the tax is nonrecoverable (available for input credits), and whether maximum unit cost is associated with a particular item.
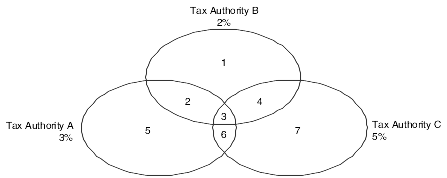
This diagram illustrates how some tax areas could be organized:
The three circles represent three tax authorities. The seven numbered areas represent tax areas.
Notice that tax authority jurisdiction can overlap and that a tax area can be assessed taxes by one or more tax authorities. The tax rate for a tax authority does not vary from one tax area to another. Tax authority A assesses a 3 percent tax in tax areas 2, 3, 5, and 6.
For each tax area, however, the total tax burden can vary. It is the cumulative effect of multiple tax authorities for a single tax area that causes the tax burden to vary from one tax area to another. For example, the businesses located in tax area 5 must remit tax to only one tax authority (Tax Authority A for 3 percent). Businesses in tax area 2 remit taxes to two tax authorities (Tax Authorities A for 3 percent and B for 2 percent), and businesses in tax area 3 remit taxes to all three tax authorities.
You can run a report to review all of the tax areas that are set up.
3.6.1.1 Tax Rate Areas for Items
You can specify tax information for an item or group of items. To specify tax information for an item, set the processing option to validate information against the Item Branch File (F4102) table and enter the item number in the tax rate/area.
To specify a tax rate for an item group, enter one of the valid options in the Sales Taxable Y/N field on the Item Branch/Plant Info. form in the Item Branch/Plant (P41026) program. Options 3 through 8 are for grouping items together based on the tax rate. You set up the tax rate by area for one of the options and then specify the option for like items on the Item Branch/Plant Info. form.
3.6.2 Understanding Nonrecoverable VAT
When they sell their goods, most countries that pay VAT fully recover the amount of VAT that they paid. In other words, VAT paid in accounts payable is offset against any VAT collected in accounts receivable to reduce the amount owed to the government or, in some cases, to generate a tax rebate. Exceptions to this rule might include expenses such as meals and entertainment, which might bee only 50 percent recoverable.
When you cannot recover all of the VAT that you pay, you must set up the tax rate area to indicate the percentage of tax that is nonrecoverable (or not available for credit). When you use the tax rate area in a transaction, the system credits the VAT account for the amount that can be recovered only. The system does not create a separate entry to an account for the nonrecoverable amount; however, it does store the amount in the Accounts Payable Ledger (F0411) and Customer Ledger (F03B11) tables.
The system only recognizes nonrecoverable VAT when using type explanation codes V,B, and C.
3.6.2.1 Example: Using Nonrecoverable VAT
When you set up a tax rate area that has nonrecoverable VAT, you enter the percent of the nonrecoverable tax on a separate line. Although the system requires a tax authority, it does not use the tax authority for reporting. When you specify a nonrecoverable percent, such as 50, the percent applies to the total tax on the tax rate area. However, if you set up the tax rate area for multiple tax authorities, the system applies the nonrecoverable tax to the first tax authority defined.
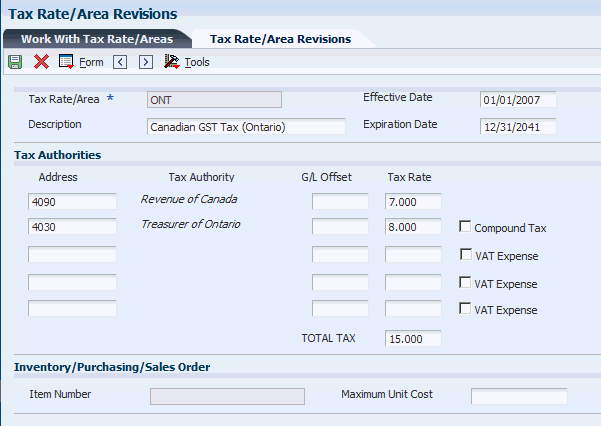
For example, this tax rate/area has two tax authorities specified, as well as a nonrecoverable percent.
When you enter a voucher or invoice and use this tax rate area (ONT), the system will apply the entire 50 percent to the account associated with the GL Offset GST.
