Defining System Settings for Email Processing
To define system settings for email processing, use the System Installation (RB_ERMS_INSTAL) component.
These topics list prerequisites and common elements and discuss how to define system settings for email processing.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
RB_ERMS_SYSDEFN |
Define settings for email processing, including:
|
|
|
RB_ERMS_TMPL_DEFN |
|
|
|
RB_PRCS_NOTIFY |
Define notifications for the PeopleSoft AE processes that are used in ERMS. |
|
|
Job Notification Page |
PRCSJOBNOTIFY |
Define the messages that are to be sent when a job finishes successfully or when an error occurs in the job. |
|
RB_EM_ACTIVITY |
Define system activities. CRM objects can be created from the email workspace. Specify corresponding application classes that are used to create them on this page. |
Before you set up system settings for ERMS:
Define the person(s) who will represent unknown senders.
Enter one name for role type 4 (Employee) and one name for role type 9 (Consumer). Set up these person(s) in the Worker component, and enter the minimum required data. The person's name for the appropriate role type appears on all emails for which the sender is not identified. To associate a role type with the name, enter each of these person names and role types on the Anonymous Object page of the Installation Options component. You might enter role type ID of 4 for the name of Anonymous Employee and role type ID of 9 for name of Anonymous User. This is, however, not necessary if you specify in the mailbox definition that you want the system to create a user automatically for unidentified email senders.
Define correspondence templates that control the presentation of the email history that the system enters into the body text of the reply.
You can use the delivered template Email History - Model 1 as a model for this. If you do not explicitly select a template, the following default text appears above the text of the original email:
<===== Received from <address@service.domain> on <date.time>======>
Define the default multichannel queue clusters for agents to use Multichannel Toolbar to receive inbound emails.
This enables you to create multichannel queues from the CRM Group Worklist page; the queues use the default queue cluster that you establish.
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Language Code |
Select the language for which you are defining templates. The language that you select limits the prompt on the Template Name field so that you can select only templates of the appropriate language. At runtime, the preferred language of the user who is sending the email determines which settings are used. |
Use the System Installations page (RB_ERMS_SYSDEFN) to define settings for email processing, including general email handling options, mailbox and queue defaults, and processing rules for the mail reader process and other ERMS processes.
Navigation
Image: System Installations page (1 of 2)
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the System Installations page (1 of 2). You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
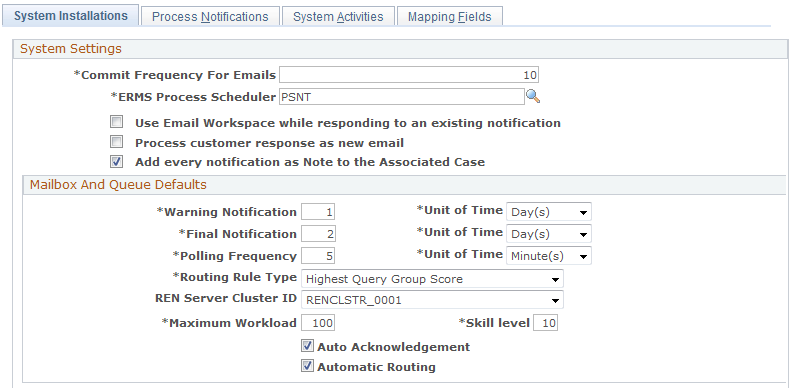
Image: System Installations page (2 of 2)
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the System Installations page (2 of 2). You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
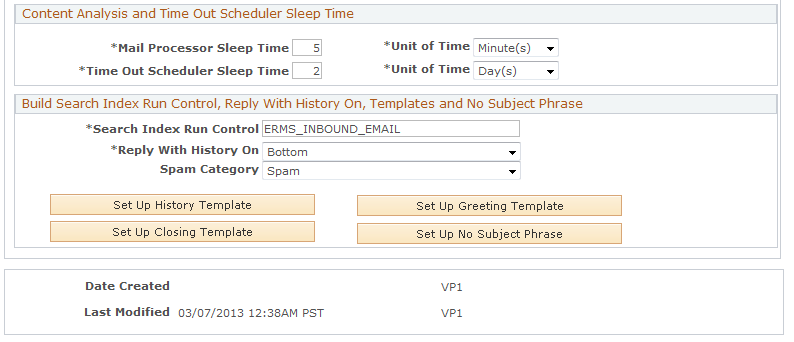
System Settings
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Commit Frequency For Emails |
Enter the number of emails that the mail reader process handles between commits. The mail reader process reads emails from an external mailbox and copies the data into the PeopleSoft CRM database. The data is saved only when the mail reader process issues a commit command. Higher numbers improve performance. Lower numbers minimize the amount of reprocessing that must be done when a process failure occurs. (Because the mail reader process removes email from the external mailbox only after committing the data, mail reader process interruptions cause reprocessing, but do not result in lost data.) The default value is 10. |
| ERMS Process Scheduler |
Enter the process scheduler server on which the ERMS processes run. Because ERMS is process-intensive, setting up a dedicated ERMS process scheduler server improves performance. |
| Use Email Workspace while responding to an existing notification |
Select to have the system launch the email workspace for agents to compose and send response to existing email. If this option is clear, the system launches the Outbound Notification page for sending email replies. |
| Process customer response as new email |
Select to have the system route any incoming threaded email as a new mail, namely using the usual routing rules for unstructured email. For example, if the system successfully identifies a context tag in the incoming threaded email, it sends the inbound email to the last group worklist associated with the previous inbound email. See Routing Methods. If this option is clear, the inbound email is routed to the group worklist to which the sender of the previous outbound email belongs. |
| Add every notification as Note to the Associated Case |
