| Oracle® Communications EAGLE Database Administration - GTT User's Guide Release 46.8 F11880-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Communications EAGLE Database Administration - GTT User's Guide Release 46.8 F11880-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This procedure is used to add a global title translation
to the database using the
ent-gtt command.
The
ent-gtt command uses these parameters.
:gta – Global title
start address – along with the
egta parameter, identifies all valid
global titles for the given translation type to translate to the given
pc or
ssn parameters. These are the non-SS7
addresses transmitted to the STP for translation.
:type/typea/typei/typeis/typen/typens/typen24 – The
translation type and network type of the translation type that is being
assigned to the global title translation. The value of this parameter is shown
in the
rtrv-tt output and provisioned in the
Adding a Translation Type
procedure.
:ttn - the translation
type name associated with the
:type/typea/typei/typeis/typen/typens/typen24 parameter
value. The value of this parameter is shown in the rtrv-tt output and
provisioned in the
Adding a Translation Type
procedure.
:egta – Global title
end address – along with the
gta parameter, identifies all valid
global titles for the given translation type to translate to the given
pc or
ssn parameters. These are the non-SS7
addresses transmitted to the STP for translation.
:force – the mated
application override. Is the global title translation to be entered without a
mated application in the database?
:xlat – Translate
indicator – defines the type of global title translation that is to be
performed.
:ri – Route indicator –
indicates whether a subsequent global title translation is required.
:pc/pca/pci/pcn/pcn24 –
The point code of the signaling point that is to receive the message.
Note:
See Chapter 2, "Configuring Destination Tables," in Database Administration - SS7 User's Guide for a definition of the point code types that are used on the EAGLE and for a definition of the different formats that can be used for ITU national point codes.:ssn – Subsystem number
– identifies the subsystem address that is to receive the message.
:gtmodid - the name of
the GT modification identifier shown in the
rtrv-gtmod output and provisioned in
the
Adding Global Title Modification Information
procedure. The GT modification identifier contains the information to modify
the numbering plan, nature of address indicator, and the prefix or suffix
digits in the called party address or calling party address portion of outbound
MSUs.
:mrnset – The MRN set
ID, shown in the
rtrv-mrn command. This parameter can
be specified only, and must be specified, if the Flexible GTT Load Sharing
feature is enabled and if the
ri=gt parameter is specified for the
global title translation. If the Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature is enabled,
the point code specified for the global title translation must be assigned to
the MRN set specified by this parameter. The status of the Flexible GTT Load
Sharing feature is shown in the
rtrv-ctrl-feat output. To enable the
Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature, perform the
Activating the Flexible GTT Load Sharing Feature
procedure.
:mapset – The MAP set
ID, shown in the
rtrv-map command. This parameter can
be specified only, and must be specified, if the Flexible GTT Load Sharing
feature is enabled and if the
ri=ssn parameter is specified for the
global title translation. If the Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature is enabled,
the point code and SSN specified for the global title translation must be
assigned to the MAP set specified by this parameter. The status of the Flexible
GTT Load Sharing feature is shown in the
rtrv-ctrl-feat output. To enable the
Flexible GTT Load Sharing feature, perform the
Activating the Flexible GTT Load Sharing Feature
procedure.
:loopset - The value of
this parameter is the name of the loopset that is assigned to the GTT. This
parameter can be specified only if the SCCP Loop Detection feature is enabled.
Enter the
rtrv-loopset command to verify that
the SCCP Loop Detection feature is enabled. Perform the
Activating the SCCP Loop Detection Feature
procedure, if necessary. By default, the value of the
loopset parameter is “none” because no
loopset is assigned to the GTT.