In this example, the AAIs associated with the tax rate area point to these accounts:
-
1.4444 for RTGST
-
1.4445 for RTPST
If you enter an invoice for a taxable amount of 1,000 USD, the system calculates the tax amount as 150 USD (1,000 x.15) and the gross amount as 1,150 (1,000 + 150). When you post the invoice, the system creates these entries:
| Doc Type | Account | Account Description | Debit | Credit | Calculation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RI | 3.5010 | Store Sales | . | 1,075 | Taxable + (Tax x 50 percent) |
| AE | 1.1210 | AR Trade | 1,150 | . | Taxable + Tax |
| AE | 1.4444 | VAT Payable (GST) | 5* | . | (1,000 x 7 percent) - 75 = - 5 |
| AE | 1.4445 | VAT Payable (PST) | . | 80 | 1,000 x 8 percent = 80 |
*Normally, the entry to VAT Payable is a credit, but because the system calculates a - 5 (credit), it debits the account.
3.6.3 Prerequisites
Before you complete the tasks in this section:
-
Set up the tax authorities in the address book.
-
Set up the necessary tax AAIs.
3.6.4 Forms Used to Set Up Tax Rate Areas
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With Tax Rate/ Areas | W4008A | Tax Setup (G00218), Tax Rate/Areas. | Review and select tax rate/area records. |
| Tax Rate/Area Revisions | W4008B | Click Add on the Work With Tax Rate/Areas form. | Add and revise tax rate/area information. |
3.6.5 Setting Processing Options for Tax Rate/Areas (P4008)
Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
3.6.5.1 Display
- 1. Item Number and Maximum Unit Cost
-
Specify a value to either display or hide the Item Number and Maximum Unit Cost fields. Values are:
1: Display
0: Hide
3.6.5.2 Edits
- 1. Validate Item Numbers
-
Specify a value to validate Item Numbers. Values are:
1: Validate
0: Do not validate
3.6.6 Setting Up Tax Rate Areas
Access the Tax Rate/Area Revisions form.
- Tax Rate/Area
-
Enter a code that identifies a tax or geographic area that has common tax rates and tax authorities. The system validates the code you enter against the F4008 table. The system uses the tax rate/area in conjunction with the tax explanation code and tax rules to calculate tax and GL distribution amounts when you create an invoice or voucher.
- Effective Date and Expiration Date
-
Enter the date when a transaction, contract, obligation, preference, or policy rule becomes effective, or ceases to be in effect.
- Tax Auth 1 (tax authority 1)
-
Enter the address book number of the tax agency that has jurisdiction in the tax area. You pay and report sales, use, or VAT taxes to this agency. Examples include states, counties, cities, transportation districts, provinces, and so on. You can specify up to five tax authorities for a single tax area.
- GL Offset (general ledger offset)
-
Enter a code that indicates how to locate the tax account for general ledger entries. This field points to automatic accounting instructions (AAIs) that, in turn, point to the tax account. Examples are:
PTyyyy - for AP (VAT only)
RTyyyy - for AR (VAT only)
GTyyyy - for GL (VAT only)
4320 - for Sales Orders
4400 and 4410 - for Purchase Orders
When setting up VAT and Canadian GST, PTyyyy, RTyyyy, and GTyyyy are the only valid values. For the AP system, a second GL Offset (PT_ _ _ _) is required when the tax setup involves VAT plus use taxes (tax explanation code B). Use AAI PT_ _ _ _ to designate the use tax portion of the setup.
Only tax explanation code V uses the GL Offset for the 2nd and subsequent tax authorities. The system ignores the field for all other tax explanation codes.
For sales taxes, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Payable and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Accounts Receivable systems ignore the values in this field. However, the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Sales Order Management and JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Procurement systems require values in this field.
- Tax Rate
-
Enter a number that identifies the percentage of tax that should be assessed or paid to the corresponding tax authority, based on the tax area.
Enter the percentage as a whole number and not as the decimal equivalent. For example, to specify 7 percent, enter 7, not .07.
If you use tax explanation codes B (VAT + Use) or C (VAT + sales), you must enter the VAT tax authority and tax rate on the first line of the tax rate/area. The nonrecoverable percent applies to the first tax rate only when using tax explanation codes C and B. For other tax explanation codes, the system multiplies the nonrecoverable percent by the total tax, but applies it to the first tax authority only.
For Canadian taxes, always specify on the first line the tax authority and tax rate for the GST portion of the tax.
- Compound Tax
-
Select this option that is used in Canada to specify whether to calculate PST tax after GST has been added to the product value.
The system calculates the PST before GST has been added to the product value.
For example, suppose that you have a tax area set up with 7 percent GST and 8 percent PST, and you select the option to calculate tax on tax. If you enter a voucher for a taxable amount of 1000 CAD, the system calculates the GST as 70 CAD, adds it to the taxable amount, and multiplies the PST by that result (1070 CAD). If you do not use compound taxes, the system calculates PST on the taxable amount only.
