|
|
|
|
|
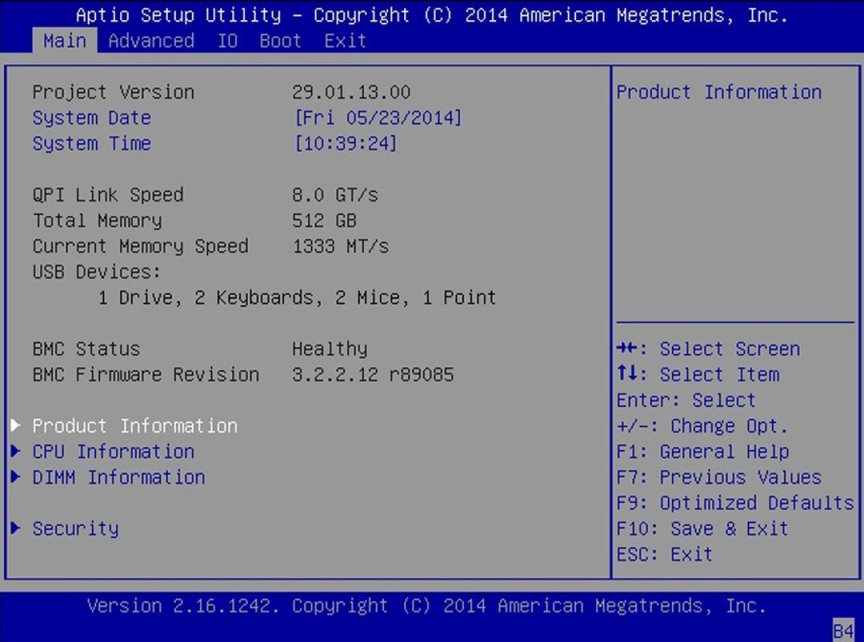
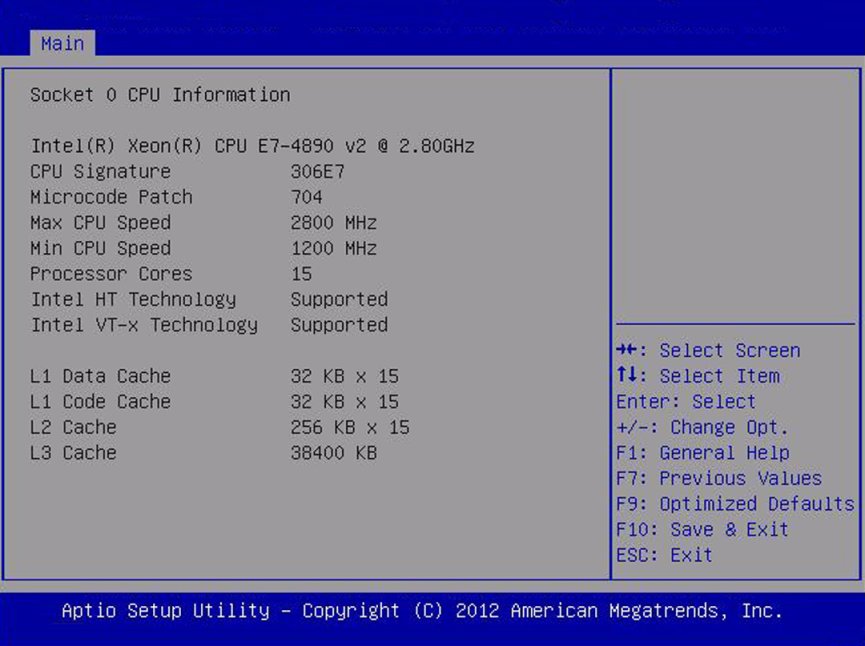
Processors
|
|
|
Enable or disable processor (CPU) features.
|
|
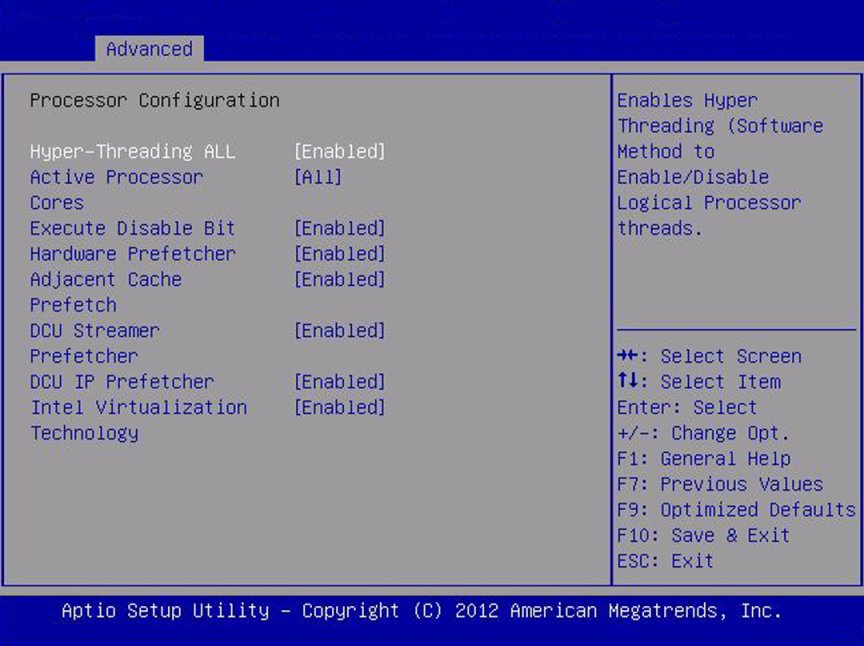
Hyper-threading
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
When enabled, two threads are available per enabled core. When
disabled, only one thread per enabled core is available.
|
|
Execute Disable Bit
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
When enabled, execute disable bit can prevent certain classes
of malicious buffer overflow attacks when combined with a
supporting OS (Oracle Solaris, Oracle VM, Windows Server, Red
Hat Enterprise Linux, SUSE Linux Enterprise Server, and VMware
ESXi).
