| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Working With the EDM for Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index Java CAPS Documentation |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Working With the EDM for Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index Java CAPS Documentation |
Working With the EDM for Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index
About Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index
Features of Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index
Learning about Patient Profiles
System Record and SBR Components for Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index
Security Permissions for the Patient EDM
Navigation Tips for the Patient EDM
Navigating the Patient EDM Functions
Logging Out of the Patient EDM
Learning About Patient Queries
About the Patient EDM Search Function
The Advanced Person Lookup (Alpha) Page
The Advanced Person Lookup (Phonetic) Page
Types of Searches on the Patient EDM
Advanced Person Lookup (Alpha)
Advanced Person Lookup (Phonetic)
Searching by Ranges on the Patient EDM
Required Fields on the Patient EDM
Searching for Patient Profiles
Performing an EUID Lookup on the Patient EDM
Performing a Social Security Number Lookup on the Patient EDM
To Perform a Social Security Number Lookup
Performing a Local ID Lookup on the Patient EDM
Performing an Advanced Alphanumeric Lookup on the Patient EDM
To Perform an Advanced Alphanumeric Lookup
About Alphanumeric Search Fields on the Patient EDM
Performing an Advanced Phonetic Lookup on the Patient EDM
To Perform an Advanced Phonetic Lookup
About Phonetic Search Fields on the Patient EDM
Performing an EUID Comparison Lookup on the Patient EDM
To Perform an EUID Comparison Lookup
Working with Search Results on the Patient EDM
Viewing the Results of a Search
Selecting a Profile from the Results List
Creating and Printing a Search Result Report
Patient Profile Transaction Histories
Patient Profile Merge Histories
Viewing a Patient's Demographic Information
To View Demographic Information
About Demographic Fields on the Patient EDM
About Address Fields on the Patient EDM
Viewing a Patient's Telephone Numbers
About Telephone Fields on the Patient EDM
About Alias Fields on the Patient EDM
Viewing a Patient's Auxiliary IDs
About Auxiliary ID Fields on the Patient EDM
Viewing Comments Associated with a Patient
About Comment Fields on the Patient EDM
Viewing a Patient's Transaction History
About Transaction History Search Fields on the Patient EDM
About Transaction History Results Fields on the Patient EDM
Transaction History Transaction Types on the Patient EDM
Comparing two Patient Profiles
To Compare twoPatient Profiles
Comparing Records in one Patient Profile
To Compare Records in one Patient Profile
Viewing a Patient Profile's Merge History
Viewing a Merge History Tree on the Patient EDM
To View a Patient's Merge History
Viewing a Patient Profile From a Merge History Tree
To View a Patient Profile From a Merge History Tree
Viewing the Patient EDM Audit Log
About Audit Log Search Fields on the Patient EDM
About Audit Log Search Results Fields on the Patient EDM
Audit Log Functions on the Patient EDM
Adding a Patient Profile on the Patient EDM
Step 1: Obtain Information about the Patient
Step 2: Specify a System and Local ID
To Specify a System and Local ID
Step 3: Specify Demographic Information
To Specify Demographic Information
Step 4: Specify Alias Information
Step 5: Specify Address Information
To Specify Address Information
Step 6: Specify Telephone Information
To Specify Telephone Information
Step 8: Add Comments to the Patient Profile
Step 9: Save the Patient Profile
Learning About Patient EDM Maintenance Tasks
Merging Profiles on the Patient EDM
Surviving and Non-surviving Profiles
Updating the SBR and Updating System Records
Maintaining Patient Information
Modifying Demographic Information in a Patient Profile
To Modify Demographic Information
Maintaining Address Information in a Patient Profile
Adding Addresses to a Patient Profile
Deleting Addresses from a Patient Profile
Maintaining Telephone Information in a Patient Profile
Adding Telephone Numbers to a Patient Profile
Modifying Telephone Information
Deleting Telephone Numbers from a Patient Profile
Maintaining Alias Information in a Patient Profile
Adding an Alias to a Patient Profile
Modifying a Patient's Alias Information
Deleting an Alias from a Patient Profile
Maintaining Auxiliary ID Information in a Patient Profile
Adding an Auxiliary ID to a Patient Profile
Modifying Auxiliary ID Information
Deleting an Auxiliary ID from a Patient Profile
Maintaining Comment Information in a Patient Profile
Adding a Comment to a Patient Profile
Modifying a Comment in a Patient Profile
Deleting a Comment from a Patient Profile
Updating the Single Best Record Directly
Locking an SBR Field on the Patient EDM
Unlocking an SBR Field on the Patient EDM
Maintaining System Records on the Patient EDM
Adding a System Record to a Patient Profile
To Add a System Record to a Patient Profile
Deactivating a System Record in a Patient Profile
Reactivating a System Record in a Patient Profile
Changing Patient Profile Status
Deactivating a Patient Profile
To Deactivate a Patient Profile
Reactivating a Patient Profile
To Reactivate a Patient Profile