Note:
This option is valid only for tax explanation codes that begin with the letters B and C. To calculate compound taxes for tax explanation code V, use tax explanation code V+.This code is available only for the second tax authority (line 2 in the list on this form) and must identify a non-GST tax authority.
- VAT Expense
-
Select this option that indicates the percent of VAT that is not recoverable. You enter the nonrecoverable percentage in the Tax Rate field to the left of this option.
Note:
This option is valid only with tax explanation codes that begin with the letters C, B, and V.This code is available only for the third, fourth, fifth tax authorities (lines 3 through 5).
- Item Number
-
Enter a number that the system assigns to an item. It can be in short, long, or third item number format.
The number of the item or item grouping to which the tax applies.
Values for item groupings are 3 through 8. If you specify a value for an item grouping, you must ensure that the processing option to validate item numbers, which appears on the Edit tab, is set to 0 (off). If this processing option is not set correctly, the system attempts to validate the item grouping number as an actual item number.
- Maximum Unit Cost
-
Enter a number that identifies the maximum amount that an item can be taxed. If the unit cost of an item is more than the amount that you specify in this field, the maximum unit cost becomes taxable.
Note:
This field is used for processing sales and purchase orders only. This field is required for processing taxes in the state of Tennessee.
3.7 Setting Up Default Tax Information
This section provides an overview of the default values that you can set up for taxes and discusses how to:
-
Set up default tax information for the business unit.
-
Set up default tax information for the supplier record.
-
Set up default tax information for the customer record.
3.7.1 Understanding Default Values for Taxes
When you enter transactions with taxes, you can enter the tax information on the transaction or set up default values that the system uses during the entry process. Default tax values include the tax rate area and tax explanation code, and can be set up in the customer or supplier record or in the business unit record (tax rate area only). Regardless of whether you establish default values, you can override the tax information when you enter the transaction.
This table shows where the system retrieves the default tax rate area and tax explanation code from for each type of transaction that you enter:
| Transaction Entered | Tax Rate Area Used | Tax Explanation Code Used |
|---|---|---|
| Purchase order | Supplier record | Supplier record
The system uses tax defaults that you set up in the supplier record when you enter purchase orders. When you enter purchase orders, you use processing options to specify whether to retrieve the tax rate/area from the ship-to or supplier address book number. The system always uses the tax explanation code from the supplier record. |
| Sales order | Customer record (Ship-to address) | Customer record (Sold-to address)
The system uses tax defaults that you set up in the customer record when you enter a sales order. When you enter direct ship, transfer orders, or sales orders with different sold-to or ship-to addresses, the system retrieves the tax rate/area from the ship-to address and the tax explanation code from the sold-to address. |
| Voucher | Business unit; then supplier record | Supplier record
When you enter a voucher, the system uses the tax rate/area associated with the business unit, if one exists. If a tax rate/area is not set up for the business unit, the system uses the tax rate/area from the supplier record. The system uses the tax explanation code from the supplier record regardless of whether it uses the tax rate/area from the business unit. |
| Invoice | Business unit; then customer record | Customer record
When you enter an invoice, the system uses the tax rate/area associated with the business unit, if one exists. If a tax rate/area is not set up for the business unit, the system uses the tax rate/area from the customer record. The system uses the tax explanation code from the customer record regardless of whether it uses the tax rate/area from the business unit. |
| Journal entry | None | None
The system does not use default tax information when you enter a journal entry with VAT. |
3.7.2 Forms Used to Set Up Default Tax Information for the Business Unit, Supplier, and Customer Records
3.8 Setting Up Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Functionality (Release 9.1 Update)
This section provides an overview of the alternate tax rate/area assignment functionality and discusses how to:
-
Set up alternate tax rate/area assignment company constants.
-
Set up alternate tax rate/area definitions.
-
Set up company address number for tax reports.
-
Set up alternate tax rate/area by country.
-
Run the Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country Integrity report (R40083).
-
Set processing options for the Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country Integrity report (R40083)
-
Set up address book records to work with the alternate tax rate/area assignment functionality.
3.8.1 Understanding Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Functionality
This goal of this functionality is to provide an alternate means of assigning the tax rate/area to transactions. Without this functionality, the system provides a default value for the tax rate/area from the customer master, supplier master, or the business unit master records. This method does not always produce accurate tax rates for the transaction.
An example of when this does not meet requirements is in the European Union (EU). EU customers registered for VAT in multiple EU countries require different tax rates based upon the ship-to and ship-from countries of their transactions. To provide for the different tax rates, multiple tax rate/areas are needed and an alternative means of assigning these tax rate/areas must be provided.