|
|
Hardware Prefetcher
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable the mid-level cache (L2) streamer prefetcher.
|
|
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable the mid-level cache (L2) prefetching of adjacent cache
lines.
|
|
DCU Streamer Prefetcher
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable prefetching of next L1 data line based on multiple
loads in same cache line.
|
|
DCP IP Prefetcher
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable prefetching of next L1 line based on sequential load
history.
|
|
Intel Virtualization Technology
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
When enabled, a Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) can utilize the
additional hardware capabilities provided by Intel
Virtualization Technology.
|
|
CPU Power Management
Configuration
|
|
|
Displays processor (CPU) information. BIOS provides C-states,
P-states, and T-states support in order for the OS to manage the
power utilization of the system. Power management is also
controlled by the service processor based on system
policies.
|
|
Power Technology
|
Disabled/ Enabled/
Efficient/ Custom
|
Efficient
|
Enable the power management features. The following options
are not displayed if Power Technology is set to Disabled.
|
|
Intel SpeedStep
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Displays only if Power Technology is set to Custom. Enable or
disable Intel SpeedStep. The Intel technology used to support
P-state transitions is referred to as Intel SpeedStep.
|
|
CPU C3 Report
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Displays only if Power Technology is set to Custom and power
state (C3) is supported by the CPU. Enable or disable CPU C3
(ACPI C2) report to the operating system.
|
|
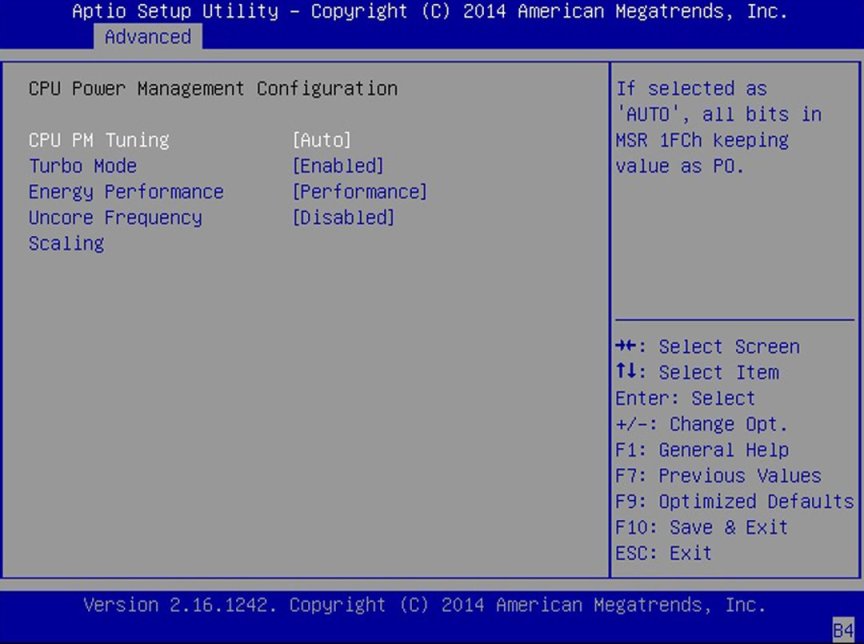
Turbo Mode
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
|
Displays only if Power Technology is set to Custom, Intel
SpeedStep is set to enabled, and TurboMode is supported in the
CPU.
|
|
Energy Performance
|
Performance/ Balanced Performance
|
Balanced Performance
|
Optimize between performance and power savings. Windows 2008
and later operating systems override this value according to its
power plan.
|
|
Uncore Frequency Scaling
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Frequency scaling for the uncore portion of the CPU.
When Enabled allows uncore portions (I/O) of the CPU to change
frequencies along with CPU cores when P-States are changed. If
Disabled, uncore portions are not affected by P-State
changes.
|
|
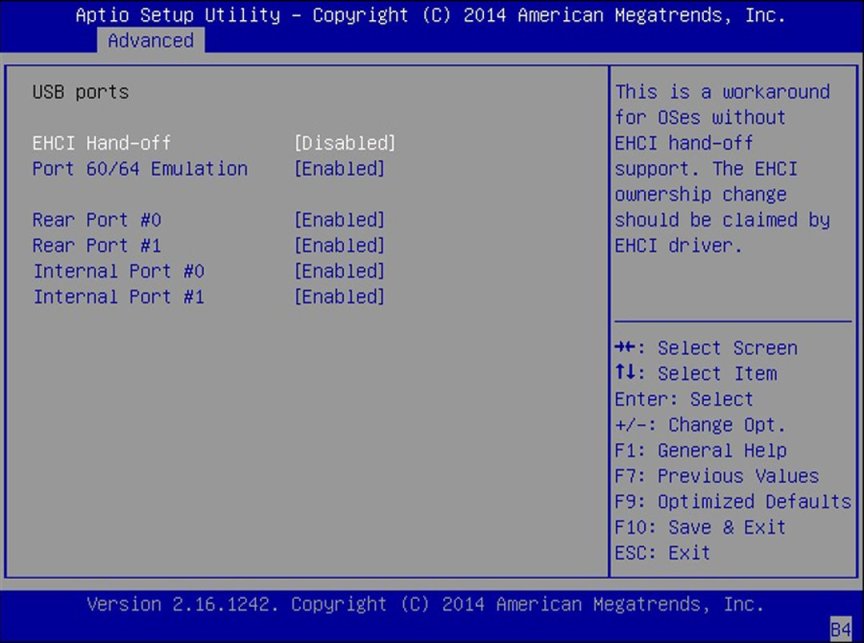
USB Ports
|
|
|
Set USB port configuration parameters.
|
|
EHCI Hand-off
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Enable or disable Enhanced Host Controller Interface (EHCI)
hand-off support.
|
|
Port 60/64 Emulation
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable I/O port 60h/64h emulation support. Enable this setting
for the complete USB keyboard legacy support for non-USB aware
operating systems.
|
|
Rear Port 0
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable rear USB Port 0.
