TCP/IP HL7 Adapter Inbound and Outbound Tutorial
The topics listed here provide information about the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter sample projects that are installed automatically as part of the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter.
What You Need to Know
These topics provide information you should know about the TCP/IP HL7 sample projects.
What You Need to Do for the Standard Inbound and Outbound Sample Project
These topics provide instructions to complete a TCP/IP HL7 Adapter sample project and demonstrate how a TCP/IP HL7 Adapter is implemented.
What You Need to Do for the Schematron Sample Project
These topics provide instructions to complete the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter sample schematron validation project.
Sample Project Overview
The TCP/IP HL7 Adapter includes several sample projects that you can use as templates to create your own customized projects to enable communication between external systems. These projects are designed to be extended and modified for your specific project requirements. The TCP/IP Adapter includes the following sample projects:
-
prjHL7Inbound
-
prjHL7Outbound
-
prjHL7Inbound-MLLPV2
-
prjHL7Outbound-MLLPV2
-
prjHL7Inbound-XML
-
prjHL7Outbound-XML
-
prjHL7V2toV3_AND_ebXML
-
prjHL7V3CommonJcdsInbound
-
prjHL7V3Inbound
-
prjHL7V3Inbound_WithSchematron
-
prjHL7V3Outbound
Some of these projects include a predefined Environment so you do not have to create one from scratch. This tutorial concentrates on two of the sample projects: prjHL7Inbound and prjHL7Outbound. Each of these projects demonstrate multiple operations (Collaborations), and the tutorial takes you through configuring, building, and deploying the projects. Ad additional section at the end of this tutorial goes through the prjHL7V3Inbound_WithSchematron sample to illustrate how to implement schematron validation in HL7 V3.
Standard Inbound and Outbound Samples
The first section of the tutorial deals with standard inbound and outbound sample projects, which include a variety of Collaborations and Connectivity Maps for you to deploy.
prjHL7Inbound Project
The prjHL7Inbound project includes the following Connectivity Maps, both of which use the same Collaboration:
-
HL7 Inbound: A standard inbound HL7 messaging operation that receives the HL7 messages from an external system, sends an acknowledgement of the message, provides sequence numbering, writes the HL7 message to a JMS data queue, and also writes the HL7 message and ACK to a JMS Journal queue.
-
HL7 Forward Message Inbound: Inbound forward message mode is used with the outbound delayed ACK. Its purpose is to get a message from an outbound forwarder and return an acknowledgement.
prjHL7Outbound Project
The prjHL7Outbound project includes the following Connectivity Maps:
-
HL7 Outbound: A standard outbound HL7 messaging operation that receives the HL7 message from the JMS data queue, provides sequence numbering, sends the HL7 message to an external system, receives an acknowledgement from the external system, and writes the HL7 message and the ACK to a JMS Journal queue.
-
HL7 Forward Outbound: Outbound forward message mode is used with the delayed ACK. Its purpose is to get a message from a JMS queue and send it to an external system. No validation is performed.
-
HL7 Outbound Delayed ACK: Delayed Acknowledgement is similar to HL7Outbound, but the initial acknowledgement is received from the receiving system. After the sender receives the first ACK, it waits for a second ACK that indicates that the message was received by the external HL7 system.
Schematron V3 Inbound Sample
The second section of the tutorial deals with standard inbound and outbound sample projects, which include a variety of Collaborations and Connectivity Maps for you to deploy. The schematron sample illustrates how to perform schematron validations against the incoming message. Schematron validation uses the concept of finding tree patterns in the parsed document rather than the grammar, which allows representation of numerous structures that are difficult in grammar-based schema languages.
The inbound schematron project includes the following Connectivity Maps, each of which process message in different ways depending on how the Adapter is configured in the Connectivity Map and which Collaboration is in use:
-
HL7 V3 Deferred Inbound
-
HL7 V3 Inbound
-
HL7 V3 Message Publisher
-
HL7 V3 Queue Manager
Sample Project Components
The TCP/IP HL7 Adapter projects provide predefined adapter components designed to be extended and modified for your specific project requirements. Projects are created using tools in the NetBeans IDE. Use Deployment Profiles to deploy projects to specific logical hosts in specific Environments. Components developed for use in one project can be used in another, and a project can internally reference another project.
The components found in a typical project include the following:
-
Services: A service provides a framework for a process or a Collaboration.
-
External Applications: The Enterprise Service Bus system integrates external applications which are logical representation of external software applications. An adapter links such applications to a Service.
-
Schedulers: A Scheduler allows a service to be performed at a prescribed interval.
-
Component Connections: When you link two components on a Connectivity Map, NetBeans places either an adapter or JMS Client connection icon on the link, depending upon the type of components you are linking. When an External Application and a Collaboration are linked, the link contains an adapter. When a Service and a Message Destination (queue or topic) are linked, the link contains a JMS Client Connection.
-
Message Destinations: A Message Destination is a container for stored data, and can follow either the topic or queue JMS model.
-
Topic: A topic is a message destination that conforms to the publish-and-subscribe messaging model (one to many).
-
Queue: A queue is a message destination that conforms to the point-to-point messaging model (one to one).
-
These components are graphically represented in a project's Connectivity Map. For example, the cmHL7Outbound Connectivity Map is shown below. This Connectivity Map does not contain a Scheduler or any Topics.
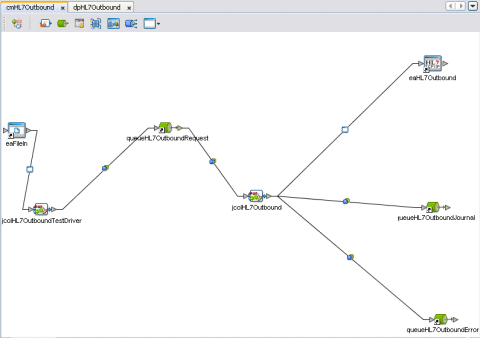
Sample Project Collaborations
The sample projects include multiple Collaborations for you to work with. These Collaborations are designed to work as is for HL7 compliant interfaces, and can be configured for your specific needs by configuring the External System properties. If an interface requires special functionality, the Collaboration's Java code is easily accessible for modification, much of which can be created graphically (drag and drop), using the Collaboration Editor's Business Rules Designer.
The Collaborations contain a number of OTDs that extend functionality for HL7 message handling, logging, error messaging, journaling, and sequence numbering. These include both generic HL7 OTDs for HL7 ACK/NAK generation or verification, and the Resource Adapter that communicates to the external system and offers services to the application server. The Collaboration controls messaging protocol and all business logic.
The Collaborations are designed to target one unit of work at a time, meaning the resolution of one message at a time. The basic structure of the Collaborations is a state machine implemented in a Java switch statement. The state machine keeps track of the messaging protocol so that when a Collaboration is invoked, it can retrieve the state of the connection just handed to it by the RA, and then execute proper actions based on the state machine.
At the end of each action, the state is set for the next execution of the Collaboration. There are three main states:
-
To Establish: A new or reset connection needs to have an HL7 session established. If sequence numbering is used, the sequence numbers need to be negotiated.
-
Messaging: This is where the exchange of messages and ACKs takes place.