Working with Potential Duplicate Patient Profiles
Finding Potential Duplicate Patient Profiles
About Matching Review Search Fields on the Patient EDM
About Potential Duplicate Results Fields on the Patient EDM
Merging Potential Duplicate Patient Profiles
Resolving Potential Duplicate Patient Profiles
To Resolve two Potential Duplicate Profiles
Working with Assumed Matches on the Patient EDM
Finding Assumed Matches on the Patient EDM
About Assumed Match Results Fields on the Patient EDM
Reversing an Assumed Match on the Patient EDM
Merging System Records on the Patient EDM
To Unmerge two Merged Patient Profiles
Unmerging System Records on the Patient EDM
To Unmerge two Merged System Records
Learning About Patient EDM Reports
Patient EDM Production Reports
Patient EDM Search Result Reports
Configuring Patient EDM Reports
Masked Data and Patient EDM Reports
All information about a patient is stored in a patient profile. The following topics provide information about the structure of a patient profile.
A patient profile, also known as an enterprise object, is a set of information that describes characteristics of an individual patient in Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index. Figure 1 illustrates an EUID tree for a patient profile, which shows all components of a profile.
Figure 1 Patient Profile Components
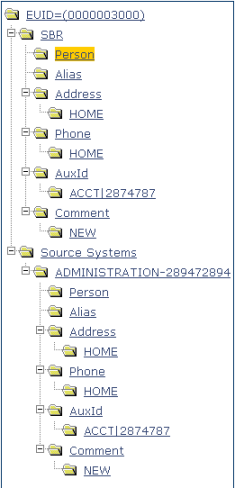
A patient profile contains two types of records:
System Records – A system record is a set of information from an external system that shares data with Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index. A patient profile might contain several system records.
Single Best Record – The single best record (SBR) is a set of information derived from the best information from each system record in a patient profile (as determined by the survivor calculator). Each patient profile has only one SBR.
System records are different from the SBR in that each system record contains a system and local ID pair and only contains data from a specific system. The information in the system records of a patient profile is used to determine the best value for the SBR in that profile. If a patient profile only contains one system record, the SBR will be identical to that system record. However, if a patient profile contains multiple system records, the SBR might be identical to one system record but will more likely include a combination of information from all system records. Certain actions against a system record will cause the SBR to be changed, such as updating, deactivating, or merging a system record. Each active patient profile must have at least one active system record. If all system records in a profile are deactivated, then the entire profile will also be deactivated.
The single best record (SBR) for a patient profile is made up of a combination of information from all active system records associated with that patient profile. The SBR represents the information that is determined by Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index to be the most reliable and current of all system records in a patient profile. The SBR is dynamic and is recalculated each time an update is made to an associated system record, a merge or unmerge affects the patient profile, or a system record in the profile is deactivated or reactivated. You can use the overwrite capability of the Patient EDM to update the SBR directly or you can update a system record and allow the survivor calculator to determine how to update the SBR (for more information, see Survivor Calculator).
If you use the overwrite capability to update a field, that field remains locked and cannot be updated by changes to system records until the field is unlocked. For more information about the overwrite function and locked fields, see Updating the SBR and Updating System Records.
The survivor calculator determines which information from each system record in a patient profile is stored in the SBR for that profile. The calculator uses information defined by the system administrator to calculate the SBR. By default, the survivor calculator uses a weighted strategy for most fields, using the relative reliability assigned to each system in combination with the reliability given to the most recently updated value.
For some fields, such as alias and auxiliary IDs, a union strategy is typically used. This means that all unique alias names and auxiliary IDs from all systems are included in the SBR. For detailed information about the survivor calculator and configuring the survival strategy, see Configuring Oracle Java CAPS Master Indexes (Repository) and Understanding Oracle Java CAPS Master Index Configuration Options (Repository).
In Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index, a patient profile or system record can have three different statuses: active, inactive, or merged. The Patient EDM uses special characters in the EUID tree to indicate profiles or system records that have a status other than active. The Patient EDM also uses indicators in the EUID tree to denote the type of profile you are viewing when a side-by-side comparison of the same EUID is displayed. For example, when a transaction history is displayed, the previous image of the profile appears in parentheses. Table 1 lists and describes each indicator.