|
|
Rear Port 1
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable rear USB Port 1.
|
|
Internal Port 0
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable internal USB Port 0. By default, internal
port 0 is reserved for Oracle System Assistant.
|
|
Internal Port 1
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable internal USB Port 1.
|
|
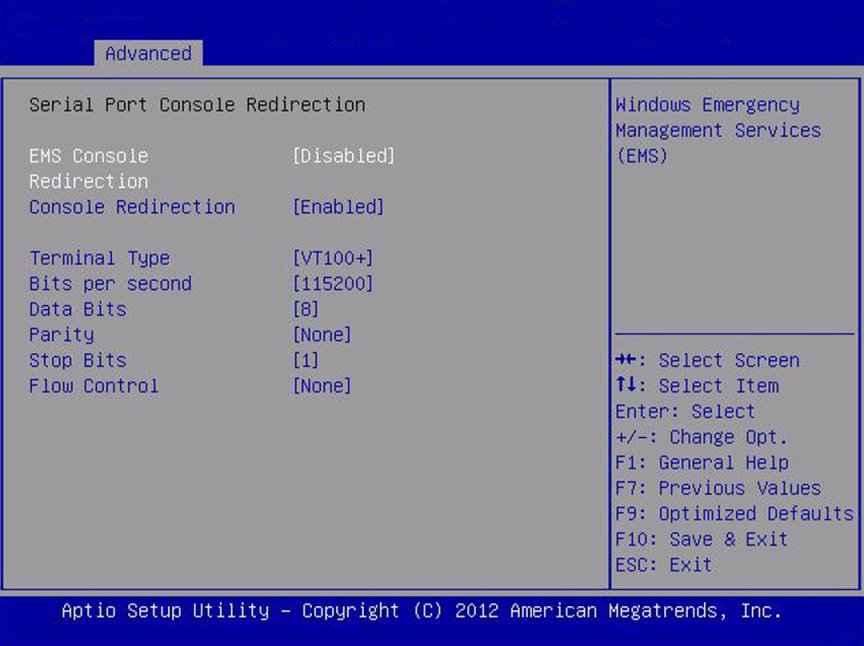
Serial Port Console
Redirection
|
|
|
Provides the capability to redirect console output/input to
the serial port. Graphic output is not redirected. BIOS serial
console redirection lets you monitor BIOS POST messages and
navigate the BIOS Setup utility menus and Option ROMs from a
terminal connected to the server using a serial
connection.
|
|
EMS Console Redirection
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Enable or disable console redirection for Windows Emergency
Management Service (EMS) administration.
|
|
Console Redirection
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable console redirection.
|
|
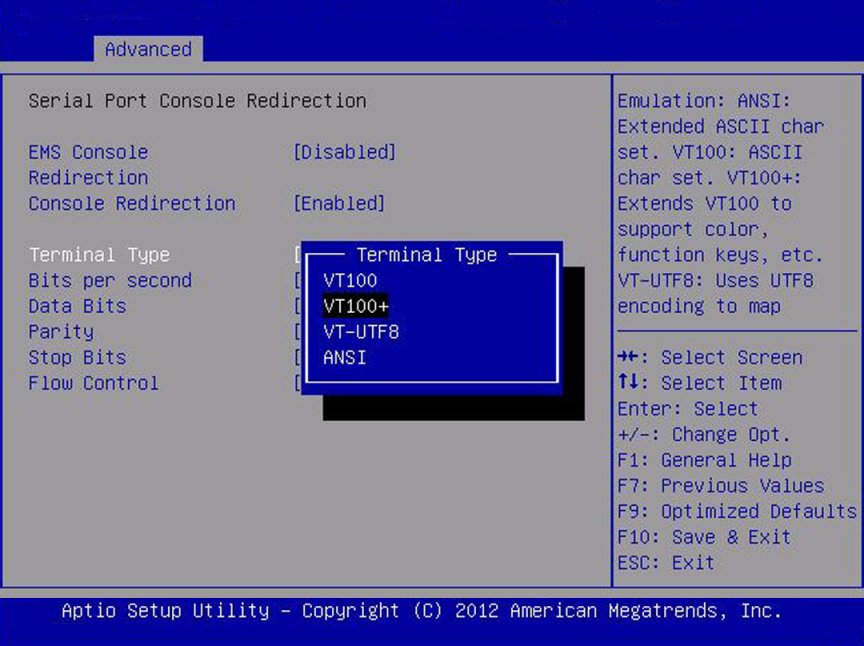
Terminal Type
|
VT100/
VT100+/
VT-UTF8/
ANSI
|
VT100+
|
Select the emulation for the terminal: VT100: ASCII character
set. VT100+: Extends VT100 to support color, function keys, etc.
VT-UTF8: Uses UTF8 encoding to map Unicode characters onto one
or more bytes. ANSI: Extended ASCII character set.
|
|
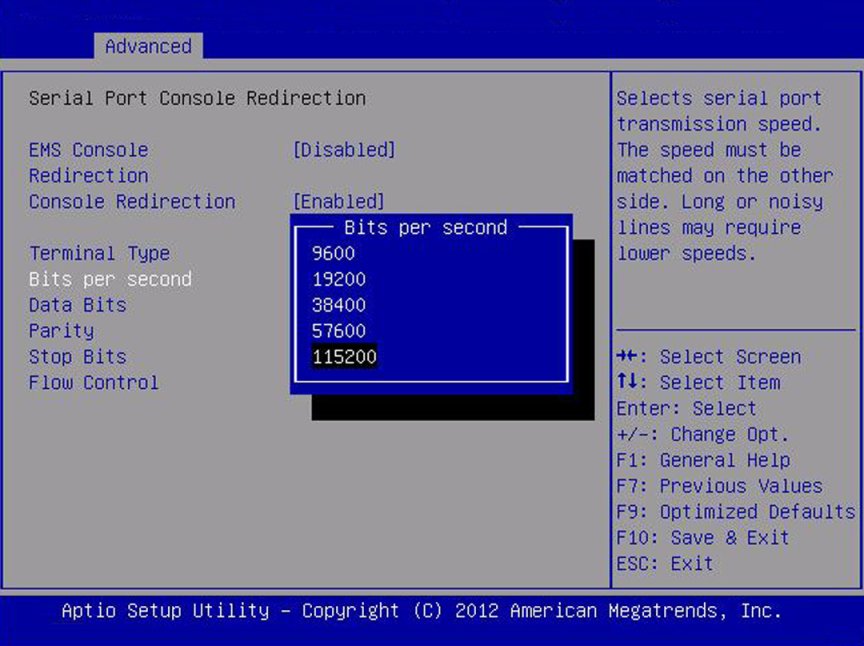
Bits per Second
|
9600/ 10200
/ 57600/ 115200
|
9600
|
Select the serial port transmission speed. The speed must be
matched on the connecting serial device. Long or noisy lines
require lower speeds.