-
Shutdown: This is where any cleanup can happen before the connection is closed, or to close the connection.
Additional Collaborations can be added to a project to increase message flow.
Note –
The TCP/IP HL7 inbound Collaboration publishes received data as a Byte message in JMS using the sendBytes() method. However, the HL7 outbound Collaboration expects a Text message from JMS. The Adapter is not designed for the HL7 outbound Collaboration to subscribe to a JMS data queue created by the HL7 inbound Collaboration directly. HL7 inbound and outbound Collaborations are designed to communicate through an HL7 Adapter TCP/IP connection.
Tutorial Overview
The following topics provide information about the process covered and this tutorial and the purpose of the sample projects:
Tutorial Process
This tutorial shows you how to work with the standard inbound and outbound sample projects that are provided with the TCP/HL7 Adapter. It also include information on working with the schematron inbound sample.
The tutorial process is divided into the following steps.
-
Install the TCP/IP Adapter, if it is not already installed, and download the sample files.
-
Import the projects into the Repository.
-
Check Out the imported project.
-
Configure the Connectivity Maps.
-
Create and configure the Environments.
-
Create the Deployment Profile.
-
Build the project.
-
Start the GlassFish server, which allows you to deploy and manage projects.
Tutorial Context
In a typical real-world situation, you have an application with access to patient information that is periodically updated (for instance, when a patient is discharged or a lab result is issued). On the other hand, you have parties who are interested in knowing when that information changes. The parties with whom you want to communicate, however, have no direct access to the data, especially to the manner in which the application internally structures the data. Instead, it is likely that other parties have their own customized methods of handling data internally. To communicate the data to them, you need to encode it in an HL7 message, which is a widely used standard for transmitting healthcare-related information. As long as the parties can handle HL7 messages, you can communicate your data to them.
For the purposes of this tutorial, the structure of the data inside your application bears little relation to the format of the data specified by the HL7 standard. What is needed is an interface between the application and the HL7 message, a way to efficiently and reliably map the desired information out of the application's data structures and into an HL7 message, which can then be sent to interested parties. The Java CAPS provides a flexible and intuitive means of designing HL7 messages and mapping the desired data into the messages, thus making the data available to the recipient in a standard format.
Working With the Standard Inbound and Outbound Sample Projects (V2.x)
To create a TCP/IP HL7 Adapter sample project, perform the following steps in the order given:
Installing the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter and Sample Projects
The TCP/IP HL7 Adapter is not installed by default with a standard Java CAPS installation; you need to install the Adapter manually. The Adapter is installed with the base HL7 OTD Library files and with V2.6. You can install additional HL7 OTD Library versions if needed. After install the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter to the Repository, the sample projects are available to download.
The Java Composite Application Platform Suite Installer is a web-based application, used to select and upload adapters and add-on files to install. The Suite Installer serves as an Update Center, Management Center, and Dashboard to gain access to available applications.
Installing the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter
If you have already installed the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter using the Suite Installer but have not installed the Adapter in NetBeans, skip to Installing the TCP/IP Adapter in the NetBeans IDE. If you have installed the Adapter in both the Repository and NetBeans, skip to Downloading the Sample Projects.
 To Install the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter
To Install the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter
Before You Begin
Java CAPS must be installed before starting this procedure.
-
Start the Java CAPS Repository.
The start_repository executable file is located in your Java CAPS home directory.
-
Open a web browser and type the following URL to access the Suite Installer:
http://localhost:port_number
where localhost is the TCP/IP host name of the Repository server and not the name of the Repository itself, and port_number is the port number you specified during installation for the Repository.
The Login page of the Suite Installer appears.
-
Enter the username and password, and then click Login.
Note –The default username is admin and the default password is adminadmin.
The Java Composite Application Platform Suite Uploader page appears.
-
On the Administration Page, click to Install Additional Products.
The Welcome to the Java Composite Application Platform Suite Uploader page appears.
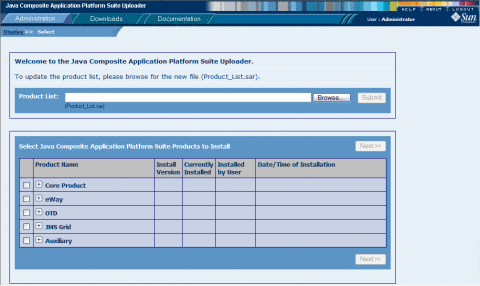
-
Expand eWay under the Product Name column, and then select HL7eWay.
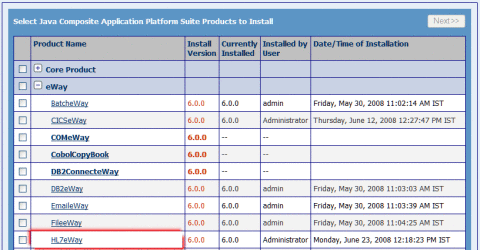
-
If you are using a version of HL7 other than V2.6, expand OTD and select HL7OTDLibrary along with the HL7 libraries for the version you are using.
Note –Note that there are several items to select to install the full V3 HL7 Library.
-
Click Next in the top-right or bottom-right corner of the page.
The Selecting Files to Install page appears.
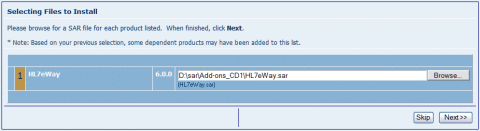
-
Click Browse, and then navigate to and select the SAR file for the listed product. Click Next.
-
Repeat the above steps for each product to install.
Note –Based on your previous selection, some dependent products may have been added to the list.
When you click Next after the last SAR file is selected, the Installation Status page appears, displaying the status of the installation. The lower portion of the page displays additional information about the installation process. Once a product is installed, a check mark appears next to it. This might take several minutes.
When the installation is complete, the following confirmation message appears: Installation finished.
Installing the TCP/IP Adapter in the NetBeans IDE
After you install the TCP/IP Adapter in the Repository, the related plug-ins can be installed in NetBeans. This allow you to incorporate the Adapter into your Repository-based projects.
 To Install the TCP/IP Adapter in the NetBeans
IDE
To Install the TCP/IP Adapter in the NetBeans
IDE
-
Start NetBeans from the Java CAPS home directory.
-
In NetBeans, connect to the Repository (Tools menu > CAPS Repository > Connect).
-
From the NetBeans IDE menu bar choose Tools and then Plugins.
-
On the Plugins window, click the Settings tab.
-
In the Configuration of Update Centers panel, select CAPS Repository Update Center and deselect all other options.
If CAPS Repository Update Center does not appear in the list, do the following:
-
On the Settings page, click Add.
The Update Center Customizer dialog box appears.
-
In the Name field, enter CAPS Repository Update Center.
-
In the URL field, enter the following:
http://HostName:PortNo/repository/RepName/data/files/InstallManager/catalog.xml
where HostName is the name of the Repository server (or localhost), PortNo is the Repository base port number, and RepName is the name of the Repository.
-
Click OK.
Tip –You might need to click Reload Catalog on the Installed tab in order to see the available Java CAPS plug-ins.
-
-
Click the Available Plugins tab.
The TCP/IP HL7 components appear in the list.