:cggtmod - The calling
party GT modification indicator. This parameter specifies whether or not
calling party global title modification is required. The values for this
parameter are
yes (calling party global title
modification is required) or
no (calling party global title
modification is not required). This parameter can be specified only if the
AMGTT or AMGTT CgPA Upgrade feature is enabled. Enter the
rtrv-ctrl-feat command to verify that
either the AMGTT or AMGTT CgPA Upgrade feature is enabled. If the AMGTT or
AMGTT CgPA Upgrade feature is not enabled, perform the
Activating the Advanced GT Modification Feature
procedure to enable the required feature.
Note:
The command line on the terminal can contain up to 150 characters. If the parameters and values specified with theent-gtt command are too long to fit on
the
ent-gtt command line, perform the
Changing a Global Title Translation
section to complete adding the GTT entry.
The
XLAT parameter does not have a SEAS
equivalent. When global title translations are configured at the SEAS
interface, the values for the SEAS parameters
RI,
DPC, and
SSN, all mandatory parameters for the
SEAS
ADD-GTT and
CHG-GTT commands, are converted to the
EAGLE parameters and values shown in the
Table 3-3
procedure.
Table 3-3 SEAS and Global Title Translation Parameter Conversion
| SEAS GTT Parameters | GTT Parameters | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RI | DPC | SSN | XLAT | RI | PC/PCA | SSN |
| G | xxx-xxx-xxx | 000 | DPC | GT | xxx-xxx-xxx | Not Specified |
| D | xxx-xxx-xxx | 002-255 | DPCSSN | SSN | xxx-xxx-xxx | 002-255 |
| G | xxx-xxx-xxx | 002-255 | DPCSSN | GT | xxx-xxx-xxx | 002-255 |
| D | xxx-xxx-xxx | 000 | DPC | SSN | xxx-xxx-xxx | Not Specified |
|
Notes:
|
||||||
The global title translation data cannot be added to the database if the translation type is defined as an alias and if the global title translation data is already assigned to that translation type.
If the translate indicator is equal to
dpc (xlat=dpc) and the routing indicator is equal to
ssn (ri=ssn), and the
force=yes parameter is not specified,
the point code specified in the
ent-gtt command must be defined in the
database as a mated application. Verify this by entering the
rtrv-map command. If this point code
is not defined as a mated application, perform one of these procedures to add
the point code and subsystem number to the database as a mated application:
The point code and subsystem number do not have to be in
the mated application table when the
ent-gtt command is executed if these
parameters are specified with the
ent-gtt command.
ri=gt
xlat=dpcssn and
ri=ssn
If the point code and subsystem, if applicable, are not
in the mated application table when either of these parameters are specified
with the
ent-gtt command, the EAGLE creates a
solitary mated application in the mated application table using the point code
and subsystem values specified in the
ent-gtt command.
If the
xlat=dpcssn parameter is specified,
the
ssn parameter must be specified.
Otherwise, the
ssn parameter cannot be specified.
If a point code is the STP’s True PC, then the value of
the
XLAT parameter must be set to
DPCSSN and the value of the
RI parameter must be set to
SSN. If the
SSN parameter is specified and a point
code is the STP’s True PC, then the subsystem number specified must exist in
the SS-APPL table. This can be verified with the
rtrv-ss-appl command. To execute the
rtrv-ss-appl command, one or more
features shown in
Table 3-4
must be enabled, and turned on if necessary. The
rtrv-ctrl-feat output shows the
required status of the features.
Table 3-4 Feature Status
| Feature | Feature's Status | Entry Displayed in the rtrv-ctrl-feat Output |
|---|---|---|
| LNP | Enabled | The entry LNP TNs with a quantity greater than zero (0) |
| EIR | Enabled and Turned On | EIR |
| INP | Enabled and Turned On | INP |
| ANSI-41 INP Query | Enabled and Turned On | ANSI-41 INP Query |
| V-Flex | Enabled and Turned On | VFLEX |
| ATINP | Enabled | ATINP |
| ANSI41 AIQ | Enabled | ANSI41 AIQ |
The point code specified in the
ent-gtt command must be defined in the
routing table or be the EAGLE’s point code. For ANSI point codes (pc/pca), the point
code specified in the
ent-gtt command, must be a full point
code. That point code can be defined as a full point code in the destination
point code table, or can be a member of a cluster point code defined in the
destination point code table. Cluster point codes or a network routing point
codes cannot be specified with this command. Enter the
rtrv-rte command to verify that the
point code is in the routing table. If the point code is not defined as a
route, perform one of the Adding a Route procedures in
Database Administration – SS7 User's Guide
to define the point code as a route.