|
|
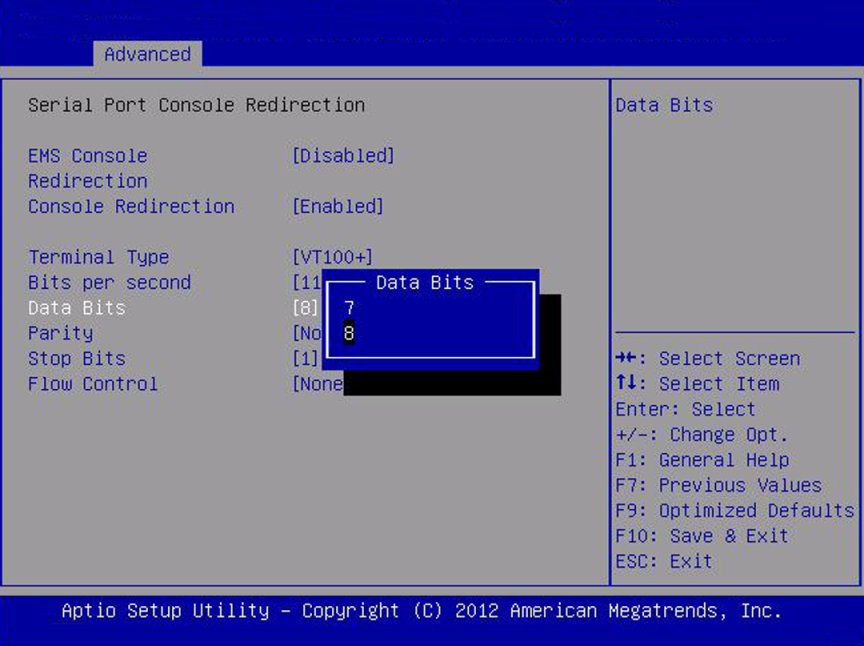
Data Bits
|
07/08/11
|
8
|
Select the data bits.
|
|
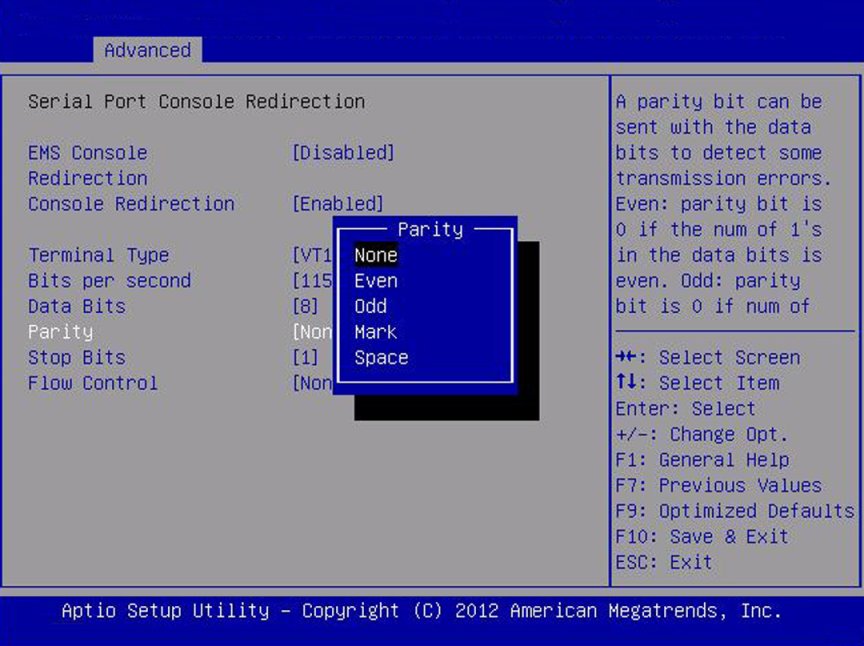
Parity
|
None/
Even/
Odd/
Mark/
Space
|
None
|
A parity bit can be sent with the data bits to detect some
transmission errors.
None: No parity bits are sent.
Even: Parity bit is 0 if the number of 1s in the data bits is
even.
Odd: Parity bit is 0 if the number of 1s in the data bits is
odd.
Mark: Parity bit is always 1.
Space: Parity bit is always 0.