-
Select the individual components to install, or right-click in the list and select Check All.
-
Click Install.
-
On the NetBeans IDE Installer, click Next, accept the license, and click Install.
Note –Ignore any validation or unsigned warnings and continue with the installation.
-
When the installation completes, click Finish.
The IDE will restart to complete the installation.
Downloading the Sample Projects
The following instructions provide the steps to download the Enterprise Manager from the Suite Installer.
Note –
Before beginning this procedure, make sure the Repository is running for the Suite Installer.
 To Download Files From the Repository
To Download Files From the Repository
-
On the Suite Installer, click the Downloads tab.
A list of components ready to be downloaded appears.
-
For the purposes of this tutorial, select HL7 Adapter Inbound Collaboration Project.
-
Save the prjHL7Inbound.zip file to a local directory.
-
Repeat the previous step for HL7 Adapter Outbound Collaboration Project.
-
If you want to work with the schematron validation Projects for HL7 V3, download HL7 Adapter Inbound Collaboration Project for HL7V3 PRPA_IN403001UV01 With Schematron Validation Enabled.
Note –In order to import the V3 projects, you must have the HL7 V3 Libraries installed.
Importing the Sample TCP/IP HL7 Adapter Projects
Before you can begin working with the sample projects, you need to import them into the NetBeans IDE. For this tutorial, you need to import two projects: prjHL7Inbound and prjHL7Outbound.
Do the following to import the sample projects and make them available for editing:
Importing the TCP/IP Adapter Sample Projects
This section describes how to import the standard inbound and outbound samples for HL7 V2.x.
 To Import TCP/IP HL7 Adapter Sample Projects
To Import TCP/IP HL7 Adapter Sample Projects
Before You Begin
In order to import the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter sample projects, the Adapter needs to be installed and the sample projects downloaded. For more information, see Installing the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter and Sample Projects.
-
On the NetBeans IDE, save all unsaved work.
-
On the NetBeans menu bar, select Tools, point to CAPS Repository, and then select Import Project from the drop-down menu.
A confirmation dialog box appears asking if you need to save any changes.
-
Click Yes to proceed with importing a project.
The Import Manager appears.
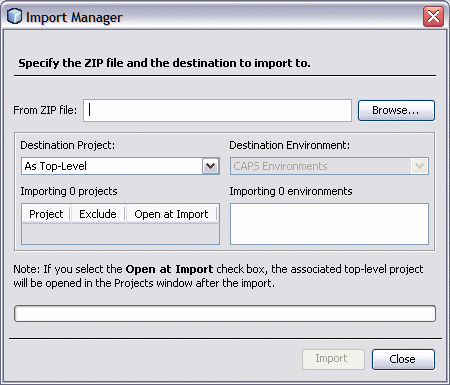
-
Click Browse, navigate to the location of the project ZIP files, and select prjHL7Inbound.zip.
Note –The associated top-level project is opened in the projects window after the import if you select the Open at Import check box.
-
Click Import.
Note –A warning message appears if you already have a project of the same name in the CAPS Repository. Determine whether you want to overwrite the existing project. In some cases the imported file will add files to an existing project. If you do not want to overwrite the existing project, cancel the import and exit the Import Manager. Rename and save the existing project, and attempt the import again.
It may take a few seconds to import the project. When the project is imported, the Import Status dialog box appears.
-
Click OK on the dialog box.
The CAPS Repository is refreshed.
-
Repeat the above steps on the Import Manager to import prjHL7Outbound.zip.
-
Close the Import Manager.
You should now have two new projects, prjHL7Inbound and prjHL7Outbound, in the tree structure of the projects window, as shown below.
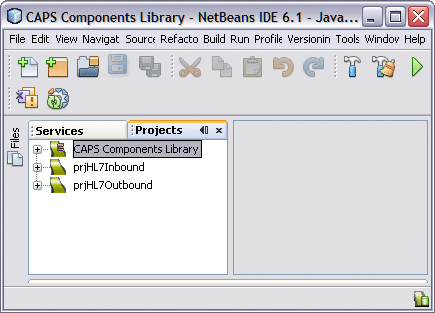
Checking Out the Imported Projects
After you import a project and the Repository refreshes, the project and all of its components are check into version control, which means they can only be viewed and not edited. You need to check the project out to edit the components.
 To Check Out the Imported Projects
To Check Out the Imported Projects
-
On the Projects window, right-click prjHL7Inbound, point to Version Control, and then select Check Out.
The Version Control - Check Out dialog box appears.
-
Select Recurse Project to ensure all components of the prjHL7Inbound are listed.
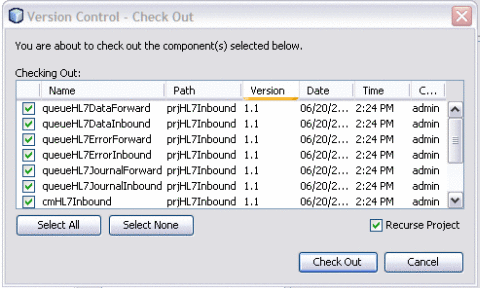
Note –You can select either one or more components.
-
Click Select All and then click Check Out.
This checks out all components of the project so you can edit them as needed.
-
Repeat the above steps for prjHL7Outbound.
Creating and Configuring the Environments
Environments include External Systems, Logical Hosts, application servers, and message servers used by a project. These contain the configuration information for these components. Environments are created using NetBeans and the Environment Editor. This section describes how to create and configure Environments for all five of the Connectivity Maps included in the inbound and outbound projects. You only need to create Environments for the operations you want to run.
The instructions are divided into the following sections:
Creating and Configuring the HL7 Outbound Environment
The components required for the HL7 outbound Environment include a Logical Host, application server, JMS IQ Manager, and two external systems.
 To Create an Environment for the prjHL7Outbound
To Create an Environment for the prjHL7Outbound
-
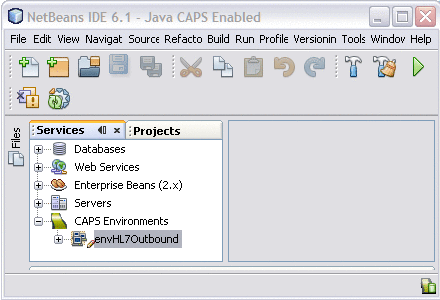
On the NetBeans Services window, right–click CAPS Environment and then select New Environment.
A new environment is created and is added to the CAPS Environment tree.
-
Rename the new Environment to envHL7Outbound.
-
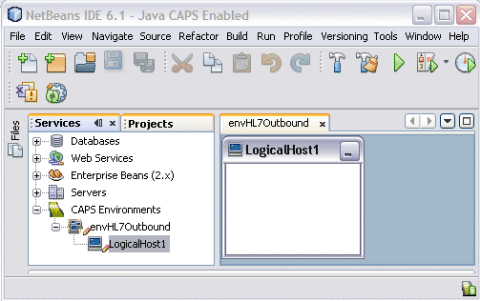
Right-click envHL7Outbound, point to New, and then select Logical Host.
It takes few seconds to process the Logical Host into the Environment.