The alternate tax rate/area assignment feature enables you to define the default tax rate/area to use based on a combination of the following fields:
-
Company
-
Ship From Country Code
-
Ship To Country Code
-
Transaction Source
-
Customer or Supplier Number
You specify the country codes for the Ship From and Ship To entities considering the location where the goods are to be shipped from and received. You use the Address Book Revisions program (P01012) to ensure that all locations for your organization, your customers, and your suppliers are available for your transactions.
The following example shows a sales order with a different ship from country:
Figure 3-3 Example: Tax Rate/Area Assignment
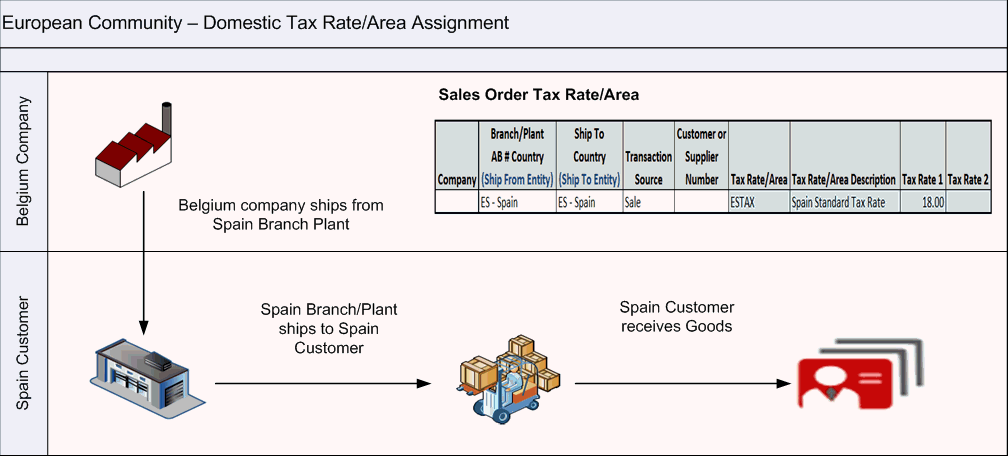
Description of ''Figure 3-3 Example: Tax Rate/Area Assignment ''
The alternate tax rate/area assignment functionality affects all sales and purchases that retrieve the tax rate/area from business units (branch plants), customers, or suppliers.
Before working with alternate tax rate/areas, you must:
-
Set up the valid countries. See Setting Up UDCs for Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment (Release 9.1 Update).
-
Enable the alternate tax rate/area assignment constant on a company level. See Setting Up the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Company Constants.
-
Set up the alternate tax rate/areas definitions to use. See Setting Up Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definitions.
-
Define an address book record for each Ship From and Ship To location. This includes business units, branch/plants, customers, and suppliers. It also includes entities such as the tenant in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Real Estate Management system and the community and subcontractor in the JD Edwards EnterpriseOne Homebuilder Management system. See Setting Up Address Book Records to Work with the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Functionality.
-
Define a valid tax ID, country, and default tax area for each customer and supplier. See Setting Up Address Book Records to Work with the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Functionality.
If you enable the alternate tax rate/area assignment functionality, the system performs the following actions when you enter or modify a transaction such as a voucher or an invoice, unless you manually override the tax rate/area:
-
Verifies the alternate tax rate/area assignment constant is enabled for the company.
-
Verifies that both the ship-to and the ship-from entities have a Tax ID number. The system does not validate that the tax ID is valid during this process.
-
Verifies that the country for the entities (supplier, customer, tenant, branch/plant, and so on) address book record exists in the Countries Alternate Tax Rate/Area (00/EC) UDC table, based on the transaction source.
-
In the case of a purchase, the system validates the country in the address book records of the ship-to location (branch/plant or business unit) and the supplier against the 00/EC UDC values.
-
In the case of a sale, the system validates the country in the address book record of the ship-from location (branch/plant or business unit) and the customer against the 00/EC UDC values.
-
When you enable the alternate tax rate/area assignment functionality and modify one of the entities that define the alternate tax rate/area assignment, the system validates the alternate tax rate/area and updates the value for the tax rate/area based on the entity setup. If you override the tax rate/area after the system retrieves the alternate tax rate/area, the system retains the manually entered value and does not attempt to retrieve a value based on the entities that define the alternate tax rate/area. After you manually assign a tax rate/area, the system does not display warning or error messages associated with the validation of the tax rate/area because it does not run validations after you manually change the value.
3.8.2 Setting Up the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Company Constants
This section provides an overview of the alternate tax rate/area assignment company constants and discusses how to set up alternate tax rate/area assignment company constants.