Mark and Space parity do not allow for error detection. They
can be used as an additional data bit.
|
|
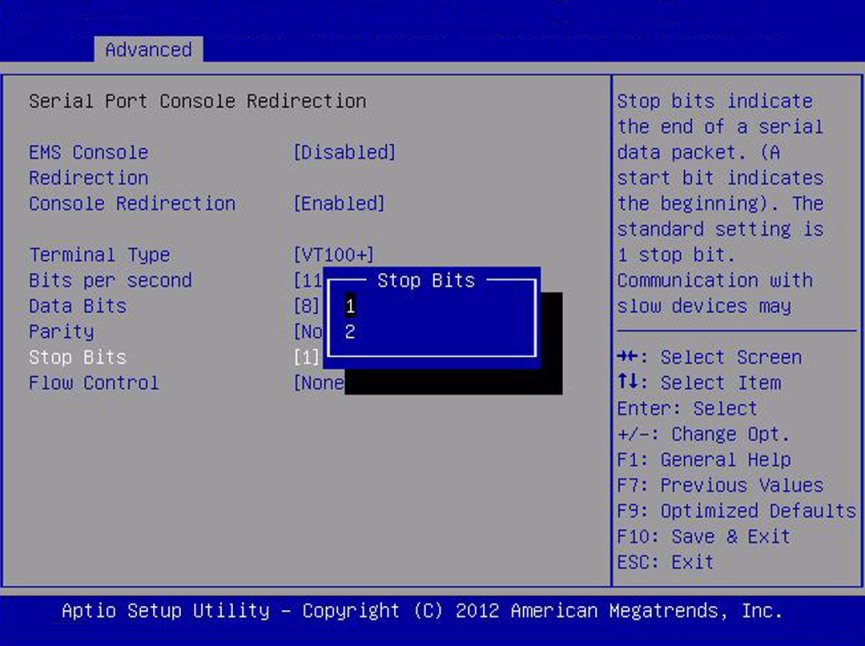
Stop Bits
|
01/02/11
|
1
|
Stop bits indicate the end of a serial data packet. (A start
bit indicates the beginning of a serial data packet.) The
standard setting is 1 stop bit. Communication with slow devices
may require more than 1 stop bit.
|
|
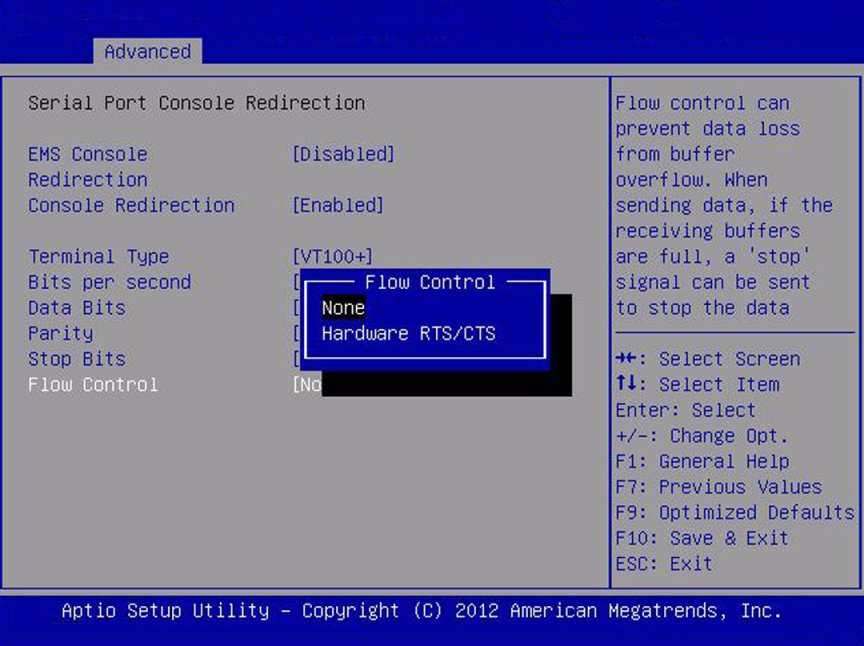
Flow Control
|
None/
Hardware/
RTS/
CTS
|
None
|
Flow control can prevent data loss from buffer overflow. When
sending data, if the receiving buffers are full, a "stop" signal
can be sent to stop the data flow. Once the buffers are empty, a
"start" signal can be sent to restart the flow. Hardware flow
control uses two wires to send start and stop RTS (request to
send) and CTS (clear to send) signals.
|
|
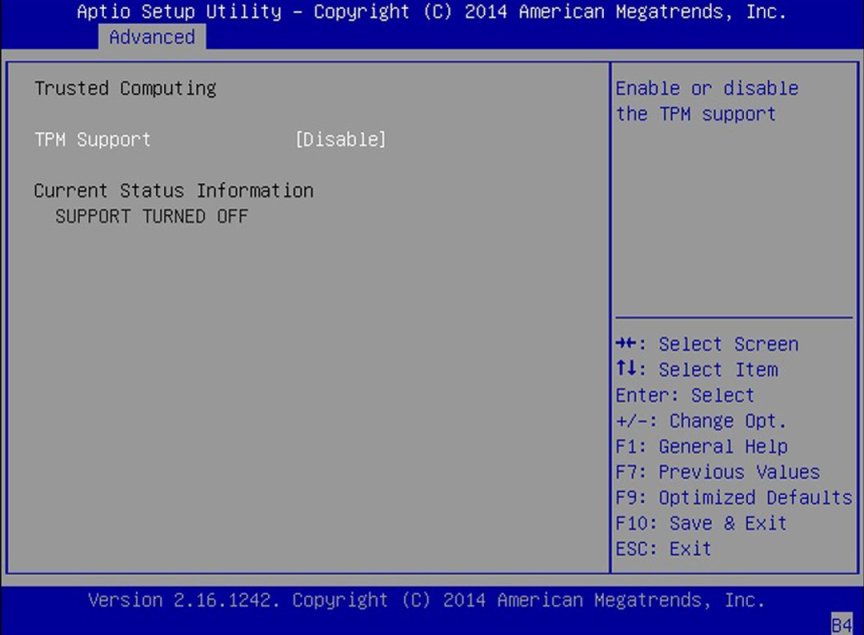
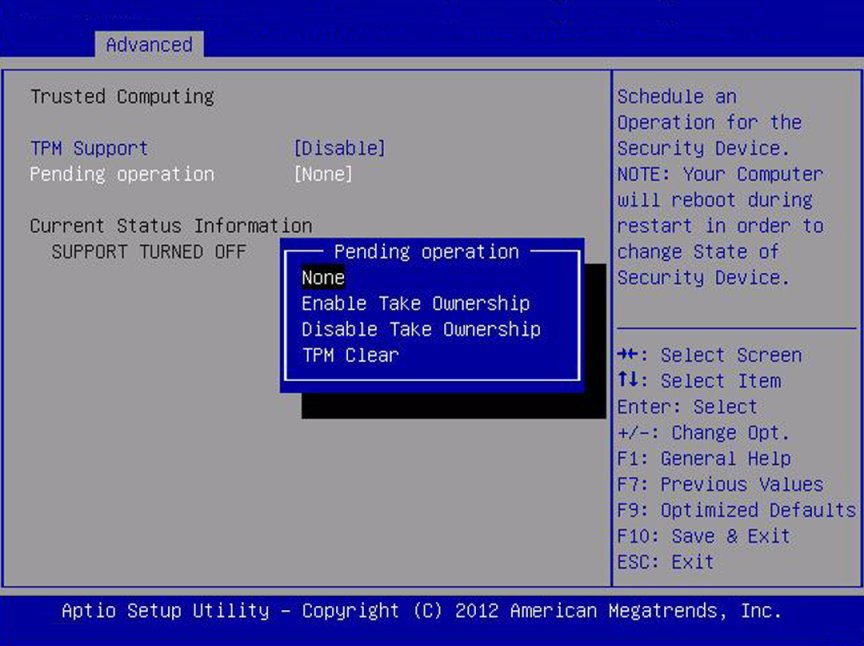
Trusted Computing
|
|
|
If you intend to use the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) feature
set, you must configure the server to support TPM. The TPM
feature is used by the OS for proof that BIOS code has not been
tampered with.