If the EAGLE’s point code is specified with the
ent-gtt command, then the
xlat=dpcssn and
ri=ssn parameters must be specified.
The EAGLE’s point code is shown in the
PCA,
PCI,
PCN, or
PCN24 fields of the
rtrv-sid command output.
If the
xlat=dpcngt parameter is specified,
the
ngt parameter and the
ri=gt parameters must be specified.
An ANSI point code or ITU international point code containing all zeros is not a valid point code and cannot be entered into the database. An ITU national point code containing all zeros is a valid point code and can be entered into the database.
Either the
type parameter or the
ttn parameter must be specified.
If the
type parameter is specified, the
translation type must be in the database. This can be verified with the
rtrv-tt command.
If the
type parameter is not specified, the
translation type name must be assigned to a translation type in the database.
This can be verified with the
rtrv-tt command.
If the
type and
ttn parameters are specified, the
specified translation type must be in the database and the specified
translation type name must be assigned to the translation type.
If the translation type is ANSI (type or
typea), the
pc type must be ANSI (pc or
pca). If the translation type is one
of the ITU types (typei,
typen,typeis,
typens, or
typen24) the
pc type may be either of the ITU types
(pci,
pcn, or
pcn24). If the ANSI/ITU SCCP
Conversion feature is enabled, the domain (ANSI or ITU) of the translation type
and point code do not have to be the same.
The end global title address (egta) must be greater than or equal to the start global
title address (gta) and its length must be
equal to the start global title address.
If the Variable-Length Global Title Translation (VGTT)
feature is off, shown the entry
VGTT = off, the global title address
length must be equal to the number of digits specified by the given translation
type. The length of the global title address can be verified with the
rtrv-tt command.
If the Variable-Length Global Title Translation (VGTT)
feature is on, shown the entry
VGTT = on, up to 10 different length
global title addresses can be assigned to a translation type. If the Activating
the Support for 16 GTT Lengths in VGTT feature is enabled and on, shown the
entry
VGTT with 16 GTT lengths in the
rtrv-ctrl-feat output, up to 16
different length global title addresses can be assigned to a translation type.
The length of the global title address is only limited by the range of values
for the
gta and
egta parameters, one to 21 digits, and
by the global title addresses already assigned to the translation type. The
ndgt parameter of the
ent-tt command has no effect on the
length of the global title address. As global title addresses of different
lengths are assigned to a specific translation type, these lengths are
displayed in the
NDGT field of the
rtrv-tt command output.
If the translation type has maximum number of different
length global title addresses assigned to it, and another global title address
is specified for the translation type, the length of the global title address
being added to the translation type must be the same as one of the lengths
already assigned to the translation type. If the length of the global title
address does not match one of the lengths already assigned to the translation
type, the
ent-gtt command is rejected with this
message.
E4007 Cmd Rej: Exceeding max GTA
Lengths supported per TT
If the translation type has less than the maximum number of different length global title addresses assigned to it, and another global title address is specified for the translation type, the length of the global title address can be from one to 21 digits and does not have to match the length of the other global title addresses assigned to the translation type.
Refer to Variable-length Global Title Translation Feature for more information about this feature.
The range, as specified by the start and end global
title addresses, cannot already exist in the global title translation data for
the specified translation type. If the ranges overlap, the range of global
title addresses cannot be split and the
ent-gtt command is rejected with this
message.