3.8.2.1 Understanding the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Company Constants
You use the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Constant (P001001) program to activate or deactivate the alternate tax rate/area assignment functionality for a company. You enable or disable this functionality using a check box for the company constant.
The system stores the alternate tax/rate area assignment company constants that you set up for alternate tax rate/area assignments in the Company Constants Tag table (F0010T).
3.8.2.2 Forms Used to Set Up the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Company Constants
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With Companies | W0010C | Organization & Account Setup (G09411), Company Names & Numbers | Review company information. |
| Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Constant - Companies | W001001A | On the Work with Companies form, select Alternate Tax Area from the Form menu. | Review and maintain alternate tax rate/area assignment constants for all companies. |
| Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Constant - Company Revision | W001001B | Select any record from the Work with Companies form and select Alternate Tax Area from the Row menu. | Enable or disable the alternate tax rate/area assignment functionality for the selected company. |
3.8.2.3 Setting Up Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Company Constants
Access the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Constant - Company Revision form.
Figure 3-4 Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Constant - Company Revision form
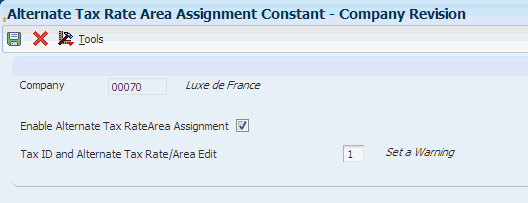
Description of ''Figure 3-4 Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Constant - Company Revision form''
- Company
-
The system displays the name and number of the company selected in the Work With Companies form.
- Enable Alternate Tax Rate Area Assignment
-
Select this check box to enable the alternate tax rate/area assignment functionality for a particular company. If this check box is not selected, the system uses the tax rate/area from the customer, supplier, or business unit for the transaction.
- Tax ID and Alternate Tax Rate/Area Edit
-
The system displays this field only if you select the Enable Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment check box. You define whether the system sets an error or warning message or bypasses the message when the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment functionality is enabled and the tax ID or Alternate Tax Rate/Area definition does not exist for the entities involved in a transaction.
You must select a value from the Edit Flag (00/EE) UDC table:
-
Blank: The system does not display error or warning messages and provides a default value for the tax rate/area from the customer, supplier, or business unit record.
-
1: If the validation fails, the system displays a warning message and enables you to continue with the transaction. The system provides a default value for the tax rate/area from the customer, supplier, or business unit record.
-
2: If the validation fails, the system displays an error message and does not enable you to continue with the transaction.
-
3.8.3 Setting Up Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definitions
This section provides an overview of alternate tax rate/area definitions and discusses how to set up an alternate tax rate/area definition.
3.8.3.1 Understanding Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definitions
You use the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definition program (P40081) to define the alternate tax rate/areas that the system automatically assigns for transactions on sales orders, purchase orders, invoices, and vouchers. Using this program, you define combinations among the following fields:
-
Company
-
Two Country Codes (Ship From, Ship To)
-
Transaction Source
-
Customer or Supplier Number
The country codes represent the countries from the entities involved in the transactions with taxes associated. These entities vary depending on the transaction source. The following table describes the relationship between transaction sources and countries:
| Transaction Source | Country 1 | Country 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Sales order / Invoice | Ship From entity (branch/plant or business unit) country. | Ship To entity (customer) country. |
| Purchase Order or Voucher | Ship To entity (branch/plant or business unit) country. | Ship From entity (supplier) country. |
The system stores the alternate tax rate/area definitions in the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definition table (F40081).
3.8.3.2 Examples of Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definitions
This table includes examples of alternate tax rate/area definitions:
| Company | Country 1 | Country 2 | Transaction Source | Tax Rate/Area |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 00001 | Belgium | Belgium | Sale | BEDOM |
| 00001 | Belgium | Germany | Sale | BEINTRA |
| 00001 | Belgium | Germany | Purchase | BEINTRA |
| 00002 | Germany | France | Purchase | GEINTRA |
3.8.3.3 Forms Used to Set Up Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definitions
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Working with Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definition | W40081A | Tax Setup (G00218), Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definition | Review alternate tax rate/area definitions. |
| Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definition Entry | W40081B | Click Add on the Working with Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definition, or select Alt Tax Area Multiple from the Form menu. | Set up multiple alternate tax rate/area definitions. |
| Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definition Revision | W40081D | Select a record on the Working with Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definition form and click Select. | Review or modify the selected alternate tax rate/area definition. |
3.8.3.4 Setting Up Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definitions
Access the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Definition Entry form.
