Oracle Solaris 11 Networking Overview
The Oracle Solaris 11 OS introduced many new networking features, which are described in the Oracle Solaris 11 networking documentation at Oracle Solaris 11.3 Documentation.
All network configuration is performed by the ipadm and dladm commands.
The “vanity name by default” feature generates generic link names, such as net0, for all physical network adapters. This feature also generates generic names for virtual switches (vswn) and virtual network devices (vnetn), which appear like physical network adapters to the OS. To identify the generic link name that is associated with a physical network device, use the dladm show-phys command.
By default in Oracle Solaris 11, physical network device names use generic “vanity” names. Generic names, such as net0, are used instead of device driver names, such as nxge0, which were used in Oracle Solaris 10.
The following command creates a virtual switch for the primary domain by specifying the generic name, net0, instead of a driver name, such as nxge0:
primary# ldm add-vsw net-dev=net0 primary-vsw0 primary
-
The Oracle Solaris 11 OS uses virtual network interface cards (VNICs) to create internal virtual networks.
A VNIC is a virtual instantiation of a physical network device that can be created from the physical network device and assigned to a zone.
-
Use the Oracle Solaris 11 DefaultFixed network configuration profile (NCP) when configuring the Oracle VM Server for SPARC software.
For Oracle Solaris 11 domains, use the DefaultFixed NCP. You can enable this profile during or after installation. During an Oracle Solaris 11 installation, select the Manual networking configuration.
Do not replace the primary network interface with the virtual switch (vsw) interface. The service domain can use the existing primary network interface to communicate with the guest domains that have virtual network devices connected to the same virtual switch.
Do not use the physical network adapter's MAC address for the virtual switch because using the physical adapter's MAC address for the virtual switch conflicts with the primary network interface.
The following Oracle Solaris 11 networking features are important to understand when you use the Oracle VM Server for SPARC software:
Note - In this release, use the DefaultFixed NCP to configure datalinks and network interfaces on Oracle Solaris 11 systems by using the dladm or ipadm command.
Ensure that the DefaultFixed NCP is enabled by using the netadm list command. See Chapter 7, Using Datalink and Interface Configuration Commands on Profiles in Oracle Solaris Administration: Network Interfaces and Network Virtualization.
The following diagram shows that a guest domain that runs the Oracle Solaris 10 OS is fully compatible with an Oracle Solaris 11 service domain. The only differences are features added or enhanced in the Oracle Solaris 11 OS.
Figure 11 Oracle VM Server for SPARC Network Overview for the Oracle Solaris 11 OS
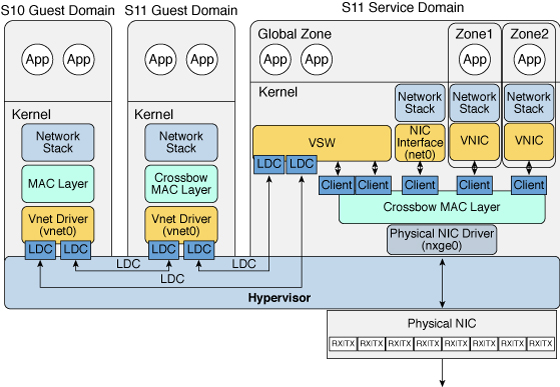
The virtual switch in the service domain is connected to the guest domains, which enables guest domains to communicate with each other.
The virtual switch is also connected to the physical network device nxge0, which enables guest domains to communicate with the physical network.
The virtual switch also enables guest domains to communicate with the service domain network interface net0 and with VNICs on the same physical network device as nxge0. This includes communication between the guest domains and the Oracle Solaris 11 service domain. Do not configure the virtual switch itself (the vswn device) as a network device, as this functionality has been deprecated in Oracle Solaris 11 and is no longer supported.
The virtual network device vnet0 in an Oracle Solaris 10 guest domain can be configured as a network interface by using the ifconfig command.
The virtual network device vnet0 in an Oracle Solaris 11 guest domain might appear with a generic link name, such as net0. It can be configured as a network interface by using the ipadm command.
The diagram shows that network device names, such as nxge0 and vnet0, can be represented by generic link names, such as netn in Oracle Solaris 11 domains. Also note the following:
A virtual switch behaves like a regular physical network switch and switches network packets between the different systems to which it is connected. A system can be a guest domain, a service domain, or a physical network.