Select to have the system add a note to a case whenever an inbound email is received or outbound email sent for that case. If the email contains attachments, they are added as case note attachments. The system creates an interaction for each inbound and outbound email. This feature applies to reminders as well (for cases). |
Mailbox and Queue Defaults
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Warning Notification, Routing Rule Type, Auto Acknowledgement, and Automatic Routing |
Set default values for the identically named fields on the Mailbox Definition page. These fields control mailbox-level characteristics, such as email routing, response time alerts, automatic acknowledgements, and so on. See Defining Mailboxes. |
| REN Server Cluster ID (real-time event notification server cluster ID) |
Set a default queue cluster to be associated with queues that the system creates when you set up queues and agents using PeopleSoft CRM group worklists. |
| Maximum Workload and Skill level |
Set default values to be associated with agent definitions that the system creates when you set up queues and agents using PeopleSoft CRM group worklists. The values in these fields are used to determine an agent's capacity to accept additional work and thus to determine the agent to whom a new email is routed. |
Content Analysis and Time Out Scheduler Sleep Time
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Mail Processor Sleep Time |
Enter the frequency with which to run the email process, which attempts to trigger proper email actions, including routing emails to worklists. This frequency determines how quickly new email is routed to agents for handling and thus can affect your agent's ability to meet email due dates. |
| Time Out Scheduler Sleep Time |
Enter the frequency with which to run the Time Out Process Handler process, which schedules reminder notifications for emails that have not been closed within the mailbox-level or worklist-level response times. |
| Unit of Time |
For each sleep time that you define, enter Minutes, Hours, or Days as the unit of time. |
Build Search Index Run Control, Reply With History On, Templates and No Subject Phrase
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Search Index Run Control |
Enter the search index run control to be used to build the search index for unstructured inbound email messages. When you save this page, the system creates the run control using the name entered here. After saving this page, navigate to the Build Search Index page () to verify the search index run control. Important! Make sure that the run control for this search index is set to always run in the Full index. Do not manually schedule a PTSF_GENFEED process to build the search index for unstructured inbound email messages. Also, make sure that the CR_CRO_INBOUND_EMAIL search definition and search category are at the deployed status. |
| Reply With History On |
Select Bottom or Top to determine whether the text of an inbound email is kept at the beginning or end of a reply. For example, if you select Bottom, then applying a template to the outbound email inserts the template text before any existing body text. |
| Spam Category |
Specify the category to be used for spam mail. The system-delivered category is called Spam. |
| Set Up History Template |
Click to access the History Templates page, where you select language-specific templates to be applied when agents choose to include the original email text in an email reply. If you do not explicitly set up history templates, the following default text appears above the text of the original email: <===== Received from <address@service.domain> on <date.time>======> |
| Set Up Greeting Template |
Click to access the Greeting Templates page, where you select language-specific greeting text phrases to be applied when agents respond to incoming email. |
| Set Up Closing Template |
Click to access the Closing Templates page, where you select language-specific closing text phrases to be applied when agents respond to incoming email. |
| Set Up No Subject Phrase |
Click to access the No Subject Phrase page, where you enter language-specific text phrases to be used as the subject of an email reply when the original email does not have a subject. |
Use the History Templates page (RB_ERMS_TMPL_DEFN) to define reply with history templates.
Navigation
Click the Set Up History Template button on the System Installations page.
Image: History Templates page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the History Templates page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
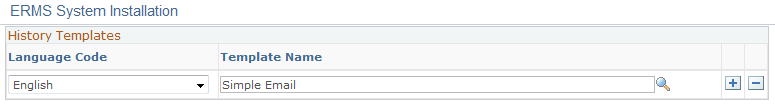
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Template Name |
Select the template for the system to use when entering the text of the original inbound email to the body of the new outbound email. Select a template, not a template package. At a minimum, the templates that you select must contain the text of the original email; use the delivered History Email Body term for this. Optionally, you can include front matter or end matter in the appropriate language. |
Use the Greeting Templates page (RB_ERMS_TMPL_DEFN) to specify email greetings.