|
|
TPM Support
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable TPM support. Only UEFI BIOS implements this
setup option. If disabled, the OS does not show TPM.
|
|
TPM State
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Displays whether TPM Support is enabled.
|
|
Current TPM Status Information (R/O)
|
|
|
If TPM Support is disabled, Current TPM Status displays "TPM
SUPPORT OFF." If TPM Support is enabled, Current TPM Status
displays: TPM Enabled
|
|
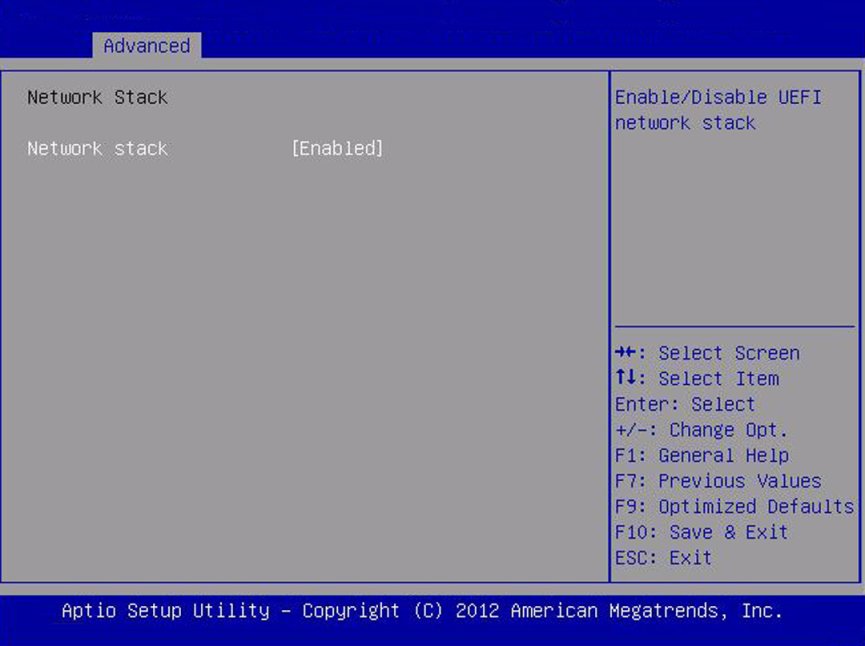
Network Stack
|
|
|
Configure network stack settings.
|
|
Network Stack
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable the UEFI network stack.
|
|
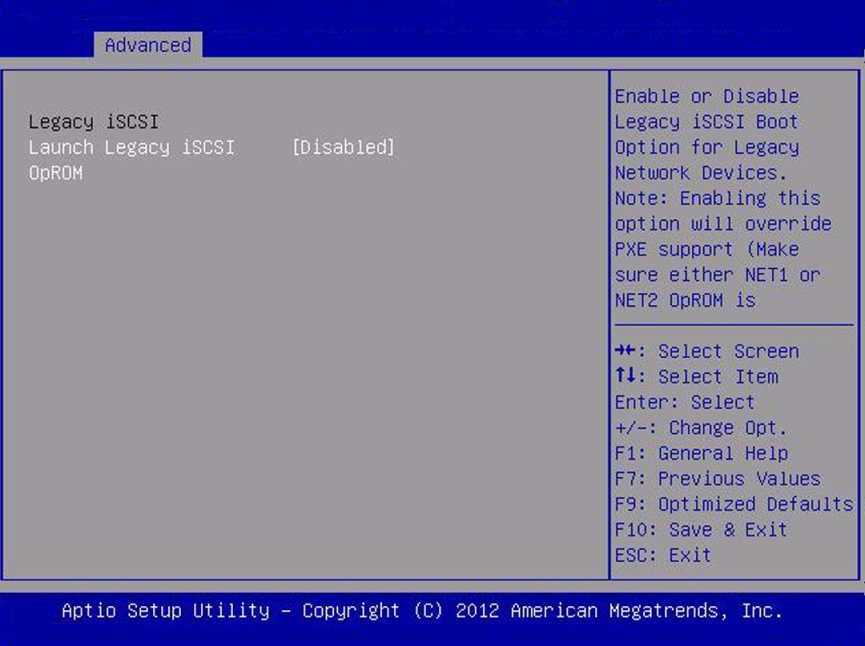
Legacy iSCSI
|
|
|
Enabled allows booting to iSCSI in Legacy Boot Mode.
|
|
BMC Network
|
|
|
Configure Baseboard Management Controller (BMC) network
parameters.
