Contents
The eXtensible Access Control Markup Language (XACML) Policy Enforcement Point
(PEP) filter enables you to configure the API Gateway to act as a PEP. The
API Gateway intercepts a user request to a resource, and enforces the decision
from the Policy Decision Point (PDP). The API Gateway queries the PDP to see if the
user has access to the resource, and depending on the PDP response, allows the
filter to pass or fail. Possible PDP responses include Permit,
Deny, NotApplicable, and Indeterminate.
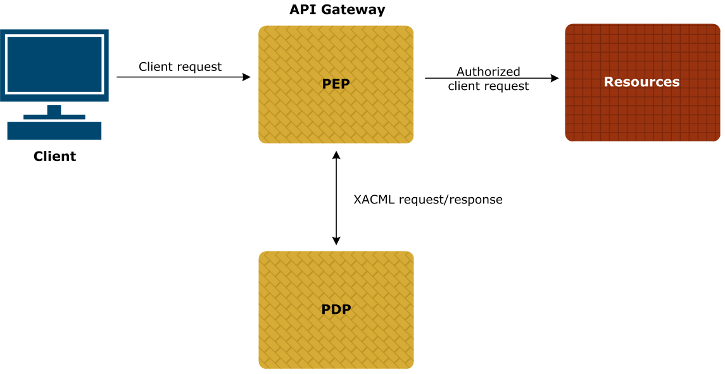
Workflow
In more detail, when the XACML PEP filter is configured in the API Gateway, the workflow is as follows:
-
The client sends a request for the resource to the XACML PEP filter.
-
The PEP filter stores the original client request, and generates the XACML request.
-
The PEP filter delegates message-level security to the polices configured on the XACML tab.
-
The PEP filter routes the XACML request to the PDP using details configured on the Routing tab.
-
The PDP decides if access should be granted, and sends the XACML response back to the API Gateway.
-
The PEP filter validates the response from the PDP.
-
By default, if the response is
Permit, the PEP filter passes, and the original client request for the resource is authorized, and the policy flow continues on the success path.
For more details on XACML, see the XACML specification at:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/xacml/2.0/access_control-xacml-2.0-core-spec-os.pdf
The following example XACML request is used to illustrate the XACML request configuration settings explained in this topic:
<Request xmlns="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:2.0:context:schema:os"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<Subject>
<Attribute AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject:subject-id"
DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">
<AttributeValue>admin</AttributeValue>
</Attribute>
<Attribute AttributeId=”department" DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/
XMLSchema#string">
<AttributeValue>sysadmin</AttributeValue>
</Attribute>
</Subject>
<Resource>
<Attribute AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:resource:resource-id"
DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">
<AttributeValue>http://localhost:8280/services/echo/echoString</AttributeValue>
</Attribute>
</Resource>
<Action>
<Attribute AttributeId="urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:action:action-id"
DataType="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string">
<AttributeValue>read</AttributeValue>
</Attribute>
</Action>
<Environment/>
</Request>
In the XACML PEP filter window, configure the following general field:
Name:
Enter an appropriate name for this filter.
The XACML tab specifies configuration settings for the generated XACML request. Configure the following fields on this tab:
XACML Version:
Select the XACML version from the list. Defaults to XACML2_0.
Create XACML Request Assertion with the following attributes:
Click the Add button on the following tabs to add attributes to the XACML request:
| Subject |
Represents the entity making the access request (wants access to the resource). The
Subject element can contain multiple Attribute elements
used to identify the Subject. Each Attribute element has
two attributes: AttributeId and DataType. You can define
your own AttributeId or use those provided by the XACML specification.
For more details on adding attributes, see the next subsection.
|
| Resource |
Defines the data, service, or system component that the Subject wants to access.
The Resource element contains one or more attributes of the resource to which
subjects request access. There can be only one Resource element per XACML request.
A specific Resource is identified by the Attribute child element.
In the the section called “Example XACML request”, the
Subject wants to access the following Resource:
http://localhost:8280/services/echo/echoString.
|
| Action |
Contains one or more attributes of the action that subjects wish to perform on the
resource. There can be only one Action element per XACML request. A
specific Action is identified by the Attribute child element.