Figure 3-5 Alternate Tax Rate / Area Definition Entry
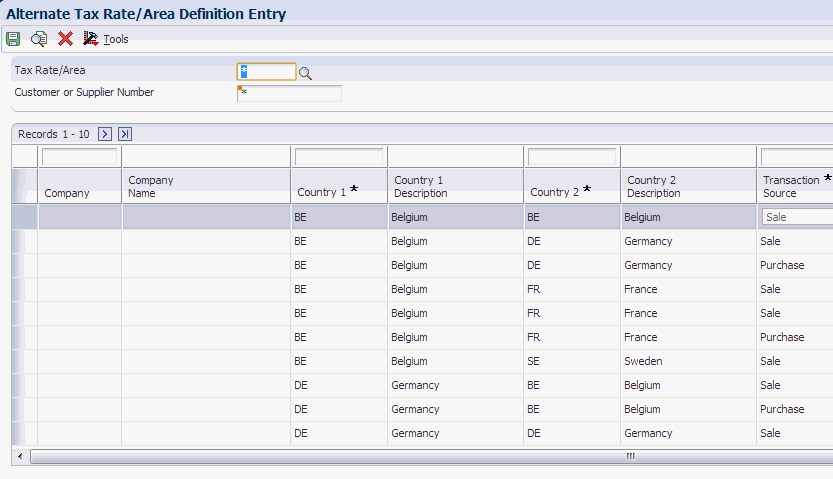
Description of ''Figure 3-5 Alternate Tax Rate / Area Definition Entry ''
- Company
-
Specify the company number for which you set up the alternate tax rate/area definitions. The system automatically retrieves the company name from the Company Master (F0010) table. This field is optional. If you leave this field blank, the system creates the definition for all companies.
- Country 1
-
Specify the first country code from the Countries Alternate Tax Area (00/EC) UDC table. When you enter a transaction, the system retrieves this country code from the business unit or branch plant setup.
- Country 2
-
Specify the second country code from the Countries Alternate Tax Area (00/EC) UDC table. When you enter a transaction, the system retrieves this country code from the customer (in the case of sales) or supplier (in the case of purchases) address book setup.
- Transaction Source
-
Specify the transaction type from the Transaction Source (00/ES) UDC table. Values are:
1: Sales transactions.
2: Purchase transactions
- Customer/Supplier Number
-
Specify the customer (in the case of sales) or supplier (in the case of purchases) address book number for which you set up the alternate tax rate/area definition. This field is optional. If you leave this field blank, the system uses this tax area definition for all customers or suppliers.
- Tax Rate/Area
-
Specify the tax rate/area to use for the combination. You must select a valid value from the Tax Rate/Area (F4008) table.
3.8.4 Setting Up Company Address Number for Tax Reports (Release 9.1 Update)
This section provides an overview of company address number for tax reports setup and discusses how to set up company address number for tax reports.
3.8.4.1 Understanding Company Address Number for Tax Reports Setup
You set up company information that identifies the company in the country instead of retrieving the information from the address book number defined for the company of the transaction when you run the VAT reports. Use the Company Address Number for Tax Reports program (P00101) to work with the address number company in a country. You can define only those address numbers for a company in a country that are set up for that country in the F0101 table.
The system saves the company, country, and address book information in the Company Information By TaxID table (F00101).
3.8.4.2 Forms Used to Set Up Company Address Number for Tax Reports
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work with Company Address Number for Tax Reports | W00101A | Alternate Tax Rate/Area Setup (G00220), Company Address Number for Tax Reports | Review the address number details for company country combinations. |
| Company Address Number for Tax Reports | W00101B | Click Add on the Work with Company Address Number for Tax Reports form to create a new relation or Select to modify an existing relation. | Add a new relation between company and address number or modify the address number. The address number identifies the company in a country. |
| Address Number By Tax ID | W00101C | Select a record and select Address By Tax Id from the Row menu on the Work with Company Address Number for Tax Reports form. | Select the address number for a specific tax ID for a country. |
3.8.4.3 Setting Up Company Address Number for Tax Reports
Access the Company Address Number for Tax Reports form.
Figure 3-6 Company Address Number for Tax Reports
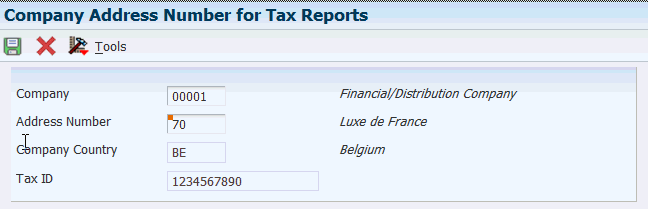
Description of ''Figure 3-6 Company Address Number for Tax Reports''
- Company
-
Specify the company number for which you set up the address number for a country. The system automatically retrieves the company name from the Company Master (F0010) table.