|
|
BMC Network: Current Active Management Port (R/O)
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Active management port settings are displayed.
|
|
Refresh
|
|
|
Refresh current BMC network information with the latest
information from the service processor.
|
|
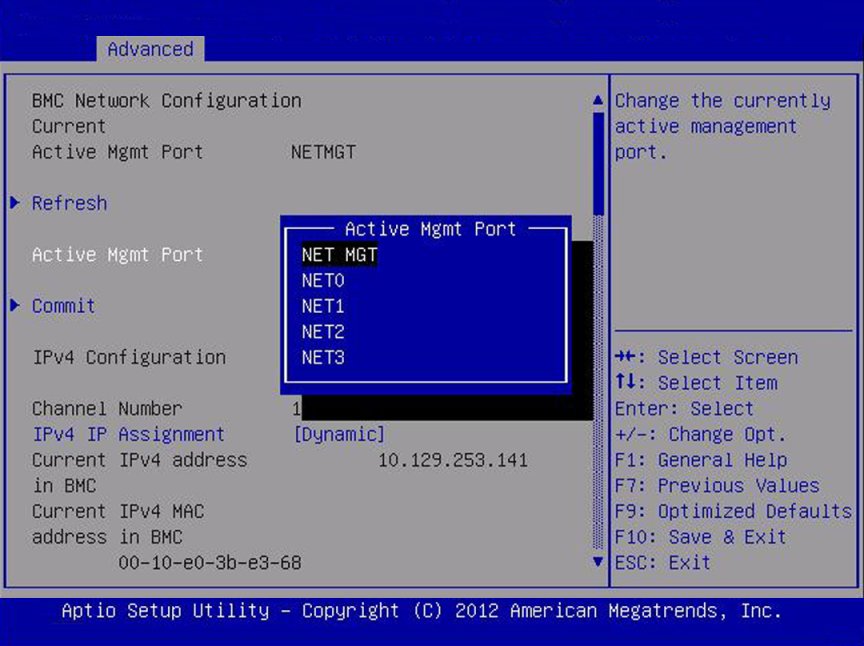
Active Management Port
|
NETMGT/
NET0/
NET1/
NET2/
NET3
|
|
Change the management port that is currently active.
|
|
Commit
|
|
|
Commit the current BMC network information.
|
|
IPv4 Configuration (R/O)
|
|
|
Current configuration of the IPv4 settings.
|
|
Channel Number (R/O)
|
|
|
Current channel number.
|
|
IPv4 Assignment (R/O)
|
Static/Dynamic
|
Static
|
View whether the service processor is assigned a static IPv4
address or assigned a dynamic IPv4 address using Dynamic Host
Control Protocol (DHCP).
|
|
Current IPv4 Address in BMC (R/O)
|
|
|
Current IPv4 address of the service processor. Example:
172.31.255.255
|
|
Current IPv4 MAC Address in BMC (R/O)
|
|
|
Current IPv4 MAC address for the service processor. Example:
00:12:46:BE:0A:02
|
|
Current IPv4 Subnet Mask in BMC (R/O)
|
|
|
Current IPv4 subnet mask address for the service processor.
Example: 255.255.255.0
|
|
Refresh
|
|
|
Select Refresh to update to the current settings.
|
|
IPv4 Address
|
|
|
If IPv4 Assignment is set to Static, set the IPv4 address for
the service processor.
|
|
IPv4 Subnet Mask
|
|
|
If the IPv4 Assignment is set to Static, set the IPv4 subnet
mask. Example: 255.255.255.0
|
|
IPv4 Default Gateway
|
|
|
If the IPv4 Assignment is set to Static, set the IPv4 default
gateway. Example: 129.144.82.254
|
|
Commit
|
|
|
Commit the IPv4 configuration settings.
|
|
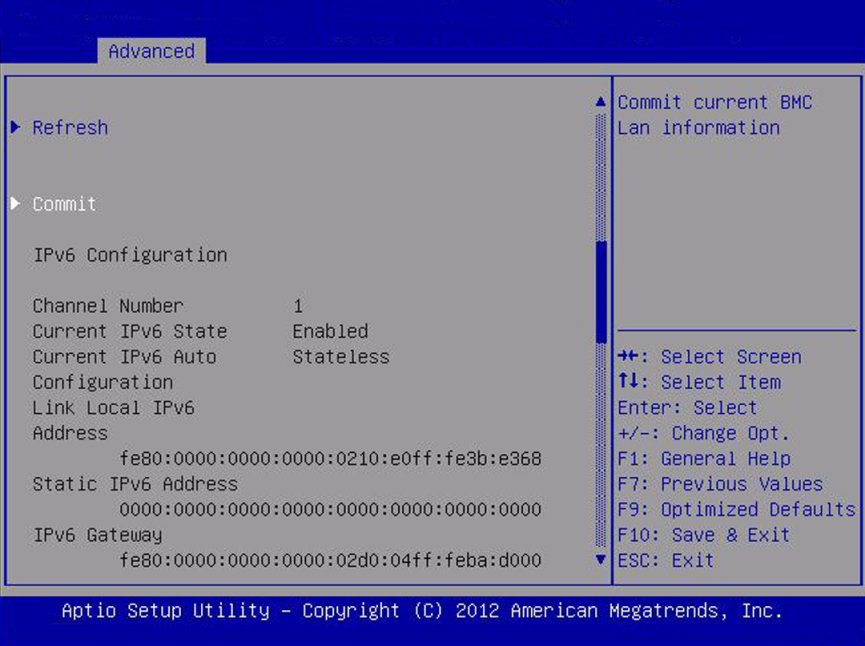
IPv6 Configuration (R/O)
|
Static/Dynamic
|
Dynamic
|
Current configuration of the IPv6 settings. IPv6 addresses are
written with hexadecimal digits and colon separators. For
example: 2001:0db0:000:82a1:0000:0000:1234:abcd. IPv6 addresses
are composed of two parts: a 64-bit subnet prefix and a 64-bit
host interface ID. To shorten the IPv6 address, you can (1) omit
all leading zeros, and (2) replace one consecutive group of
zeros with a double colon (::). For example:
2001:db0:0:82a1::1234:abcd
|
|
Channel Number (R/O)
|
|
1
|
Current channel number.