-
Rename the Logical Host lhHL7Outbound
-
Create and configure an application server:
-
Right-click lhHL7Outbound, point to New, and then select Sun Java System Application Server.
A new application server is added to the Environment tree .
-
Rename the server gfHL7Outbound.
-
Right-click gfHL7Outbound and select Properties.
The Properties Editor appears.
-
Click the ellipses button next to the Password property.
The Password Settings dialog box appears.
-
Click the ellipses available at the end of the field.
The Password Settings dialog box appears.
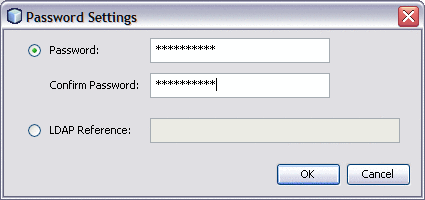
-
Enter the password in the Password and the Confirm Password fields.
The default Password is adminadmin and the default Confirm Password is adminadmin.
-
Click OK.
-
On the Properties Editor, verify the remaining properties and then click OK.
-
-
Create and configure a JMS IQ Manager:
-
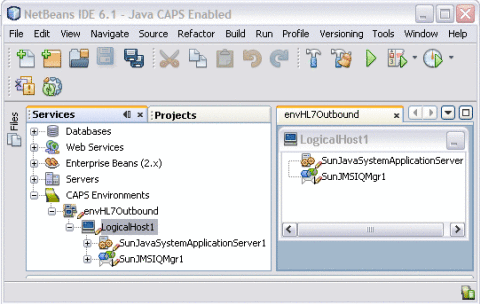
Right-click lhHL7Outbound, point to New, and then select Sun JMS IQ Manager.
A new JMS IQ Manager is added to the Environment tree.
-
Rename the IQ Manager iqHL7Outbound.
-
Right-click iqHL7Outbound, and select Properties.
The Properties Editor appears.
-
In the Sun JMS IQ Manager URL property, enter the URL of the IQ Manager.
The default URL is stcms://localhost:18007.
-
Enter a password as described for the application server above.
-
Verify the remaining fields, and then click OK.
-
-
Create and configure a File External System:
-
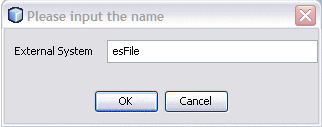
Right-click envHL7Outbound, point to New, and then select File External System.
-
On the dialog box that appears, enter esFile as the name.
-
Click OK.
The external system is added to the Environment tree.
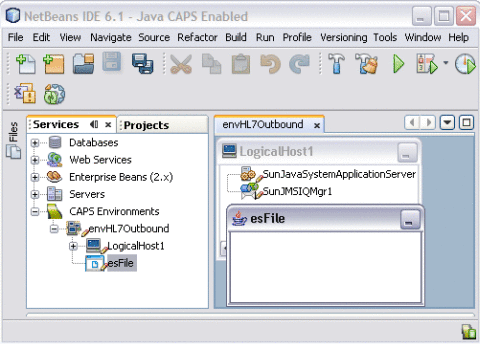
-
Right-click esFile and select Properties.
The Properties Editor appears.
-
On the Properties Editor, expand Inbound File eWay, and modify the directory from which the File Adapter will pick up the input file.
-
Click OK.
-
-
Create and Configure an HL7 External System:
-
Right-click envHL7Outbound, point to New, and then select HL7 External System.
-
On the dialog box that appears, enter esHL7 as the name.
-
Click OK.
The External System is added to the Environment tree.
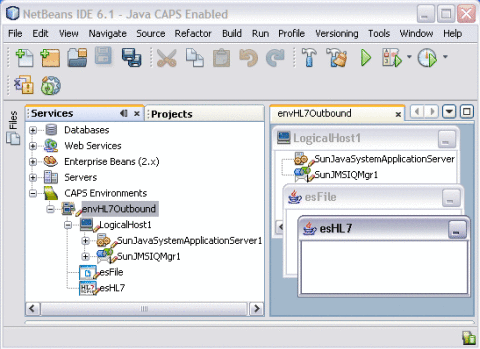
-
Right-click eHL7 and select Properties.
The Properties Editor appears.
-
On the Properties Editor, expand HL7 Outbound eWay, and select TCPIP Outbound Settings.
-
Make sure the hostname and port are correct for the application that is listening for HL7 messages.
-
Click OK.
-
-
On the NetBeans toolbar, click Save All.
Creating Environments for the HL7 Inbound and Outbound Samples
Follow the example given in the previous section, create Environments for the remaining TCP/IP HL7 samples. You only need to create Environments for the samples you want to run. Make sure the configure the URL and authentication information for all the application servers and JMS IQ Managers you add. Any additional required configuration is listed below.
Tip –
Even if you do not modify the Environment components of an External System, be sure to open the Properties Editor for each External System. Otherwise, the build process may fail.
HL7 Inbound Sample
Create the envHL7Inbound Environment with the following components:
HL7 Inbound Forward MSG Sample
Create the envHL7InboundForwardMSG Environment with the following components:
HL7 Outbound Delayed ACK Sample
Create the envHL7OutboundDelayedACK Environment with the following components:
-
HL7 External System
Configure the HL7 Outbound eWay > TCPIP Outbound Settings properties.
-
File External System
Configure the Inbound File eWay > Parameter Settings properties.
-
Logical Host
-
GlassFish (Sun Java System Application) Server
-
Sun JMS IQ Manager
-
HL7 Outbound Forward Sample
Create the envHL7OutboundForward Environment with the following components:
-
HL7 External System
Configure the HL7 Outbound eWay > TCPIP Outbound Settings properties.
-
Logical Host
-
GlassFish (Sun Java System Application) Server
-
Sun JMS IQ Manager
-
Configuring the Connectivity Map Properties
For certain sample projects, the Connectivity Maps do not need to be configured. For Connectivity Maps that include the File Adapter, the name of the input files needs to be configured. If you are running the HL7 outbound or the HL7 outbound delayed ACK sample, perform the task below.
 To Configure the Connectivity Map Properties
To Configure the Connectivity Map Properties
-
On the Projects window, expand prjHL7Outbound.
-
Open either cmHL7Outbound or cmHL7OutboundDelayedAck in the Connectivity Map Editor.
-
Double-click the Adapter icon on the line connecting the File External System to the Service.
The Properties Editor appears.
-
In the Input File Name field, enter the name or the name pattern for the input file.
-
Click OK.
Creating the Deployment Profile
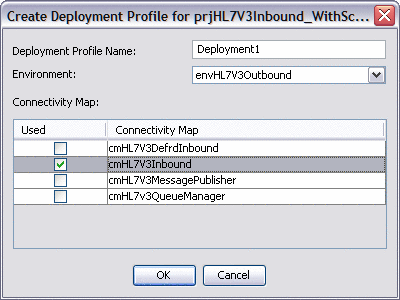
A Deployment Profile is used to assign the connectivity components to the Environment components, including the application server and message server. You only need to create a Deployment Profile for the sample projects that you will run. The following procedure describes how to create a Deployment Profile for the HL7 outbound sample. Connectivity Map and Environment combinations for the other samples are listed at the end of this procedure.
