Configuring Virtual SCSI HBA Multipathing
The virtual SCSI HBA subsystem supports multipathing in the guest domain and in the service domain by leveraging the Oracle Solaris I/O multipathing implementation. For more information, see Managing SAN Devices and Multipathing in Oracle Solaris 11.3.
As in Oracle Solaris I/O multipathing, a specific back-end SCSI device can be accessed by one or more paths. For the virtual SCSI HBA subsystem, each path is associated with one virtual LUN. The scsi_vhci module implements the Oracle Solaris I/O multipathing behavior, which sends I/O requests to the set of virtual LUNs based on arguments passed to the associated mpathadm administrative command. For more information, see the scsi_vhci(7D) and mpathadm(1M) man pages.
When multipathing is enabled in the service domain, as shown in Configuring Virtual SCSI HBA Multipathing in a Service Domain, the ldm add-vsan command enables you to create a vsan instance that represents all of the paths that reference the SCSI devices that are reachable through a specified initiator port. However, when multipathing is disabled in the service domain, the vsan instance only represents those paths that originate at the specified initiator port and reference the SCSI devices.
To configure multipathing, you must configure two or more distinct paths from the guest domain or the service domain to the same back-end device. Note that multipathing still operates with one configured path. However, the expected configuration has two or more paths that send their I/O requests through distinct physical SCSI HBA initiator ports that reside on distinct service domains.
Execute a pair of ldm add-vhba and ldm add-vsan commands for each separate path to the back-end storage.
Enable Oracle Solaris I/O multipathing in the guest domain for the initiator ports that are managed by the vhba virtual HBA module.
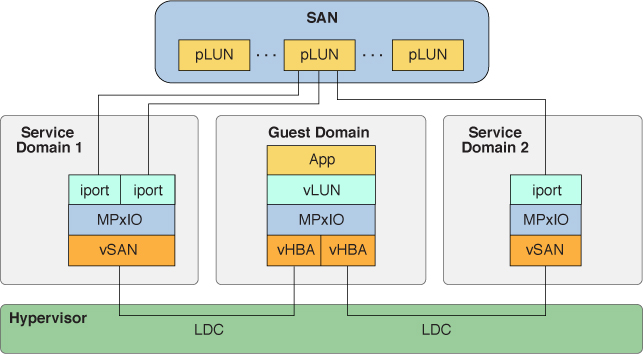
The following figure is an example of a multipathing configuration in a guest domain. It shows one physical LUN of a SAN that is accessed by two paths that are managed by Oracle Solaris I/O multipathing. For a procedure that describes how to create the configuration shown in this figure, see How to Configure Virtual SCSI HBA Multipathing.
Figure 9 Configuring Virtual SCSI HBA Multipathing in a Guest Domain
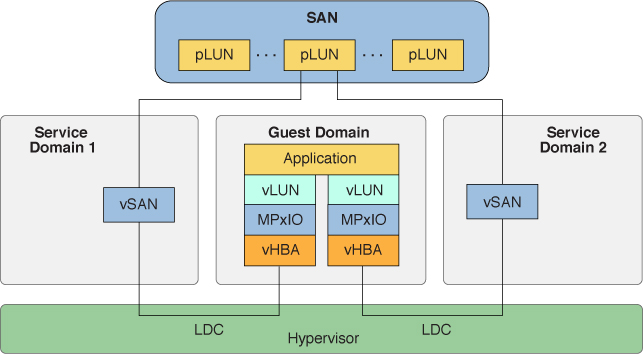
Figure 10 Configuring Virtual SCSI HBA Multipathing in a Service Domain