E2401 Cmd Rej:GTA range overlaps a current
range. GTA range overlaps a current range
Along with error message 2401, a list of the overlapped global title addresses is displayed as shown in the following example.
rlghncxa03w 07-02-24 08:29:15 GMT EAGLE5 35.6.0 The following GTA ranges overlap the input GTA range START GTA END GTA 8005550000 8005551999 8005552000 8005553999 8005554000 8005555999 ENT-GTT: MASP A - Command Aborted
Table 3-5 shows the valid combinations for the parameters. All other combinations are rejected.
Table 3-5 Valid Parameter Combinations for the
ent-gtt Routing Parameters
| XLAT Value | RI Value | Routing Action | SSN Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| DPC | GT | Translate DPC only and route on GT | Cannot specify |
| DPC | SSN | Translate DPC only and route on SSN | Cannot specify |
| DPCSSN | GT | Translate DPC and SSN and route on GT | Must specify |
| DPCSSN | SSN | Translate DPC and SSN and route on SSN | Must specify |
| DPCNGT | GT | Translate New GT and route on GT | Cannot specify |
The EAGLE can contain 269,999, 400,000, or 1,000,000 global title translations. The system default is 269,999 global title translations. This quantity can be increased to 400,000 by enabling the feature access key for part number 893-0061-01, or to 1,000,000 by enabling the feature access key for part number 893-0061-10. For more information on enabling these feature access keys, perform the Enabling the XGTT Table Expansion Feature procedure.
Canceling the
RTRV-GTT Command
Because the
rtrv-gtt command used in this
procedure can output information for a long period of time, the
rtrv-gtt command can be canceled and
the output to the terminal stopped. There are three ways that the
rtrv-gtt command can be canceled.