In the the section called “Example XACML request”,
the Subject wants read access the following Resource:
http://localhost:8280/services/echo/echoString.
|
| Environment |
A more complex request context may contain some attributes not associated with the
Subject, Resource, or Action. These are placed
in an optional Environment element after the Action element.
|
When you click the Add button on each tab, the XACML dialog is displayed to enable you to add attributes. Complete the following fields on this dialog:
| Attribute ID |
Enter a custom AttributeId or select one provided by the XACML
specification from the list. For example, the XACML special identifiers defined
for the Subject include the following:
urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject:
In the the section called “Example XACML request”,
the first attribute under the Subject element uses the
urn:oasis:names:tc:xacml:1.0:subject:subject-id identifier. The next
is a custom department attribute. This can be any custom attribute for
example, mail, givenName, or accessList),
which is identified by the XACML policy defined where this request is evaluated.
|
| Value(s) | Click the Add button to add an attribute value. Enter the value in the Add dialog, and click OK. You can add multiple values for a single attribute. |
| Type |
Select the type of data that the AttributeValue element should contain
from the list. For example, the set of data types defined in XACML includes the
following:
http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string
In the the section called “Example XACML request”,
the Attributes are of type http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema#string.
|
| Issuer | Specify an optional issuer for the attribute. For example, this may be a Distinguished Name, or some other identifier agreed with the issuer. |
AuthzDecisionQuery Settings
This section enables you to configure settings for the Authorization Decision Query, which is sent in the XACML request to the PDP. Complete the following fields in this group:
| Decision based on external XACML attributes |
If this is selected, the authorization decision must be made based only on the
information contained in the XACML Authz Decision Query, and external XACML attributes
must not be used. If this is unselected, the authorization decision can be made based on
XACML attributes not contained in the XACML Authz Decision Query. This is unselected by
default, which is equivalent to the following setting in the XACML Authz Decision Query:
<InputContextOnly value="false">
|
| Return Context |
If this is selected, the PDP must include an xacmlcontext:Request instance
in the XACMLAuthzDecision statement in the XACMLAuthzDecision
response. The xacmlcontext:Request instance must include all attributes
supplied by the PEP in the xacml-samlp:XACMLAuthzDecisionQuery used to make
the authorization decision. If this is unselected, the PDP must not include an
xacmlcontext:Request instance in the XACMLAuthzDecision statement
in the XACMLAuthzDecision response. This is unselected by default, which is
equivalent to the following setting in the XACML request:
<ReturnContext value="false">
|
| Combine Policies |
If this is selected, the PDP must insert all policies passed in the
xacmlsamlp:XACMLAuthzDecisionQuery into the set of policies
or policy sets that define the PDP. If this is unselected, there must be
no more than one xacml:Policy or xacml:PolicySet
passed in the xacml-samlp:XACMLAuthzDecisionQuery. This is
selected by default, which is equivalent to the following setting in the
XACML request:
<CombinePolicies value="true">
|
XACML Message Security
This section enables you to delegate message-level security to the configured custom security polices. Complete the following fields in this group:
| XACML Request Security | Click the browse button, select a policy in the XACML request security policy dialog, and click OK. |
| XACML Response Security | Click the browse button, select a policy in the XACML response security policy dialog, and click OK. |
XACML Response:
Select the Required response decision from the PDP that is required
for this XACML PEP filter to pass. Defaults to Permit.
Possible values are as follows:
-
Permit -
Deny -
Indeterminate -
NotApplicable
The Routing tab enables you to specify configuration settings for routing the XACML request to the PDP. You can specify a direct connection to the PDP using a URL. Alternatively, if the routing behavior is more complex, you can delegate to a custom routing policy, which takes care of the added complexity.
Use the following URL:
To route XACML requests to a URL, select this option, and enter the
URL. You can also specify the URL as a selector so that the URL
is built dynamically at runtime from the specified message attributes.
For example, ${host}:${port}, or
${http.destination.protocol}://${http.destination.host}:${http.destination.port}.
For more details on selectors, see Select configuration values at runtime.
You can configure SSL settings, credential profiles for authentication, and other settings for the direct connection using the tabs in the Connection Details group. For more details, see the Connect to URL topic.
Delegate routing to the following policy:
To use a dedicated routing policy to send XACML requests to the PDP, select this option. Click the browse button next to the Routing Policy field. Select the policy to use to route XACML requests, and click OK.
Configure the following settings on the Advanced tab:
SOAP Settings:
The available SOAP settings are as follows:
| SOAP version required |
Specifies the SOAP version required when creating the XACML request message.
The available options are as follows:
SOAP1_1.
|
| SOAP Operation |
Specifies the SOAP operation name used in the XACML request message.
Defaults to XACMLAuthzDecisionQuery.
|
| Prefix |
Specifies the prefix name used in the XACML request message. Defaults to
xacml-samlp.
|
| Namespace |
Specifies the namespace used in the XACML request message. Defaults to
urn:oasis:xacml:2.0:saml:protocol:schema:os.
|
| SOAP Action |
You can specify an optional SOAPAction field used in the XACML
request header to indicate the intent of the request message.
|
Advanced Settings:
The available advanced settings are as follows:
| Store and restore original message | Specifies whether to store the original client request before generating the XACML request, and then to restore the original client request after access is granted. This option is selected by default. |
| Split subject attributes into individual elements |
Specifies whether to split Subject attributes into individual
elements in the XACML request. This option is not selected by default.
|
| Split resource attributes into individual elements |
Specifies whether to split Resource attributes into individual
elements in the XACML request. This option is not selected by default.
|