The LDAP RBAC filter combines Local Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) with Role-Based
Access Control (RBAC). This filter enables you to authorize a backend service based on user roles stored
using LDAP. You can use the LDAP RBAC filter to read an attribute from LDAP, and compare
it against some known values (for example, if role contains engineering, authorize
the user). This filter combines functionality available in the Retrieve from Directory Server
and Compare Attribute filters.
The LDAP RBAC filter enables you to define LDAP connection and search settings, and to configure how specified message attributes are processed. This filter also enables you to configure optional settings such as results caching and actions to take if a returned attribute is multi-valued.
You must configure the following general setting:
Name:
Enter an appropriate name for this filter.
You must configure the following fields on the Settings tab:
Connection:
Click the button on the right to select your pre-configured LDAP directory server
(for example, openldap.qa.vordel.com). For details on how to configure
LDAP servers, see Configure LDAP directories.
Search Base:
Enter the Distinguished Name (DN) to use as the base from which the search starts (for
example, o=Vordel Ltd.,l=Dublin 4,st=Dublin,C=IE).
Filter:
Enter the search filter to use. For example:
(&(objectclass=inetOrgPerson)(cn=${authentication.subject.id}))
Scope:
Select one of the following search scopes from the list.
-
Object: Searches on the base DN only (compare)
-
One Level: Searches the direct children of the base DN
-
Subtree: Searches the base DN and all its descendants
Defaults to Subtree.
Attribute validation rules:
When the search completes, the attributes returned in the results are processed by the rules
in the Attribute validation rules table. This processing is the same as the
Compare Attribute filter. You can logically AND and OR
rules together in the Filter will pass if list by selecting all
or one.
For example, if Filter will pass if is set to all, and Rule A, Rule B, and Rule C all evaluate to true, the filter passes. However, if Rule A evaluates to false, the filter fails. If the Filter will pass is set to one, and Rule A and Rule B evaluate to false, but Rule C evaluates to true, the filter passes. However, if Rule C evaluates to false, the filter fails.
Select all or one of the specified conditions to apply. Click the Add button at the bottom right to specify a rule condition. In the Attribute filter rule dialog, perform the following steps:
-
Enter a message attribute name in the LDAP attribute named field on the left (for example,
memberormail). -
Select one of the following rule conditions from the drop-down list:
-
contains -
doesn't contain -
doesn't match regular expression -
ends with -
is -
is not -
matches regular expression -
starts with
-
-
Enter a value to compare with in the text box on the right (for example,
POST). Alternatively, you can enter a selector that is expanded at runtime (for example,${http.request.uri}). For more details on selectors, see Select configuration values at runtime. -
Click OK.
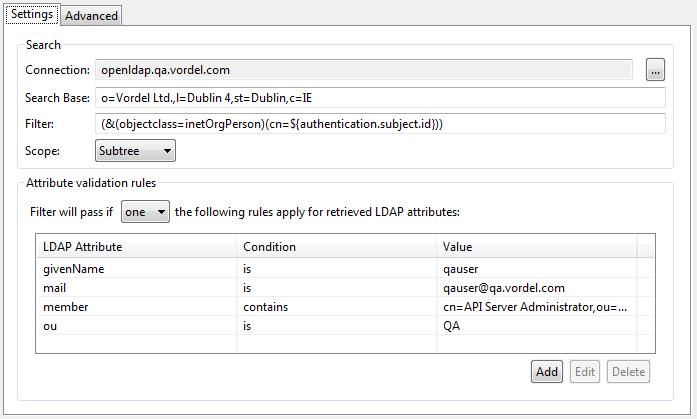
The following screen shows some example search settings and attribute validation rules:
![[Tip]](../common_oracle/images/admon/tip.png) |
Tip |
|---|---|
|
When using this filter to determine if a user is a member of a
Because each attribute is not checked individually, you must create the regular expression string
appropriately. For example, an expression such as |
You can configure the following optional settings on the Advanced tab:
Cache settings:
Select whether to cache the LDAP search results. This setting is selected by default.
Store results in the cache:
Click the button on the right to select the pre-configured cache in which to store results. For more details, see Global caches. Select one of the following settings:
-
Use the LDAP search filter as cache key: Uses the LDAP search filter configured on the Settings tab as the cache key.
-
Or use the following value as the cache key: Enter a specific value for the cache key.
If returned attribute contains multiple values:
Select one of the following settings:
-
Concatenate values with the following: Enter the character used to concatenate multiple attribute values. This setting is selected as a comma by default.
-
Use value at index: Enter the index number of the attribute value to use. Defaults to
0.