F9 function key on the keyboard at
the terminal where the
rtrv-gtt command was entered.
canc-cmd without the
trm parameter at the terminal where
the
rtrv-gtt command was entered.
canc-cmd:trm=<xx>, where
<xx> is the terminal where the
rtrv-gtt command was entered, from
another terminal other that the terminal where the
rtrv-gtt command was entered. To
enter the
canc-cmd:trm=<xx> command, the
terminal must allow Security Administration commands to be entered from it and
the user must be allowed to enter Security Administration commands. The
terminal’s permissions can be verified with the
rtrv-secu-trm command. The user’s
permissions can be verified with the
rtrv-user or
rtrv-secu-user commands.
For more information about the
canc-cmd command, go to
Commands User's Guide.
Figure 3-11 Add a Global Title Translation - Sheet 1 of 10
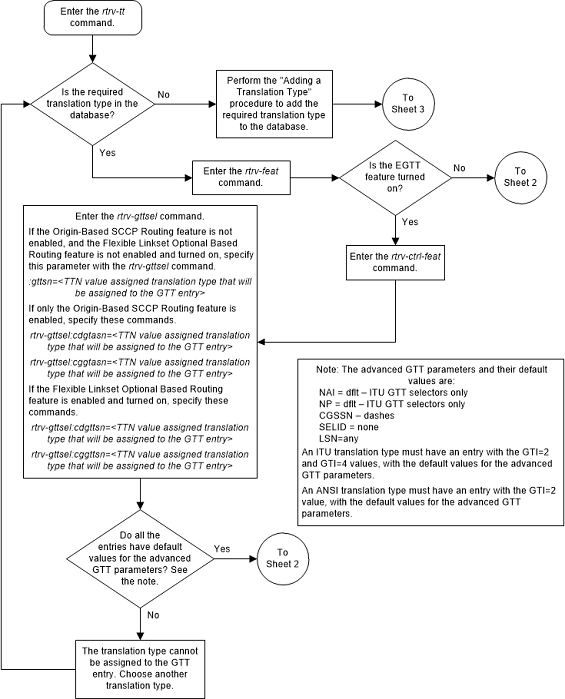
