Use Case: Configuring a Private Virtual Network
This use case shows how to create a private virtual network and enable it to send network traffic outside the system.
This use case is based on the configuration shown in the following figure.
Figure 6 Use Case: Private Virtual Network Setup
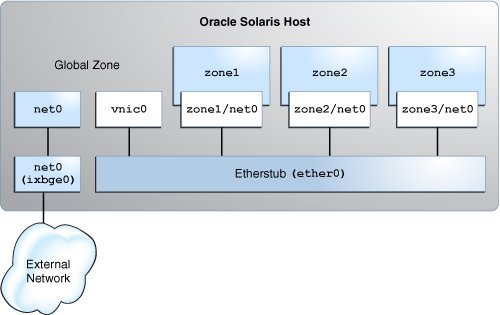
The configuration on the Oracle Solaris host is as follows:
-
The primary interface of the global zone is net0.
-
The zones, zone1, zone2, and zone3, are configured with the VNIC anet resources and the etherstub ether0 is set as the lower link for the zones.
-
The VNIC vnic0 is configured over the etherstub ether0.
This use case is based on the following assumptions:
-
The primary interface, net0, is configured for the system with the IP address 192.0.2.20/27 and the default router IP address 192.0.2.1/27.
-
The first zone, zone1, is created as a new zone. The second zone zone2 already exists on the system and needs to be reconfigured with an anet resource.
-
The third zone, zone3, is reconfigured by using Live Zone Reconfiguration. For more information, see Chapter 6, Live Zone Reconfiguration in Creating and Using Oracle Solaris Zones.
The following table shows the IP addresses that are configured for the zones and their respective default routers in the private virtual network setup.
|