 To Create the Deployment Profile
To Create the Deployment Profile
-
On the Projects window, right-click prjHL7Outbound Project, point to New, and then select Deployment Profile.
The Create Deployment Profile dialog box appears.
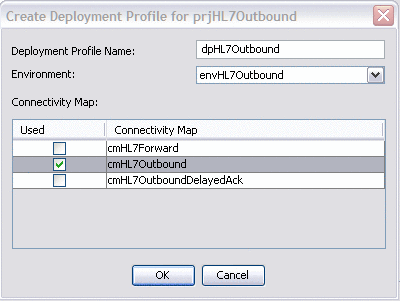
-
For the Deployment Profile Name, enter dpHL7Outbound.
-
For the Environment, select envHL7Outbound.
-
For the Connectivity Map, select cmHL7Outbound and deselect all other Connectivity Maps.
-
Click OK.
The Deployment Editor appears.
-
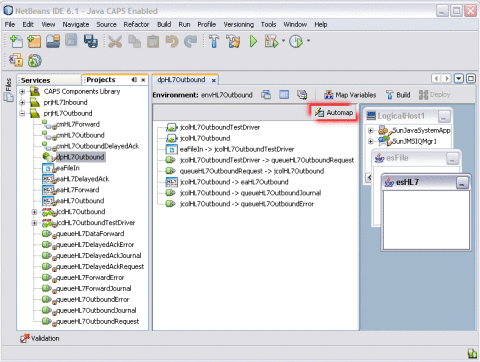
Click Automap.
-
On the Automap confirmation dialog box, click Close.
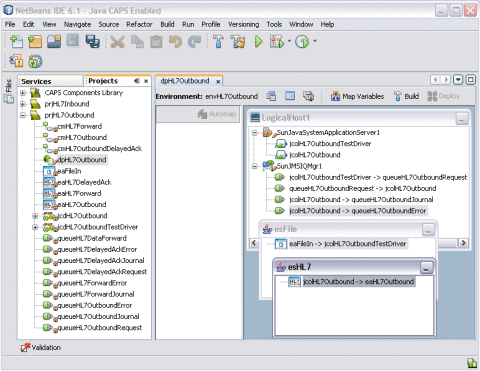
The tree structure of the mapped Environment appears, as shown. below
-
Save the Deployment Profile.
Creating Deployment Profiles for the HL7 Inbound and Outbound Samples
Create Deployment Profiles for the remaining TCP/IP HL7 samples following the procedure above and using the following combinations of Environments and Connectivity Maps.
HL7Inbound Inbound Sample
Use the following to create the dpHL7Inbound Deployment Profile:
-
Environment: envHL7Inbound
-
Connectivity Map: cmHL7Inbound
HL7Inbound ForwardMSG Sample
Use the following to create the dpHL7InboundForwardMSG Deployment Profile:
-
Environment: envHL7InboundForwardMSG
-
Connectivity Map: cmHL7InboundForwardMSG
HL7Outbound OutboundDelayedACK Sample
Use the following to create the dpOutboundDelayedACK Deployment Profile:
-
Environment: envOutboundDelayedACK
-
Connectivity Map: cmOutboundDelayedACK
HL7Outbound Forward Sample
Use the following to create the dpHL7OutboundForward Deployment Profile:
-
Environment: envHL7OutboundForward
-
Connectivity Map: cmHL7OutboundForward
Building and Deploying the Project
The Build process compiles and validates the project's Java files and creates a project enterprise application archives (EAR) file. This file runs on an application server. Deploying the projects deploys the EAR file to the application server.
Perform the following steps for each of the Deployment Profiles you want to deploy:
Starting the GlassFish Server
The deployment will fail if the application server is not started.
 To Start the GlassFish Server
To Start the GlassFish Server
Before you can deploy a project, you need to start the application server.
-
On the Services window, expand Servers.
-
Right-click GlassFish V2 and select Start.
The GlassFish server starts. This may take a few minutes
Building a Project
Once the Deployment Profile is created and the Connectivity Map and Environment components are mapped, you can build the project. This creates the EAR file that gets deployed to the application server.
 To Build a Project
To Build a Project
-
Open the Deployment Profile you want to build.
-
Click the Build icon on the Deployment Editor toolbar.
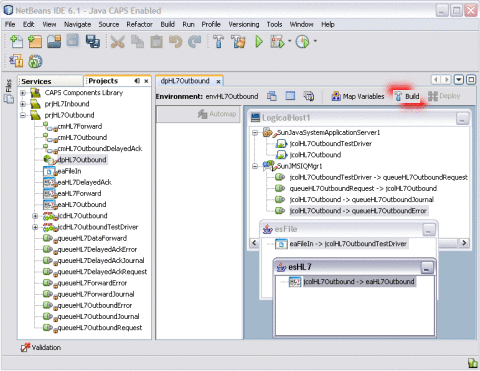
Note –If the build fails, an error dialog box appears and the errors are listed in the Validation window. Correct any errors and rebuild. Validation errors will occur if you did not open the External System Properties Editors in the Environment.
-
When the build is complete, a confirmation dialog appears. Click OK to close it.
Deploying the Project
Once you deploy the project, it will immediately begin running. If there are any input files in the specified input directory, they will be processed.
 To Deploy the Project
To Deploy the Project
-
On the Deployment Editor toolbar, click Deploy.
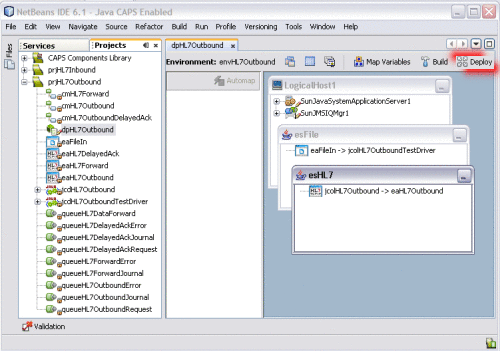
A message appears in the lower left side of the window when the project is successfully deployed.
Running the Samples
The inbound and outbound TCP/IP HL7 sample projects demonstrate several different operations. Only deploy the Connectivity Maps that contain the scenario you want to run. For the outbound projects that use a File Adapter, use the following procedure to run data in. For the other projects, you will need an HL7 simulator or HL7 application to send and receive messages.
 To Run a Sample Project
To Run a Sample Project
Before You Begin
Make sure the Connectivity Map you want to run is deployed.
-
Create a text file with the following content. Name the file HL7Msg1.txt (unless you modified the file name in the Connectivity Map properties).
MSH|^~\&|REGADT|MCM|RSP1P99|MCM|199601051530|SEC|ADT^A44^ADT_A43|00000037|P|2.3.1| |||||UTF-8~ISO-8859-1~ISO-8859-2|||c1^sc1&c2 EVN|A44|199601051530 PID|||MR2^^^XYZ^MR||JONES^WILLIAM^A^JR||19501010|M|||123 EAST STREET^^NY^NY10021| |(212)111-3333|||S|ACCT|1 MRG|MR1^^^XYZ^MR||ACCT1 Z01|A44|199601051530
-
Place the sample input file in the configured input directory for the File Adapter.
When the File Adapter picks up the file, it appends “.~in” to the filename.
-
Verify the output data from your output directory.
