Boot Pools and Fallback Boot Images
The boot process has been enhanced to enable booting from devices that are not directly accessible to OpenBoot. This feature requires OS support (Oracle Solaris 11.3 includes this support) and support in OpenBoot (available in OpenBoot version 4.37.3 and later. To identify the OpenBoot version,see Obtain Virtual machine Information with OpenBoot Commands).
The systems that support this feature boot from an OpenBoot accessible boot pool that is located in the system, for example, from an eUSB device in each physical domain. Then the boot process uses certain OpenBoot configuration variables and properties (shown in this illustration) to enable the virtual machine to locate an OS that is not directly accessible to OpenBoot.
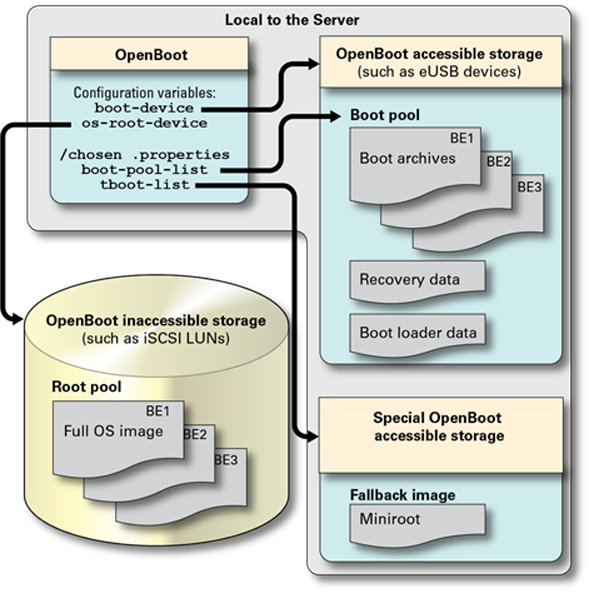
The OpenBoot parameters perform these functions:
Note - Except for the boot-device variable, the variables and properties listed here are usually automatically maintained and do not require intervention.
-
boot-device – Is an OpenBoot configuration variable that specifies boot devices. In this diagram, the boot-device variable is set to the path of a local device, such as an eUSB device, where a boot pool is available. The setting is viewable using the OpenBoot printenv command or by using the Oracle Solaris eeprom command.
-
os-root-device – Is an OpenBoot configuration variable that specifies properties that describe to the OS how to access the root file system. This setting is viewable using the OpenBoot printenv command or by using the Oracle Solaris eeprom command.
-
boot-pool-list – Is an OpenBoot property for the /chosen node. This property specifies platform-defined devices that can be used to comprise a boot pool. Note - the list does not indicate if a device provides a boot pool or not. You can view this read-only property with the .properties command under the /chosen node at the OpenBoot prompt.
-
tboot-list – Is an OpenBoot property for the /chosen node. This property contains a list of device paths that might allow access to fallback boot images (only if the platform has installed or flashed the image in non-volatile storage or if bootable media is inserted in the devices referenced by the property). You can view this read-only property with the .properties command under the /chosen node at the OpenBoot prompt.
The other items shown in the illustrations serve these purposes:
-
Boot pool – A collection of boot archives that are stored on firmware-assessable devices. Each dataset in the boot pool is linked to a specific boot environment on a specific root pool.
-
Boot archive – Is a file that contains the OS kernel and modules necessary to locate and mount the root file system to complete the second stage of booting the OS.
-
Recovery data and Boot loader data– Provide a means to reconstitute the os-root-device property in the event that the property is reset, corrupted, or erased.
-
Root pool – Is a ZFS pool that contains a set of boot environments (datasets of the form pool_name/ROOT/BE_name), each of which constitutes a root file system for an instance of the Oracle Solaris OS. A root pool can reside on a device such as an iSCSI device accessed through IP over Infiniband (IPoIB). This storage might not be directly accessible from OpenBoot. In such cases, when a root pool is created, a new boot pool is also automatically created on OpenBoot-accessible devices.
-
Fallback boot image – (Also known as the fallback miniroot) is a boot image that can be booted if no devices in the boot pool are accessible from OpenBoot. This image is managed differently depending on the platform. For example, on some systems the boot image is directly accessible to root domains to which the USB controller for the RKVMS is associated. In other systems, no tboot-list may exist and so the fallback image must be manually managed and added to the boot-device list, This is because the Oracle Solaris installer does not know which device references a fallback miniroot image. For further details, refer to your platform documentation.
For detailed instructions on how you can manage and configure boot pools, refer to the Oracle Solaris 11.3 documentation at http://www.oracle.com/goto/solaris11/docs. Refer to the document titled Booting and Shutting Down Oracle Solaris 11.3 Systems.
Also refer to the documentation for your server platform to determine if these features are supported. Server documentation is available at: http://docs.oracle.com/en/servers/