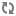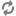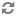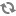The process for handling XML or JSON output is very similar to that for JSPs, with some minor modifications. The architecture diagram for an XML or JSON response looks like the following (note that this diagram is identical to the JSP diagram except for steps 13 and 14):
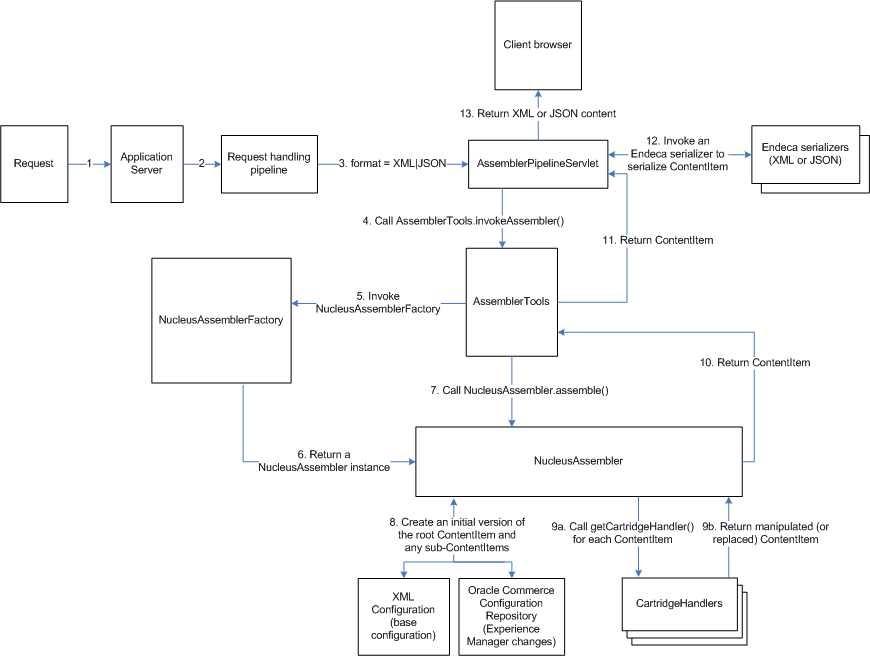
Serializing the content to XML or JSON is controlled by the AssemblerPipelineServlet.formatParamName property. This property specifies the name of the request parameter that must be passed in order to serialize the content. This property defaults to format, meaning that, in order to serialize output, the request must include a format parameter with an acceptable value. Acceptable values are xml and json. For example, the following URL returns json for a content folder request:
http://localhost:8080/assembler/assembler?assemblerContentCollection=/content/BrowsePageCollection&format=json
This example returns json for a page request:
http://localhost:8080/assembler/browse?format=json
If the request specifies the format parameter and either XML or JSON as the value, then after the AssemblerPipelineServlet component receives the response ContentItem from AssemblerTools, it calls the appropriate serializer to reformat the response into XML or JSON, respectively. The AssemblerPipelineServlet component then returns the reformatted content to the client browser.
Setting the AssemblerPipelineServlet.formatParamName property to null disables the serializing feature and suppresses the rendering of the response entirely. This feature allows you to suppress content as needed in production environments.