This sample contains messages that the recipient will accept as valid and properly formatted. The sample messages are used to design the interface.
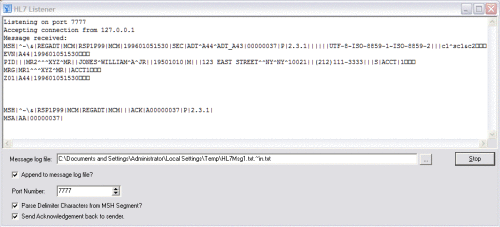
HL7 Messages are ASCII messages (unlike protocols such as DICOM), and the standard requires that they be human readable.
Monitoring the HL7 Adapters
You can monitor a running HL7 Adapter on the Enterprise Manager. In order to do this, you need to have the HL7 Adapter plug-in installed on the Enterprise Manager. See Installing Additional Components for Java CAPS 6 for more information.
Note –
For the outbound adapter, monitoring is performed periodically based on a time period defined in the HL7 Adapter web applications deployment descriptor, web.xml/
 To Monitor the HL7 Adapters
To Monitor the HL7 Adapters
-
Start the Enterprise Manager.
Tip –You can use the start_emanager shortcut in the Java CAPS home directory.
-
Open a web browser and log in to the Enterprise Manager using the following URL:
http://host-name:port-number
where host-name is the name of the server on which Enterprise Manager is installed, and port-number is the Enterprise Manager port number (15000 by default).
-
In the left pane of the Enterprise Manager expand Java EE > prjHL7Inbound > Deployment1 > cmHL7Inbound, and then select eaHL7Inbound.
A new frame appears with a list of actions under a node named eaHL7Inbound => jcdHL7inbound1.
-
Execute the sample project using an HL7 simulator.
-
Under eaHL7Inbound => jcdHL7inbound1, select Logging to view log messages.
-
Select Alerts to view alerts and their statuses.
-
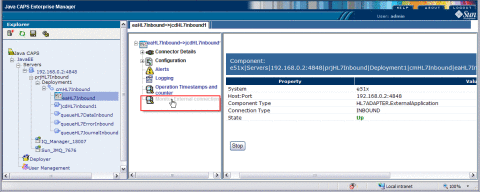
Select Monitor External Connection to view information about the connection to the external system.
This action displays the screen as shown below.
-
Terminate the external system and observe that the status information of the terminated system no longer appears in the status table
Working With the Schematron HL7 V3 Sample Project
This sample project receives an HL7 V3 message, PRPA_IN403001UV01, and sends an HL7 V3 ACK or NAK, MCCI_IN000004UV01. This project is same as prjHL7V3Inbound except for the schematron validation for the input XML.
Follow these steps in the order given to complete the schematron sample:
Importing the Sample Project
In order to work with the sample project, you need to download it from the Repository using the Suite Uploader and then import it using NetBeans.
 To Import the Sample Project
To Import the Sample Project
Before You Begin
Make sure the required Message Libraries are installed. In addition to the HL7 OTD Library and HL7 OTD Generic Library, which are installed with the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter by default, you need to install the following two libraries:
-
HL7V32006PatientAdmin.sar
-
HL7V32006TransInfra.sar
-
If the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter is not already installed, install it now as described in Installing the TCP/IP HL7 Adapter and Installing the TCP/IP Adapter in the NetBeans IDE.
-
Download the schematron sample project and the HL7 V3 outbound project, as described in Downloading the Sample Projects.
-
Import the project file.
-
On the NetBeans IDE, save all unsaved work.
-
On the NetBeans menu bar, select Tools, point to CAPS Repository, and then select Import Project from the drop-down menu.
A confirmation dialog box appears asking if you need to save any changes.
-
Click Yes to proceed.
The Import Manager appears.
-
Click Browse, navigate to the location of the project ZIP files, and select prjHL7Inbound_WithSchematron.zip.
-
Click Import.
Note –A warning message appears if you already have a project of the same name in the CAPS Repository. Determine whether you want to overwrite the existing project. In some cases the imported file will add files to an existing project. If you do not want to overwrite the existing project, cancel the import and exit the Import Manager. Rename and save the existing project, and attempt the import again.
It may take a few seconds to import the project. When the project is imported, the Import Status dialog box appears.
-
Click OK on the dialog box.
The CAPS Repository is refreshed.
-
Close the Import Manager.
You should now have two new projects in the tree structure of the Projects window.
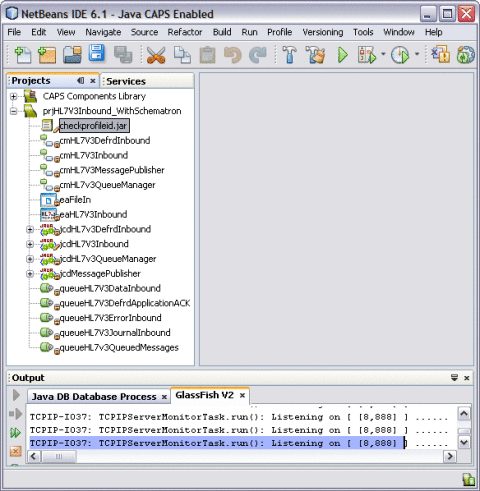
Note –In the current example, the JAR file (checkprofileid.jar) is bundled along with the sample project file imported from Java CAPS Repository, prjHL7V3Inbound_WithSchematron.
-
Checking Out the Project
When you first import a project, all of its components are checked in to version control. This means you cannot edit the project. You need to check the components out first.
 To Check Out the Project
To Check Out the Project
-
In the NetBeans Projects window, right–click prjHL7V3Inbound_WithSchematron .
-
Point to Version Control, and then select Check Out.
-
On the Version Control dialog box, click Recurse Project, and then click Select All.
-
Click Check Out.
Modifying the Connectivity Map
 To Modify the Connectivity Map
To Modify the Connectivity Map
-
On the NetBeans Projects window, double-click cmHL7V3Inbound.
The Connectivity Map appears in the Connectivity Map Editor.
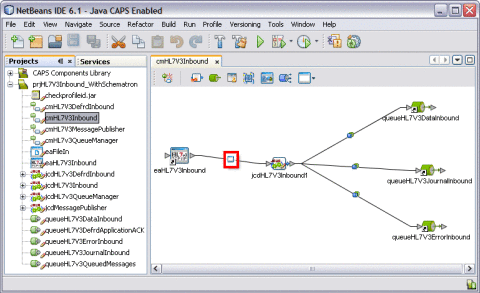
-
Double-click the Adapter icon on the connecting line between the eaHL7V3Inbound External System and the jcdHL7V3Inbound1 service.
The Properties Editor appears.
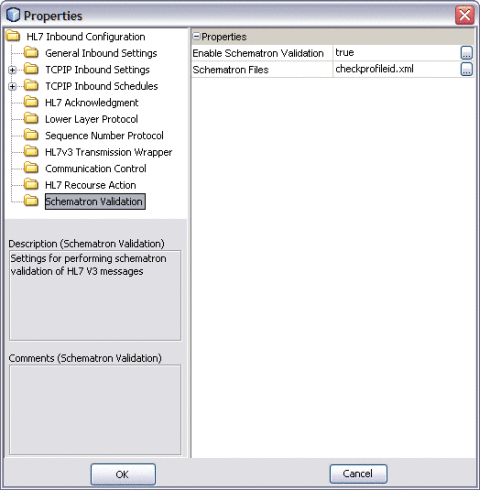
-
Select Schematron Validation in the left panel.