Figure 3-12 Add a Global Title Translation - Sheet 2 of 10
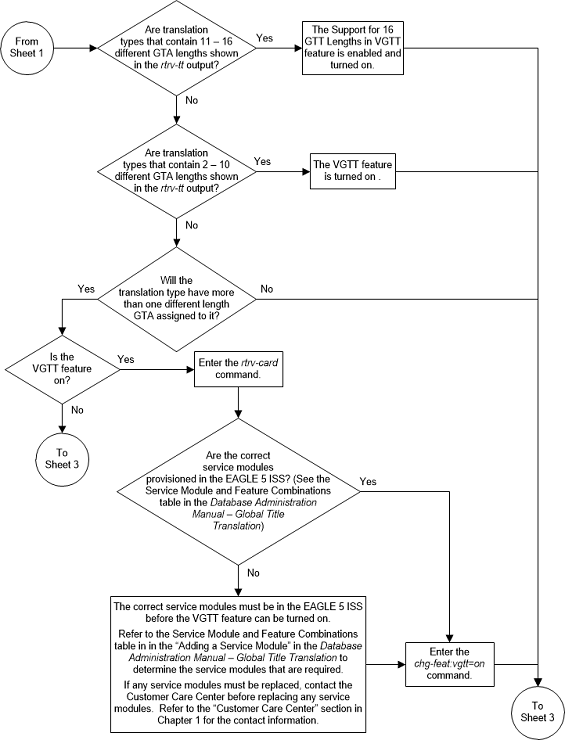
Figure 3-13 Add a Global Title Translation - Sheet 3 of 10
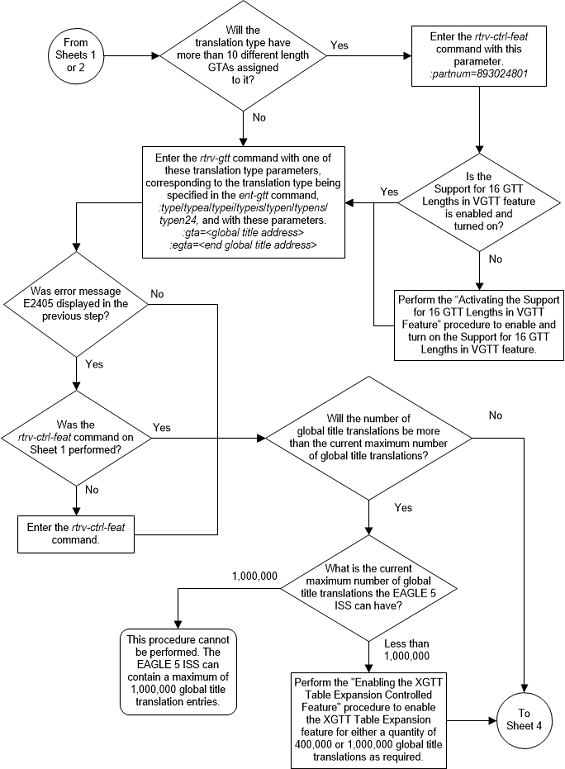
Figure 3-14 Add a Global Title Translation - Sheet 4 of 10
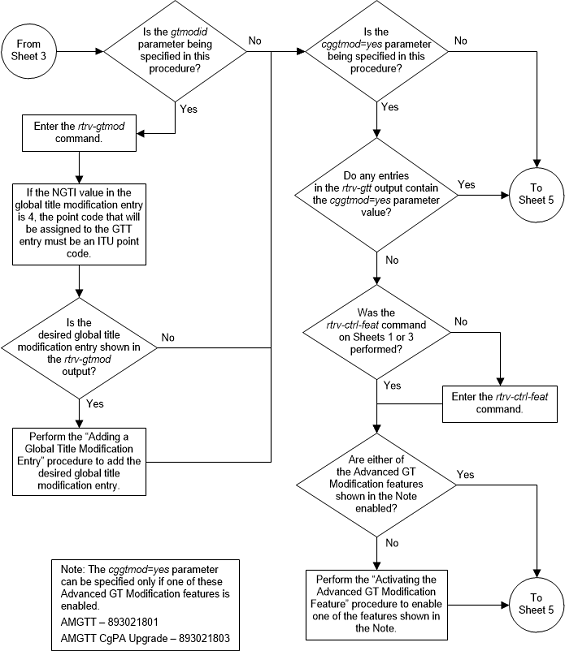
Figure 3-15 Add a Global Title Translation - Sheet 5 of 10
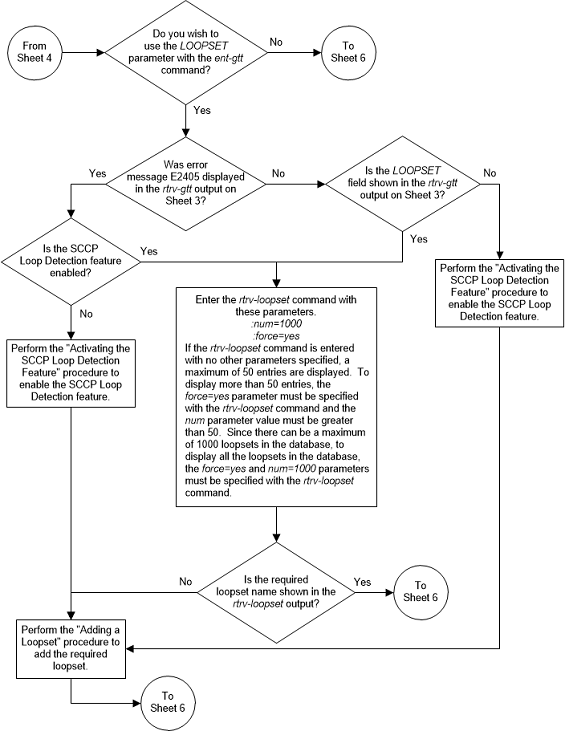
Figure 3-16 Add a Global Title Translation - Sheet 6 of 10
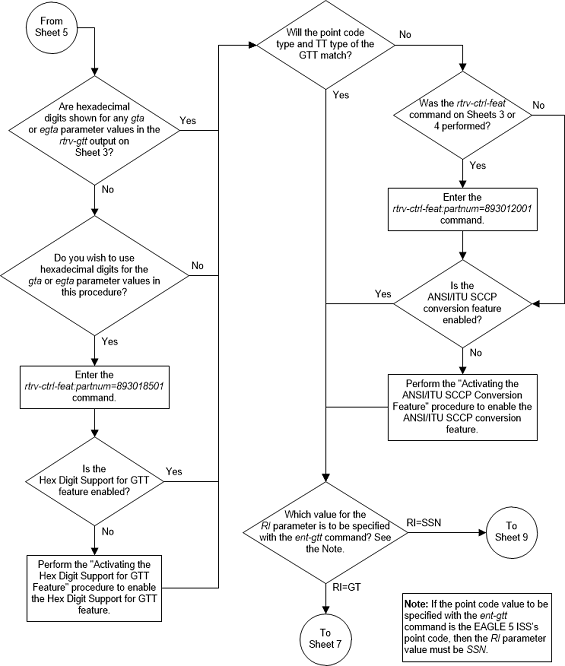
Figure 3-17 Add a Global Title Translation - Sheet 7 of 10
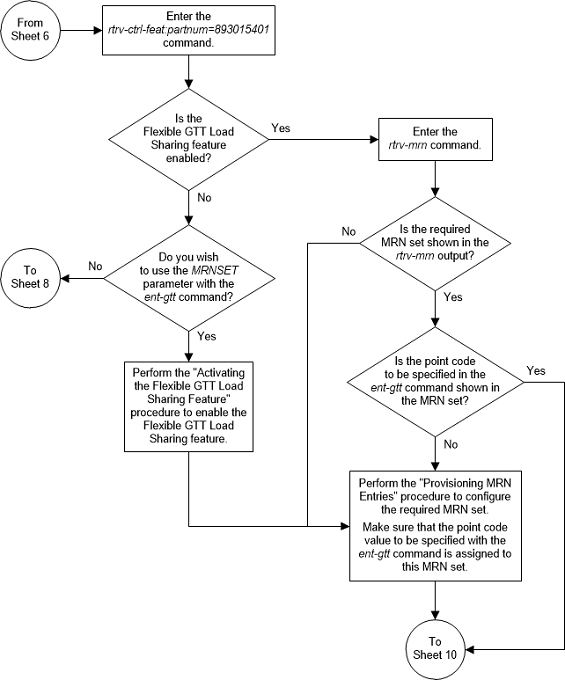
Figure 3-18 Add a Global Title Translation - Sheet 8 of 10
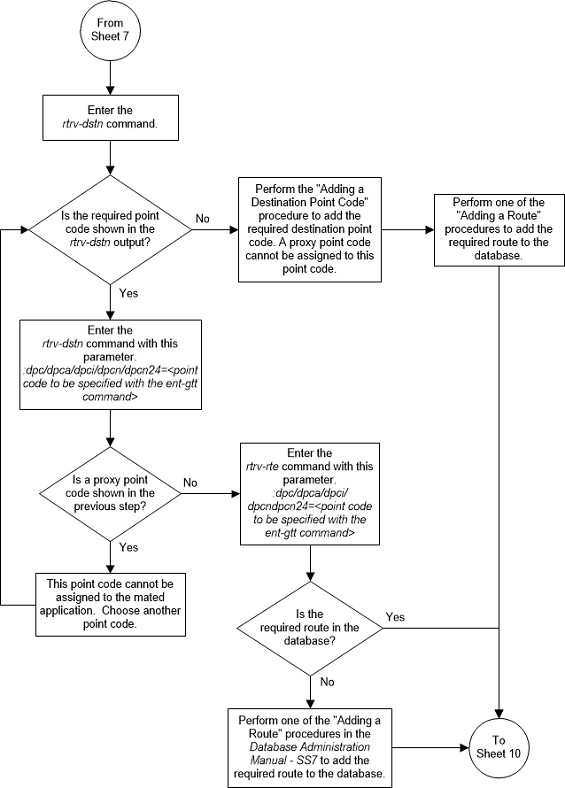
Figure 3-19 Add a Global Title Translation - Sheet 9 of 10
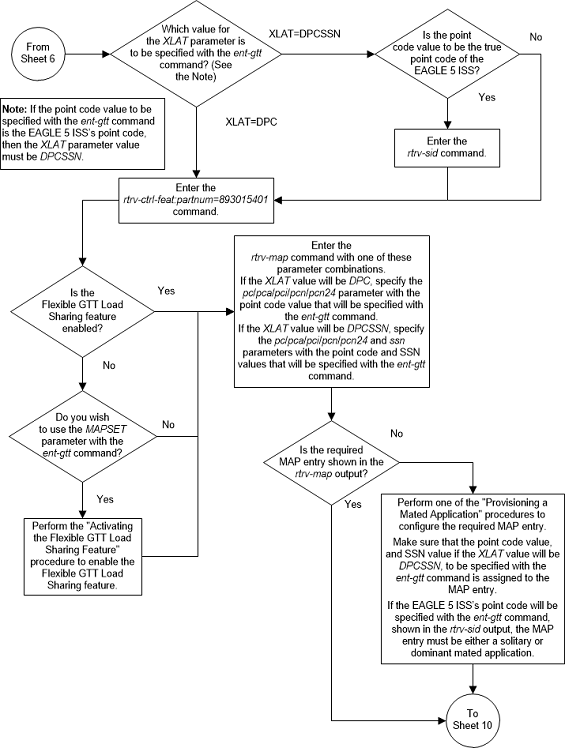
Figure 3-20 Add a Global Title Translation - Sheet 10 of 10