- Address Number
-
Specify the address book number that you want to relate to the company. You must select a valid value from the Address Book table. The system retrieves tax id and country based on the address number. (Release 9.1 Update)
3.8.5 Setting Up Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country (Release 9.1 Update)
This section provides an overview of alternate tax rate/area by country and discusses how to set up an alternate tax rate/area by country.
3.8.5.1 Understanding Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country
You use the Alternate Tax Rate/Area by Country program (P40082) to define the companies and alternate tax rate/areas for a country. Using this program, you define combinations among the following fields:
-
Tax Area
-
Company
You can define new tax rate/areas or import them from the Alternate Tax Rate/Area table (F40081). When you set up the company and tax rate/area for a country, the system stores these details in the F40082 table.
If you want to copy records from the F40081 table, you can retrieve the records using the Import feature of the program and then save the records to the F40082 table.
3.8.5.2 Forms Used to Set Up Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work with Alternate Tax Rate/Area by Country | W40082A | Alternate Tax Rate/Area Setup (G00220), Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country | Review alternate tax rate/area by country setups. |
| Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country | W40082B | Click Add on the Working with Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country. | Set up alternate tax rate/area by country. You can also select a record and click Select to modify the country on an existing setup.(Release 9.1 Update) |
| Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country - Import | W40082D | Click Import on the Form menu from the Work with Alternate Tax Rate/Area by Country form. | Import records from the F40081 table. |
| Alternate Tax Rate/Area by Country Multiple Update | W40082E | Click Multiple on the Form menu from the Work with Alternate Tax Rate/Area by Country form. (Release 9.1 Update) | Update country for multiple alternate tax rate/area by country setups. |
3.8.5.3 Setting Up Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country
Access the Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country form.
Figure 3-7 Alternate Tax Rate / Area By Country
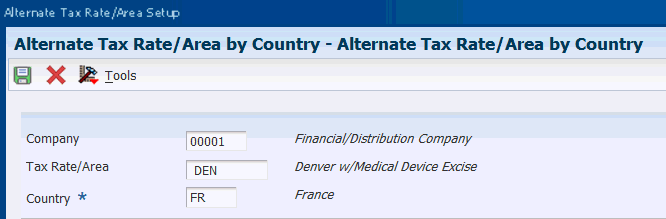
Description of ''Figure 3-7 Alternate Tax Rate / Area By Country ''
- Company
-
Specify the company number for which you set up the alternate tax rate/area by country. The system automatically retrieves the company name from the Company Master (F0010) table.
- Tax Rate/Area
-
Specify the tax rate/area to use for the country and company combination. You must select a valid value from the Tax Rate/Area (F4008) table.
- Country
-
Specify the country code from the Countries Alternate Tax Area (00/EC) UDC table. This is a mandatory field.
|
Note: The VAT reports process transactions by country. The system while processing VAT reports checks whether the transaction belongs to the specified country. The system identifies the transaction with the company and the tax rate area. If it finds a value for country, it processes transactions belonging to that country. The system gets the value for country using the values in the Company and Tax Rate/Area fields, value in the Tax Rate/Area field, or value in the Company field. |
3.8.6 Running the Alternate Tax Rate/Area By Country Integrity Report (Release 9.1 Update)
You use the Alternate Tax Rate/Area by Country Integrity report (R40083) to check whether all transactions in the F0018 table are on a country within a date range.
Select Alternate Tax Rate/Area Setup (G700220), Alternate Tax Rate/Area by Country Integrity
3.8.7 Setting Processing Options for Alternate Tax Rate/Area by Country Integrity (R40083) (Release 9.1 Update)
Processing options enable you to specify the default processing for programs and reports.
3.8.7.1 Process
- 1. Company
-
Specify the company number for which you want to run the report. You must specify a value from the F0010 table.
- 2. G/L Date From
-
Specify the beginning of the date range to use to select records from the Taxes table (F0018). If you leave this blank, the system selects all records until the value in the G/L Date To processing option.
- 3. G/L Date To
-
Specify the end of the date range to use to select records from the F0018 table. If you leave this field blank, the system retrieves all records through the current date.
- 4. Print Alternate Tax Rate/Area
-
Specify whether to display the transactions with the country combination. This is an optional field. Values are:
Blank: Display all alternate tax rate/area transactions without country.
1: Display alternate tax rate/area transactions with country.
