9 Introduction: Lifecycle Allocation and Replenishment
Oracle Retail Inventory Planning Optimization Cloud Service-Lifecycle Allocation and Replenishment (IPOCS-Lifecycle Allocation and Replenishment) is an automated allocation and replenishment planning system that constantly monitors inventory conditions and based on these conditions creates point in time replenishment orders or transfers to consumer demand, while considering various constraints. Inventory movement varies from Warehouse to Store, Warehouse to 3rd Party, Customer Order Fulfillment, and Store to Store.
Figure 9-1 Orders and Transfers Overview
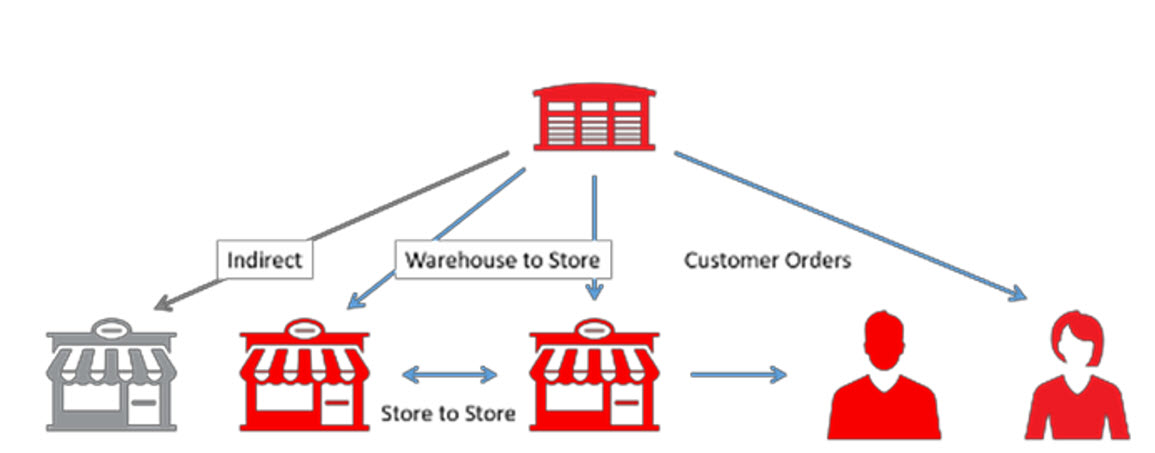
IPOCS-Lifecycle Allocation and Replenishment is appropriate for retailers where:
-
Lead time is longer than the product lifecycle
-
Items have low weekly sales by location
-
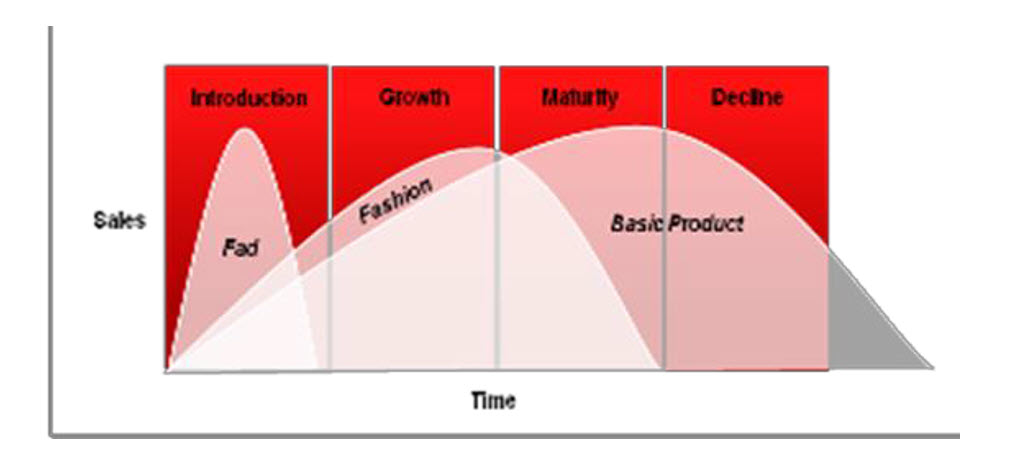
Over the product’s life it goes through a cycle of Initial Allocation (Product Introduction), Replenishment (Product Growth and Maturity) and Final Allocation (Product End of Life/Decline), as depicted in the following image.
Figure 9-2 Lifecycle Overview
This guide contains these chapters and appendices for the IPOCS-Lifecycle Allocation and Replenishment module:
Key Features
-
A pre-defined set of business processes, measures and rules used to support the customer requirements and business process
-
Rule-based replenishment parameters management
-
Assignment of replenishment parameters at item location based on rules
-
User parameters focus by exception only
-
Forecast-based location Target Stock (TS) level calculation
-
TS can be calculated through different methods, ranging from a simple Fixed Units quantity to more sophisticated methods based on demand volatility and service level, to fit different product types and demand behaviors throughout the product lifecycle
-
-
Analysis Capabilities
-
Ability to analyze supply chain performance indicators such as days of stock at any level of the location/Merchandise hierarchies combined with product and/or location attributes
-
-
Product Lifecycle Recognition
-
Lifecycles are used to rule the replenishment approach over time, based on the item lifecycle phase
-
Supported Replenishment
-
Predict how much stores will sell
-
Determine how much inventory stores should carry, for example, store Target Stock (TS) level
-
Predict how much the warehouse will ship to stores
-
Distribution of constrained stock
-
Determine how much inventory the warehouse should carry
-
Generate/Review/Approve orders for all locations
Supported Allocation
-
Post-distribute goods housed in warehouses to stores (end-of-life management).
-
Manage store-to-store transfers when supply is limited or for stock re- balancing across stores.
User Experience and Workflow
The user experience is delivered on our experience inspired Retail Predictive Application Server Cloud Edition (RPASCE) user interface (UI). RPASCE provides end-users with a next-generation cloud-native UI that is purpose-built to accelerate intent into action for planners and forecasters. This includes interactive and visual dashboards to assess priorities, responsive and flexible workspaces to implement decisions and a coordinated exceptions framework that ties business processes all the way from dashboard to mobile phone.