-
Modify the properties as follows:
-
Enable Schematron Validation: true
-
Schematron Files: Provide a list of Schematron files. Use a comma to separate multiple files.
-
Modifying the Java Collaboration Definition
The JCD is edited as described in the steps below.
 Modify the Collaboration Editor
Modify the Collaboration Editor
-
In the NetBeans Projects window, double-click jcdHL7V3Inbound.
The Collaboration appears in the Java Collaboration Editor.
-
Modify the Collaboration rules as needed.
The following sections describe parts of the JCD that define schematron validation.
Schematron Validation Inside the JCD
The schematron validation API is invoked from the JCD. The JCD follows the standard HL7 V3 validation; the schematron validation API is only invoked if the Enable Schematron Validation property is true. Following is an excerpt from the JCD code that scans the schematron files list and calls the method validateWithSchematron() if schematron validation is enabled.
Excerpt for Beginning Schematron Validation
boolean validated = validateHL7Message( HL7message );
java.util.ArrayList outputList = new java.util.ArrayList();
if (validated) {
boolean schematronValidationEnabled =
input.getHL7v3MessageInfo().getSchematronValidationInfo().
isSchematronValidationEnabled();
log( LOG_LEVEL_INFO, "SchematronEnabled = " + schematronValidationEnabled );
if (schematronValidationEnabled) {
String[] schFiles =
input.getHL7v3MessageInfo().getSchematronValidationInfo().
getSchematronFilesList();
log( LOG_LEVEL_INFO, "schFilesList = " + schFiles );
for (int i = 0; i < schFiles.length; i++) {
log( LOG_LEVEL_INFO, "Adding schematron file for validation = "
+ schFiles[i] );
com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.ValidationOutput output =
validateWithSchematron( "/" + schFiles[i], HL7message );
outputList.add( output );
}
for (int i = 0; i < outputList.size(); i++) {
com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.ValidationOutput output =
(com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.ValidationOutput) outputList.get( i );
if (!output.isValid()) {
validated = false;
schematronValidationError = true;
log( LOG_LEVEL_INFO, "Schematron Validation failed." );
break;
} else {
validated = true;
}
}
|
The above text has been wrapped for display purposes. The images below show the code as it appears in the Collaboration Editor.
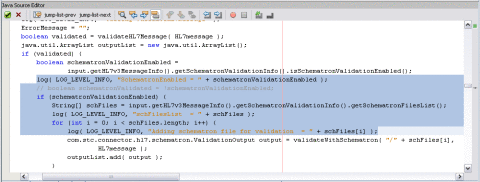
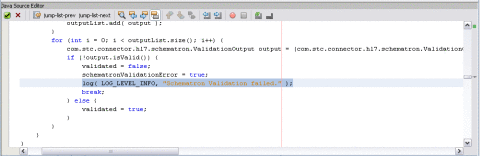
validateWithSchematron() method
The schematron method invokes the schematron API. It reads the schematron files from classpath and constructs a DOM source. The DOM source passes it to obtain the SchematronValidator object. The object invokes the validate() method to pass the hl7payload. The following excerpt from the JCD defines the validation method.
private com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.ValidationOutput
validateWithSchematron( String schematronFile, byte[] hl7payload )
throws Exception
{
com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.SchematronValidatorFactory
factory =com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.SchematronValidatorFactory.
getSchematronValidatorFactory();
log( LOG_LEVEL_INFO, "Schematron URI :" +
this.getClass().getResource( schematronFile ).toString() );
java.io.InputStream in = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream( schematronFile );
java.io.BufferedReader bufReader = new java.io.
BufferedReader( new java.io.InputStreamReader( in ) );
StringBuffer schematronXml = new StringBuffer();
String line = bufReader.readLine();
while (line != null) {
schematronXml.append( line );
line = bufReader.readLine();
}
bufReader.close();
javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory domBuilderFactory =
javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
domBuilderFactory.setNamespaceAware( true );
org.w3c.dom.Document doc = domBuilderFactory.newDocumentBuilder().
parse( new org.xml.sax.InputSource( new java.io.ByteArrayInputStream
(schematronXml.toString().getBytes() ) ) );
javax.xml.transform.dom.DOMSource domSource = new
javax.xml.transform.dom.DOMSource( doc.getDocumentElement() );
com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.SchematronValidator
validator = factory.getDefaultValidator( domSource );
javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamSource dataSrc = new javax.xml.
transform.stream.StreamSource(new java.io.ByteArrayInputStream( hl7payload ) );
com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.ValidationOutput output =
validator.validate( dataSrc );
return output;
}
|
The above text has been wrapped for display purposes. The images below show the code as it appears in the Collaboration Editor.
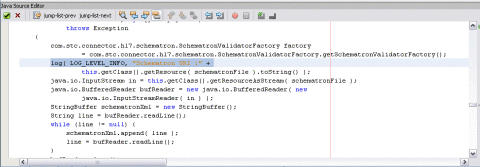
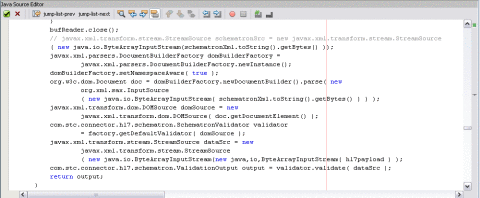
Retrieving the Validation Results
The makeNAK() method retrieves the XML document generated from the schematron validation. The XML document is embedded in the AcknowledgementDetail section of HL7V3 Acknowledgement XML. The following excerpt defines the makeNAK() method.
makeNAK() method
if (schematronValidationError) {
log( LOG_LEVEL_INFO, "Schematron validationOutputList.size="
+ validationOutputList.size());
for (int i = 0; i < validationOutputList.size(); i++) {
com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.ValidationOutput output =
(com.stc.connector.hl7.schematron.ValidationOutput)
validationOutputList.get( i );
String outputStr = output.getOutputAsString();
otd_MCCI_IN000004UV01_1.getAcknowledgement( 0 ).
getAcknowledgementDetail( i ).getTypeCode().setCode( "E" );
otd_MCCI_IN000004UV01_1.getAcknowledgement( 0 ).
getAcknowledgementDetail( i ).getCode().setCode
( "Validation Failure: Schematron Validation Failed" );
otd_MCCI_IN000004UV01_1.getAcknowledgement( 0 ).
getAcknowledgementDetail( i ).getText().setMediaType( "text/xml" );
otd_MCCI_IN000004UV01_1.getAcknowledgement( 0 ).
getAcknowledgementDetail( i ).getText().setX__PCDATA__MX( outputStr );
log( LOG_LEVEL_INFO, "Schematron Validation Output = " + outputStr );
}
}
|
The above text has been wrapped for display purposes. The image below shows the code as it appears in the Collaboration Editor.