Navigation
Click the Set Up Greeting Template button on the System Installations page.
Image: Greeting Templates page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Greeting Templates page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
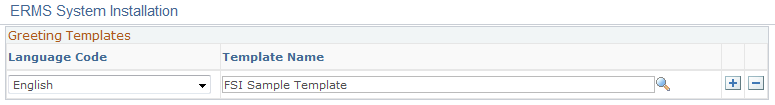
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Template Name |
Select the template for the system to include a greeting in the new outbound email. Select a template, not a template package. |
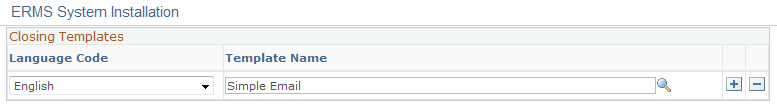
Use the Closing Templates page (RB_ERMS_TMPL_DEFN) to specify closing text for email.
Navigation
Click the Set Up Closing Template button on the System Installations page.
Image: Closing Templates page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Closing Templates page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Template Name |
Select the template for the system to include a closing message in the new outbound email (for example, a diser from your company). Select a template, not a template package. |
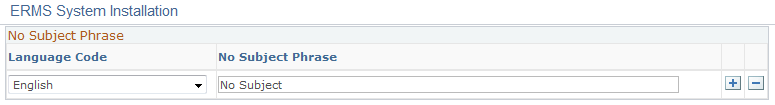
Use the No Subject Phrase page (RB_ERMS_TMPL_DEFN) to define the default subject text to use when replying to an email that has no subject.
Navigation
Click the Set Up No Subject Phrase button on the System Installations page.
Image: No Subject Phrase page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the No Subject Phrase page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| No Subject Phrase |
Enter a default subject to use for replies to email with no subject text to avoid sending replies with insufficient identifying information in the subject. |
Use the Process Notifications page (RB_PRCS_NOTIFY) to define notifications for the PeopleSoft AE processes that are used in ERMS.
Navigation
Image: Process Notifications page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Process Notifications page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
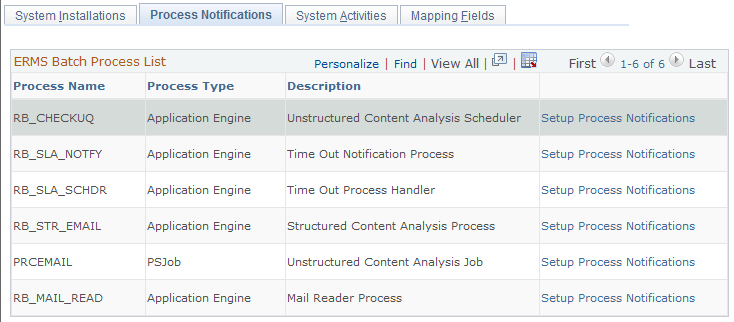
The grid on this page lists all ERMS processes: five PeopleSoft Application Engine processes and one job, which consists of two other PeopleSoft Application Engine processes.
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Setup Process Notifications |
Click to access the Processes - Notification page (for any of the PeopleSoft AE processes) or the Job Notification page (for the unstructured content analysis job). These are both PeopleSoft Process Scheduler pages. Use these pages to define messages to be sent when the process or job finishes successfully or when an error occurs in the process or job. |
See the product documentation for PeopleTools: PeopleSoft Process Scheduler.
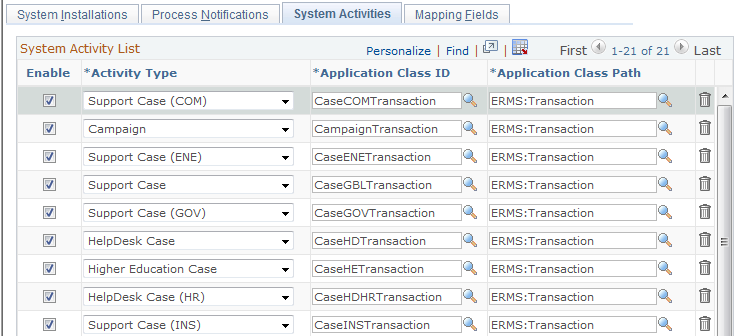
Use the System Activities page (RB_EM_ACTIVITY) to define system activities.
CRM objects can be created from the email workspace. Specify corresponding application classes that are used to create them on this page.
Navigation
Image: System Activities page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the System Activities page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Enable |
Select the transactions that agents can search for or create within the email workspace and associate them with email. |
| Activity Type |
Select the CRM object that agents can create from the email workspace. |
| Application Class ID and Application Class Path |
Specify the path and ID of the application class program that is written to create transactions of the corresponding CRM object. |