|
|
Current IPv6 State (R/O)
|
|
|
Current IPv6 state.
|
|
Current IPv6 Auto Configuration (R/O)
|
|
|
Current IPv6 autoconfiguration parameters are displayed.
|
|
Link Local IPv6 Address (R/O)
|
|
|
Current link local IPv6 address. Example:
fe80::214:4fff:feca:5f7e/64
|
|
Static IPv6 Address (R/O)
|
|
|
Current static IPv6 address. Example:
2001:0db0:000:82a1:0000:0000:1234:abcd
|
|
IPv6 Gateway (R/O)
|
|
|
Current IPv6 gateway address. Example:
fe80::211:5dff:febe:5000/128
|
|
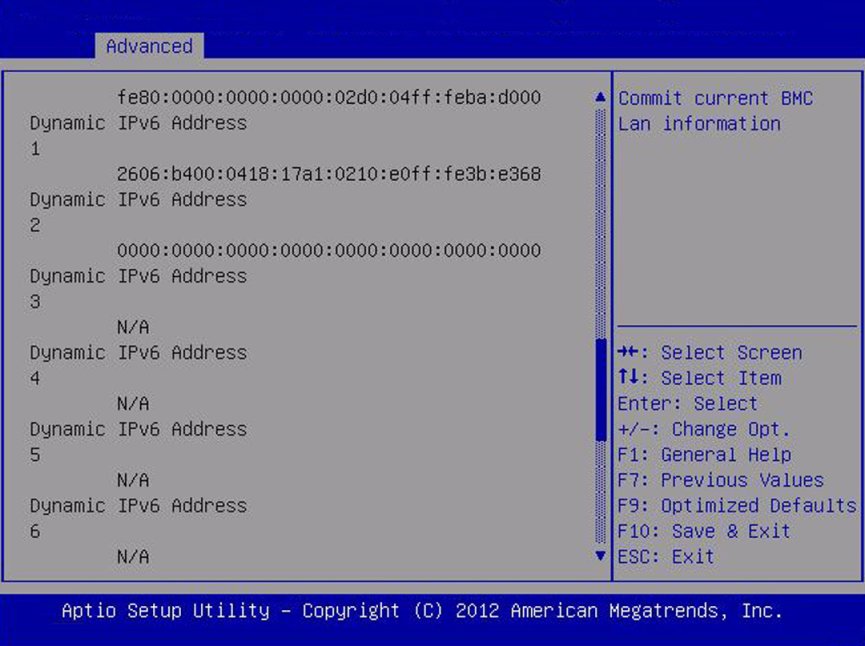
Dynamic IPv6 Address 1 – (R/O)
|
|
|
Current dynamic IPv6 address. Example:
fec0:a:8:b7:214:4fff:feca:5f7e/64
|
|
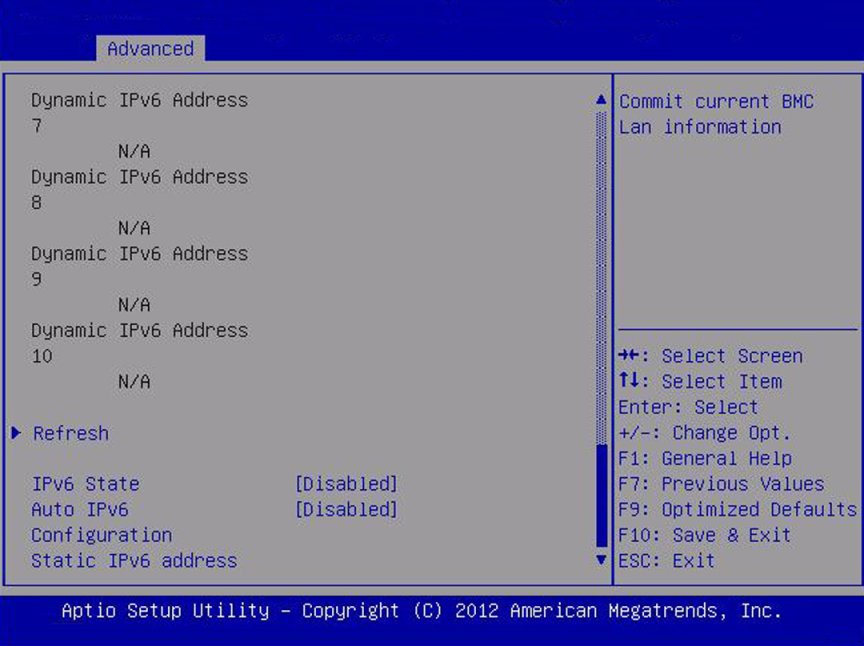
Refresh
|
|
|
Select Refresh to update to the current settings.
|
|
IPv6 State (R/O)
|
Disabled/ Enabled
|
|
View whether the IPv6 state is enabled or disabled.
|
|
Auto IPv6 Configuration
|
Disabled/
Stateless/
Dhcpv6_ stateless/
Dhcpv6_ stateful
|
Disabled
|
Autoconfiguration options are:
Disabled: When autoconfiguration is disabled, only the Link
Local address is set. None of the autoconfiguration options to
configure an IPv6 address are run.
Stateless: When enabled, the IPv6 Stateless autoconfiguration
is run to learn the IPv6 addresses for the device.
Dhcpv6_stateless: When enabled, the Dhcpv6_stateless
autoconfiguration is run to learn the DNS and domain information
for the device.
Dhcpv6_stateful: When enabled, the Dhcpv6_stateful
autoconfiguration is run to learn the IP addresses and DNS
information for the device.
|
|
Static IPv6 Address
|
|
|
Set the static IPv6 address. Example:
2001:0db0:000.82a1:0000:0000:1234:abcd
|
|
Commit
|
|
|
Commit the IPv6 configuration settings.
|