Table 1 Patient Profile Indicators
|
In Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index, each system record and SBR in a patient profile contains a set of sub-objects that store different types of information about the patient. Generally, a record contains a parent object and several child objects. By default, the parent object is a person object, which is associated with these child objects: address, telephone, alias, auxiliary ID, and comment. A record can have only one parent object, but can have multiple child objects and multiple instances of each child object with each instance being identified by a unique field. For example, a record can only contain one patient name and social security number (contained in the parent object), but could have multiple addresses and telephone numbers (contained in child objects). Each address must be of a different type, such as a home address, billing address, or mailing address.
The person object is the primary object in a system record or SBR, and stores demographic information about a patient. Each record can have only one person object. By default, the person object of the SBR contains the information from each system that is determined to be the best information by the survivor calculator. Certain fields must be entered in the person object in order to save a patient profile. By default, these fields include first and last names, date of birth, and gender.
Address objects store a patient’s address information in a system record or SBR. Each address is identified by an address type. Each system record or SBR can store multiple addresses, but can only store one address of each type. For example, a record can have a home and a business address, but cannot have two home addresses. By default, the survivor calculator determines which system record addresses to store in the SBR by looking at all system record addresses. If each address type is unique, then all addresses are included in the SBR. If there are multiple addresses of one type, the survivor calculator determines which address to store in the SBR.
Phone objects store a patient’s telephone numbers in a system record or SBR. Each telephone number is identified by a phone type. Each system record or SBR can store multiple telephone numbers, but can only store one number of each type. For example, a record can have a home and a cellular telephone number, but cannot have two home telephone numbers. By default, the survivor calculator determines which system record telephone numbers to store in the SBR by looking at all system record numbers. If each phone type is unique, then all telephone numbers are included in the SBR. If there are multiple telephone numbers of one type, the survivor calculator determines which number to store in the SBR.
Alias objects store nicknames, maiden names, or any other names used by a patient. Each system record or SBR can have multiple alias names. By default, all unique alias names from each system record in a patient profile are included in the SBR. If two system records contain identical alias objects, then only one of those objects is stored in the SBR.
AuxId objects store a patient’s auxiliary IDs in a system record or SBR. Auxiliary IDs are identifiers assigned to a patient that are not necessarily unique to each patient. For example, they can be used to store a credit card number for a joint credit card, an account number for a joint checking account, or an insurance policy number for a policy that covers all members of a family. Each system record or SBR can store multiple auxiliary IDs. By default, all auxiliary IDs from each system record in a patient profile are included in the SBR. If two system records contain identical auxiliary ID objects, then only one of those objects is stored in the SBR.
Additional information about patients appears in the form of comments. Comment objects contain free-form fields in which you can enter information about a patient that does not appear in standard Patient EDM fields. Each comment you add to a patient profile must include a comment code that is unique for the patient profile. This code is used to identify the comment. By default, the survivor calculator determines which system record comments to store in the SBR by looking at all system record comments. If each comment type is unique, then all comments are included in the SBR. If there are multiple comments of one type, the survivor calculator determines which comment to store in the SBR.
Comments can be used to store information about such issues as resolving or merging potential duplicates or reasons for merging or unmerging profiles. They can also be used to store additional information about a patient, such as recording information from a conversation with the patient.
Each patient profile in Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index is assigned a unique identification number in addition to the local IDs assigned by individual systems. Each patient has one unique identification number throughout your organization, and a unique identification number within each system with which they are registered. Patients might also have several auxiliary IDs, meaning that they share these identification numbers with other patients.
Every patient profile in the master index application is assigned an enterprise-wide unique identification number. This number is the same for that patient regardless of the system from which the patient information originates. This number is called the enterprise-wide unique identifier (EUID) and is used to cross-reference patient profiles in order to accurately identify the patients throughout your organization.
A local ID is a unique local identification number that is assigned to a patient in each system at which they are registered. These numbers are assigned using a numbering system unique to each local system, and are used internally by the systems to identify each patient. Oracle Java CAPS Master Patient Index uses a patient’s EUID to cross-reference their local IDs in different systems. Note that the name of the Local ID field is configurable and might be different for your implementation.
An auxiliary ID is an identification code that does not necessarily uniquely identify a single patient within the database, but might identify a group of patients. For example, if a family shares the same account or insurance policy, every family member would have the same identification code for that account or policy.