- 5. Print Transactions per alternate tax rate area
-
Specify whether to display details of the records from the F0018 table. This is an optional field. Values are:
Blank: Do not show details of transactions.
1: Display details of transactions.
3.8.8 Setting Up Address Book Records to Work with the Alternate Tax Rate/Area Assignment Functionality
In addition to the specific setup required to work with this functionality, you must verify that the business units, branch/plants, customers, or suppliers involved have the following information set up:
-
Unique address number
-
Valid tax ID
-
Country
-
Default tax rate/area
3.9 Assigning Tax Information to General Ledger Accounts
This section provides an overview of tax information for general ledger accounts and discusses how to assign tax information to general ledger accounts.
3.9.1 Understanding Tax Information for General Ledger Accounts
If you track taxes by tax rate/area, you must specify that the general ledger account is taxable by selecting the Taxable Account option on the account. When you specify that an account is taxable, the system enables you to specify a default tax rate area to use. The system uses the tax rate area for the account for journal entries that the system automatically generates or when the corresponding field is left blank on the distribution form of the voucher or invoice and you have specified to track taxes.
3.9.2 Forms Used to Assign Tax Information to General Ledger Accounts
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work With Accounts | W0901H | Organization & Account Setup (G09411), Review and Revise Accounts. | Review and select object accounts by company. |
| Revise Single Account | W0901A | On the Work With Accounts form, select an account and click Select. | Add and revise tax information. |
3.9.3 Assigning Tax Information to General Ledger Accounts
Access the Revise Single Account form.
3.9.3.1 More
Select the More tab.
- Taxable Account
-
Select this option to specify whether an account is taxable. When the option is turned on, the account is taxable and the system updates the record in the F0901 table with 1.
- Default Tax Rate/Area
-
Enter a code that identifies a tax or geographic area that has common tax rates and tax authorities. The system validates the code you enter against the Taxes table (F4008). The system uses the tax rate/area in conjunction with the tax explanation code and tax rules to calculate tax and GL distribution amounts when you create an invoice or voucher.
If the account is taxable, you can specify a default tax rate/area for the system to use. The system uses this value only during voucher and invoice entry when the user specifies to track taxes for a general ledger account and does not enter a tax rate/area.
3.10 Setting Up the Tax Constant by Company
This section provides an overview of tax capture settings and discusses how to set the tax constant for companies.
3.10.1 Understanding Tax Capture Settings
If you track taxes by pay item and G/L account, use the Invoice and Voucher Company Tax Constants program (P00218) to specify whether the system balances G/L distribution entries with revenue or expense accounts by pay item and tax information (tax rate area, tax explanation code, and tax item number) based on the source transaction in the Customer Ledger table (F03B11) or Accounts Payable Ledger table (F0411).
|
Note: When you use the track taxes by pay item and G/L account method, the system uses tax information from the voucher or invoice record, not from the general ledger account. |
You must select the tax constant for every company in which you want to track taxes by pay item and G/L account. When you set up the tax constant for a company, the system applies the functionality to all programs in which you enter account distribution for invoices and vouchers.
|
Note: Selecting the tax constant does not affect transactions that existed previously for a company. |
The system stores the tax capture constant information in the Company Constants Tag Table (F0010T).
3.10.2 Forms Used to Set the Tax Constant by Company
| Form Name | Form ID | Navigation | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Work with Invoice and Voucher Company Tax Constants | W00218A | Tax Setup (G00218), Invoice and Voucher Company Tax Constants | Review and select company records.
Note: The system only displays AR companies that have the Offset Method constant set to S. |
| Edit Invoice and Voucher Company Tax Constant | W00218B | Click Add on the Work with Invoice and Voucher Company Tax Constants form. | Set the tax constant for companies. |
3.10.3 Setting the Tax Constant by Company
Navigate to the Work with Invoice and Voucher Company Tax Constants form.
Figure 3-8 Edit Invoice and Voucher Company Tax Constant form
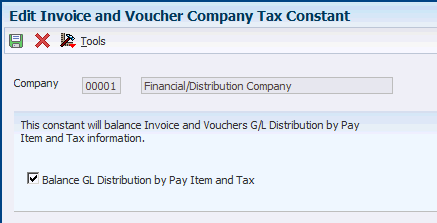
Description of ''Figure 3-8 Edit Invoice and Voucher Company Tax Constant form''
- Balance GL Distribution by Pay Item and Tax
-
Select this check box to balance G/L distribution of revenue or expense accounts in the F0911 table by pay item and tax information with the source transaction in the F03B11 or F0411 tables.
Do not change this constant after it has been set.