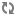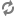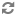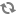This section describes query parameters that you can use to control what data is returned in endpoint responses.
Controlling the set of items returned (limit and offset)
To prevent the response from becoming too large, the number of items returned is limited by default to 250. You can override this value by using the limit query parameter to specify a different number. For example, the following call limits the number of orders returned to 5:
GET /ccadmin/v1/orders?limit=5
To page through the results, you can use the offset parameter. For example, suppose you have returned the first group of 250 orders using this call:
GET /ccadmin/v1/orders
You can return the next group of 250 using the following call:
GET /ccadmin/v1/orders?offset=250
The default value of offset is 0, which means the listing begins with the first item. So setting offset to 250 means the listing begins with the 251st item.
You can use limit and offset together. For example, to return the 401st through 600th order:
GET /ccadmin/v1/orders?limit=200&offset=400
Controlling the set of properties returned (fields and exclude)
Another way to reduce the size of responses is to return only certain properties. For example, products can have a large number of properties, but you may need only certain ones.
You can use the fields parameter to restrict the set of properties returned to only those you explicitly specify. The properties are specified as a comma-separated list. For example, to return only the id and displayName properties of products:
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?fields=items.id,items.displayName
Note that items is the key for the array of objects returned, so top-level properties are referred to as items.propertyName (for example, items.displayName). Properties of nested objects are specified using additional period delimiters. For example:
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?fields=items.listPrices.defaultPriceGroup
You can also use a special field, totalResults, to return the total number of items available (such as the total number of products in the catalog). For example:
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?fields=items.id,totalResults
Note that if a call does not use the fields parameter, totalResults is included in the response by default. For calls that use the fields parameter, totalResults is suppressed unless it is explicitly listed as one of the fields to include.
As an alternative to the fields parameter, which explicitly specifies the properties to include, you can use the exclude parameter to include all properties except the ones specified. For example, to return all of the properties of products except longDescription:
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?exclude=items.longDescription
As with the fields parameter, properties of nested objects can specified for the exclude parameter using additional period delimiters (for example, items.listPrices.defaultPriceGroup).
Controlling the order of items returned (sort)
By default, the items returned are sorted by a predetermined property that depends on the type of item. For example, products are sorted by displayName.
You can use the sort parameter to specify a different property to sort by. For example:
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?sort=id
You can append :asc or :desc to the property name to specify sorting in ascending or descending order. For example, to sort by id descending:
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?sort=id:desc
If you do not specify a sort order, it defaults to ascending.
You can specify multiple properties for sorting. The following call returns results sorted first by listPrice, and then by displayName (for items with identical listPrice values):
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?sort=listPrice,displayName
Note that sorting is done before applying limit and offset values, so it can affect not only the order in which items appear in the response, but also which items are returned. For example, if limit=200 and offset=400, items 401 to 600 are selected from the sorted list of all items. If you change the sorting criteria, items 401 to 600 may not be the same ones as before.
Filtering results (q)
You can use the q query parameter to specify a filter expression for restricting the set of the items returned, based on numeric comparisons or string matching with the values of the item’s properties. The q parameter accepts filter expressions in the format described in Section 3.2.2.2 of the System for Cross-Domain Identity Management (SCIM) specification, which is available at https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-scim-api-12. Note that Commerce Cloud currently supports the q parameter only for product listings.
For example, the following call returns only those products whose orderLimit property has a value of less than 10:
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?q=orderLimit lt 10
Text, date, and time values appearing in filter expressions must be enclosed in quotation marks, with date and time values using ISO-8601 format. (Numeric and boolean values should not be quoted.) For example, the following call returns products whose description property starts with pa:
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?q=description sw "pa"
The operators are case-insensitive, as are strings used for matching. So, for example, the following calls return identical results:
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?q=displayName co "shirt"
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?q=displayName CO "sHIrt"
Note that filter expressions must be URL encoded, so you must ensure that characters such as the quotation mark (") are escaped properly.
SCIM also supports the logical operators AND, OR, and NOT. For example, the following call returns products whose orderLimit property has a value between 5 and 10:
GET /ccadmin/v1/products?q=orderLimit gt 5 and orderLimit lt 10
Not all product properties can be used in filter expressions. The following are some limitations you should be aware of:
You can use only top-level properties of products in filter expressions. You cannot include properties of subobjects such as child SKUs.
You can use a property in filter expressions only if it is returned by the endpoint you are calling. For example, if a specific product property is not returned by the
GET/ccadmin/v1/productsendpoint, then the property cannot be used with theqparameter for that endpoint. Note, however, that theGET/ccadmin/v1/productsandGET/ccstore/v1/productsendpoints do not return identical sets of properties, so a property that is not returned by one of these endpoints may be returned by the other.If you have multiple custom product types, and two or more types have a custom property with the same name, this property cannot be used in filter expressions. For example, if you have two custom product types, Shoes and Hats, and each has a custom property called
material, then you cannot usematerialin filter expressions. If only one custom product type has amaterialproperty, you can use the property in filter expressions.