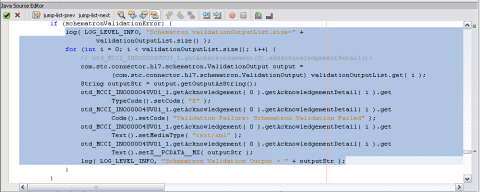
Creating and Importing Sample Files
This section provides sample schematron validation and input files, and also gives instructions on importing the validation file for use in the JCD.
Sample Schematron
Below is a sample schematron validation file that checks for the presence of the profileid field in the PRPA_IN403001UV01 OTD.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<sch:schema xmlns:sch="http://www.ascc.net/xml/schematron">
<sch:ns prefix="hl7v3" uri="urn:hl7-org:v3"/>
<sch:pattern name="Check structure">
<sch:rule context="hl7v3:PRPA_IN403001UV01">
<sch:assert test="count(hl7v3:profileId) = 1">The profileId should
be present. It is missing.</sch:assert>
</sch:rule>
</sch:pattern>
</sch:schema>
|
Sample Input Document
<PRPA_IN403001UV01 xmlns="urn:hl7-org:v3" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="urn:hl7-org:v3 PRPA_IN403001UV01.xsd"> <id root="1.1.2.3.4.6" extension="5929" assigningAuthorityName="Litware Inc."/> <creationTime value="20050303180027"/> <versionCode code="V3PR1"/> <interactionId root="1.1.6.7.8" extension="PRPA_IN403001UV01" assigningAuthorityName="HL7"/> <profileId root="1.1.1.1"/> <processingCode code="D"/> <processingModeCode code="T"/> <acceptAckCode code="AL"/> ... ... ... |
Note –
The above text has been wrapped for display purposes. It contains extra line breaks.
Importing a Schematron XML File
This tutorial includes a JAR file, checkprofileid.jar. which includes the sample schematron validation file described above. Follow this procedure if you want to create your own validation file and package it for the JCD.
 To Import a Schematron XML and Add it to the
JCD
To Import a Schematron XML and Add it to the
JCD
-
Create a JAR file containing the schematron validation file in XML format.
-
Do the following to import the JAR file:
-
Open the Collaboration in the Collaboration Editor.
-
On the Collaboration Editor toolbar, click Add JAR.
-
On the Add/Remove Jar Files dialog box, click Add.
-
Navigate to and select he JAR file to add, and then click Import.
-
On the Add/Remove Jar Files dialog box, click Close.
Creating the Environment
Follow the steps below to create an Environment for the cmHL7V3Inbound Connectivity Map in the schematron sample project.
 To Create an Environment
To Create an Environment
-
On the NetBeans Services window, right-click CAPS Environments, point to New, and then select Environment.
A new environment is created and is added to the CAPS Environment tree.
-
Rename the new environment to envHL7V3Outbound.
-
Right-click envHL7V3Outbound, point to New, and then select Logical Host from the drop-down menu.
It takes few seconds to process the Logical Host into the Environment.
-
Right-click LogicalHost1, point to New, and then select Sun Java System Application Server.
A new application server (SunJavaSystemApplicationServer1) is added to the Environment Explorer tree under LogicalHost1.
-
Right-click LogicalHost1, point to New, and then select Sun JMS IQ Manager.
A new JMS IQ Manager (SunJmsIQMgr1) is added to the Environment tree under LogicalHost1.
-
-
Right-click envHL7V3Outbound, point to New, and then select File External System.
The External System is added to the Environment tree.
-
Right-click envHL7V3Outbound, point to New, and then select HL7V3 External System.
The new External System is added to the Environment tree.
-
On the NetBeans toolbar, click Save All.
Building and Deploying the Sample Project
Once you create the Environment, you need to create a Deployment Profile in order to build and deploy the project.
 To Build and Deploy the Sample Project
To Build and Deploy the Sample Project
-
Create a Deployment Profile.
-
Click Automap.
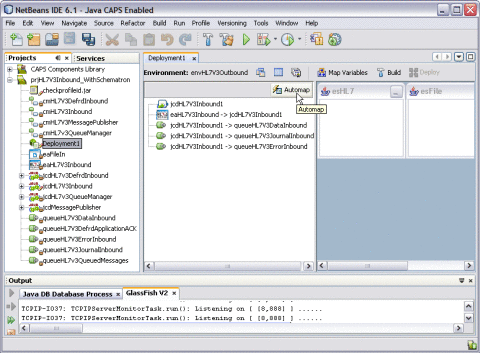
The Automap Results dialog box appears.
-
Click Close.
-
On the NetBeans toolbar, click Save All.
-
On the Deployment Editor toolbar, click Build.
-
When the Build confirmation dialog box appears, click OK.
-
On the Deployment Editor toolbar, click Deploy.
Executing a Sample Project
To run data through the sample project, you need to use an HL7 simulator or HL7 application.
 To Execute the Sample Project
To Execute the Sample Project
-
Create a sample file named PRPA_IN403001UV01.xml.
-
Enter the following text into the file (you can copy and paste this excerpt).
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <PRPA_IN403001UV01 xmlns="urn:hl7-org:v3" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="urn:hl7-org:v3 PRPA_IN403001UV01.xsd"> <id root="1.1.2.3.4.6" extension="5929" assigningAuthorityName="Litware Inc."/> <creationTime value="20050303180027"/> <versionCode code="V3PR1"/> <interactionId root="1.1.6.7.8" extension="PRPA_IN403001UV01" assigningAuthorityName="HL7"/> <!--profileId root="1.1.1.1"/--> <processingCode code="D"/> <processingModeCode code="T"/> <acceptAckCode code="AL"/> <receiver typeCode="RCV"> <device classCode="DEV" determinerCode="INSTANCE"> <id root="1.4.7.8.3"/> </device> </receiver> <sender typeCode="SND"> <device classCode="DEV" determinerCode="INSTANCE"> <id root="1.45.6.7.98"/> </device> </sender> <controlActProcess classCode="CACT" moodCode="EVN"> <subject typeCode="SUBJ" contextConductionInd="false"> <encounterEvent classCode="ENC" moodCode="EVN"> <id root="1.56.3.4.7.5" extension="122345" assigningAuthorityName="Maple Hospital Emergency"/> <code code="EMER" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.5.4"/> <statusCode code="active"/> <subject contextControlCode="OP"> <patient classCode="PAT"> <id root="1.56.3.4.7.9" extension="55321" assigningAuthorityName="Maple Hospital Patients"/> <patientPerson classCode="PSN" determinerCode="INSTANCE"> <name> <given>Rob</given> <given>P</given> <family>Young</family> </name> <administrativeGenderCode code="M" codeSystem="2.16.840.1.113883.5.1"/> <birthTime value="19800309"/> </patientPerson> </patient> </subject> </encounterEvent> </subject> </controlActProcess> </PRPA_IN403001UV01>The above text has been wrapped to fit the page. The following image shows the text in an XML editor.

-
Copy the XML file to a location where the simulator or HL7 application will pick it up.
-
Open the server log file and check the results at the following location:
Drivename:\JavaCAPS6U1\appserver\domains\domian1\logs
This action displays the following message.
Schematron Validation Failed
- © 2010, Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates