Using JavaFX UI Controls
12 Table View
In this chapter, you learn how to perform basic operations with tables in JavaFX applications, such as adding a table, populating the table with data, and editing table rows.
Several classes in the JavaFX SDK API are designed to represent data in a tabular form. The most important classes for creating tables in JavaFX applications are TableView, TableColumn, and TableCell. You can populate a table by implementing the data model and by applying a cell factory.
The table classes provide built-in capabilities to sort data in columns and to resize columns when necessary.
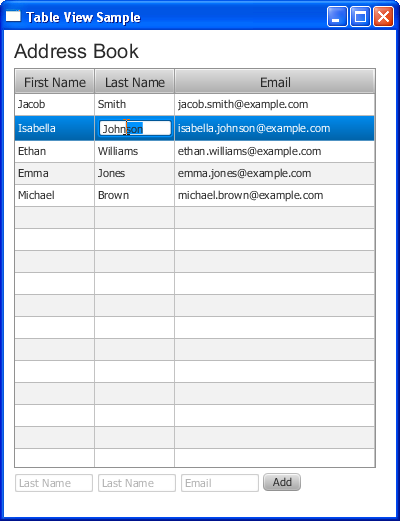
Figure 12-1 shows a typical table representing contact information from an address book.
Creating a Table
The code fragment in Example 12-1 creates an empty table with three columns and adds it to the application scene.
Example 12-1 Adding a Table
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn;
import javafx.scene.control.TableView;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class TableViewSample extends Application {
private TableView table = new TableView();
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
Scene scene = new Scene(new Group());
stage.setTitle("Table View Sample");
stage.setWidth(300);
stage.setHeight(500);
final Label label = new Label("Address Book");
label.setFont(new Font("Arial", 20));
table.setEditable(true);
TableColumn firstNameCol = new TableColumn("First Name");
TableColumn lastNameCol = new TableColumn("Last Name");
TableColumn emailCol = new TableColumn("Email");
table.getColumns().addAll(firstNameCol, lastNameCol, emailCol);
final VBox vbox = new VBox();
vbox.setSpacing(5);
vbox.setPadding(new Insets(10, 0, 0, 10));
vbox.getChildren().addAll(label, table);
((Group) scene.getRoot()).getChildren().addAll(vbox);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
}
The table control is created by instantiating the TableView class. In Example 12-1, it is added to the VBox layout container, however, you can add it directly to the application scene.
Example 12-1 defines three columns to store the following information in an address book: a contact's first name and last name, and an email address. The columns are created by using the TableColumn class.
The getColumns method of the TableView class adds the previously created columns to the table. In your applications, you can use this method to dynamically add and remove columns.
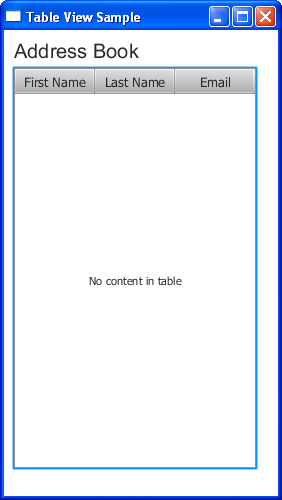
Compiling and running this application produces the output shown in Figure 12-2.
You can manage visibility of the columns by calling the setVisible method. For example, if the logic of your application requires hiding user email addresses, you can implement this task as follows: emailCol.setVisible(false).
When the structure of your data requires a more complicated representation, you can create nested columns.
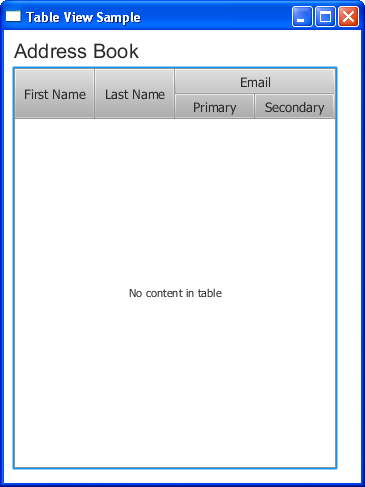
For example, suppose that the contacts in the address book have two email accounts. Then you need two columns to show the primary and the secondary email addresses. Create two subcolumns, and call the getColumns method on emailCol as shown in Example 12-2.
Example 12-2 Creating Nested Columns
TableColumn firstEmailCol = new TableColumn("Primary");
TableColumn secondEmailCol = new TableColumn("Secondary");
emailCol.getColumns().addAll(firstEmailCol, secondEmailCol);
After you have added these lines to Example 12-1, and compiled and run the application code, the table appears as shown in Figure 12-3.
Although the table is added to the application, the standard caption "No content in table" appears, because no data is defined. Instead of showing this caption, you can use the setPlaceholder method to specify a Node object to appear in an empty table.
Defining the Data Model
When you create a table in a JavaFX application, it is a best practice to implement a class that defines the data model and provides methods and fields to further work with the table. Example 12-3 creates the Person class to define data in an address book.
Example 12-3 Creating the Person Class
public static class Person {
private final SimpleStringProperty firstName;
private final SimpleStringProperty lastName;
private final SimpleStringProperty email;
private Person(String fName, String lName, String email) {
this.firstName = new SimpleStringProperty(fName);
this.lastName = new SimpleStringProperty(lName);
this.email = new SimpleStringProperty(email);
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName.get();
}
public void setFirstName(String fName) {
firstName.set(fName);
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName.get();
}
public void setLastName(String fName) {
lastName.set(fName);
}
public String getEmail() {
return email.get();
}
public void setEmail(String fName) {
email.set(fName);
}
}
The firstName, lastName, and email string properties are created to enable the referencing of a particular data element.
Additionally, the get and set methods are provided for each data element. Thus, for example, the getFirstName method returns the value of the firstName property, and the setFirstName method specifies a value for this property.
When the data model is outlined in the Person class, you can create an ObservableList array and define as many data rows as you would like to show in your table. The code fragment in Example 12-4 implements this task.
Example 12-4 Defining Table Data in an Observable List
final ObservableList<Person> data = FXCollections.observableArrayList(
new Person("Jacob", "Smith", "jacob.smith@example.com"),
new Person("Isabella", "Johnson", "isabella.johnson@example.com"),
new Person("Ethan", "Williams", "ethan.williams@example.com"),
new Person("Emma", "Jones", "emma.jones@example.com"),
new Person("Michael", "Brown", "michael.brown@example.com")
);
The next step is to associate the data with the table columns. You can do this through the properties defined for each data element, as shown in Example 12-5.
Example 12-5 Setting Data Properties to Columns
firstNameCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person,String>("firstName")
);
lastNameCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person,String>("lastName")
);
emailCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person,String>("email")
);
The setCellValueFactory method specifies a cell factory for each column. The cell factories are implemented by using the PropertyValueFactory class, which uses the firstName, lastName, and email properties of the table columns as references to the corresponding methods of the Person class.
When the data model is defined, and the data is added and associated with the columns, you can add the data to the table by using the setItems method of the TableView class: table.setItems(data).
Because the ObservableList object enables the tracking of any changes to its elements, the TableView content automatically updates whenever the data changes.
Examine the application code shown in Example 12-6.
Example 12-6 Creating a Table and Adding Data to It
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.beans.property.SimpleStringProperty;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn;
import javafx.scene.control.TableView;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.PropertyValueFactory;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class TableViewSample extends Application {
private TableView<Person> table = new TableView<Person>();
private final ObservableList<Person> data =
FXCollections.observableArrayList(
new Person("Jacob", "Smith", "jacob.smith@example.com"),
new Person("Isabella", "Johnson", "isabella.johnson@example.com"),
new Person("Ethan", "Williams", "ethan.williams@example.com"),
new Person("Emma", "Jones", "emma.jones@example.com"),
new Person("Michael", "Brown", "michael.brown@example.com")
);
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
Scene scene = new Scene(new Group());
stage.setTitle("Table View Sample");
stage.setWidth(450);
stage.setHeight(500);
final Label label = new Label("Address Book");
label.setFont(new Font("Arial", 20));
table.setEditable(true);
TableColumn firstNameCol = new TableColumn("First Name");
firstNameCol.setMinWidth(100);
firstNameCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("firstName"));
TableColumn lastNameCol = new TableColumn("Last Name");
lastNameCol.setMinWidth(100);
lastNameCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("lastName"));
TableColumn emailCol = new TableColumn("Email");
emailCol.setMinWidth(200);
emailCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("email"));
table.setItems(data);
table.getColumns().addAll(firstNameCol, lastNameCol, emailCol);
final VBox vbox = new VBox();
vbox.setSpacing(5);
vbox.setPadding(new Insets(10, 0, 0, 10));
vbox.getChildren().addAll(label, table);
((Group) scene.getRoot()).getChildren().addAll(vbox);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static class Person {
private final SimpleStringProperty firstName;
private final SimpleStringProperty lastName;
private final SimpleStringProperty email;
private Person(String fName, String lName, String email) {
this.firstName = new SimpleStringProperty(fName);
this.lastName = new SimpleStringProperty(lName);
this.email = new SimpleStringProperty(email);
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName.get();
}
public void setFirstName(String fName) {
firstName.set(fName);
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName.get();
}
public void setLastName(String fName) {
lastName.set(fName);
}
public String getEmail() {
return email.get();
}
public void setEmail(String fName) {
email.set(fName);
}
}
}
When you compile and run this application code, the table shown in Figure 12-4 appears.
Adding New Rows
The table in Figure 12-4 contains five rows of data, which cannot be modified so far.
You can use text fields to enter new values into the First Name, Last Name, and Email columns. The Text Field control enables your application to receive text input from a user. Example 12-7 creates three text fields, defines the prompt text for each field, and creates the Add button.
Example 12-7 Using Text Fields to Enter New Items in the Table
final TextField addFirstName = new TextField();
addFirstName.setPromptText("First Name");
addFirstName.setMaxWidth(firstNameCol.getPrefWidth());
final TextField addLastName = new TextField();
addLastName.setMaxWidth(lastNameCol.getPrefWidth());
addLastName.setPromptText("Last Name");
final TextField addEmail = new TextField();
addEmail.setMaxWidth(emailCol.getPrefWidth());
addEmail.setPromptText("Email");
final Button addButton = new Button("Add");
addButton.setOnAction(new EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
@Override public void handle(ActionEvent e) {
data.add(new Person(
addFirstName.getText(),
addLastName.getText(),
addEmail.getText()
));
addFirstName.clear();
addLastName.clear();
addEmail.clear();
}
});
When a user clicks the Add button, the values entered in the text fields are included in a Person constructor and added to the data observable list. Thus, the new entry with contact information appears in the table.
Examine the application code shown in Example 12-8.
Example 12-8 Table with the Text Fields to Enter New Items
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.beans.property.SimpleStringProperty;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.event.ActionEvent;
import javafx.event.EventHandler;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn;
import javafx.scene.control.TableView;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.PropertyValueFactory;
import javafx.scene.layout.HBox;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class FileChooserSample extends Application {
private TableView<Person> table = new TableView<Person>();
private final ObservableList<Person> data =
FXCollections.observableArrayList(
new Person("Jacob", "Smith", "jacob.smith@example.com"),
new Person("Isabella", "Johnson", "isabella.johnson@example.com"),
new Person("Ethan", "Williams", "ethan.williams@example.com"),
new Person("Emma", "Jones", "emma.jones@example.com"),
new Person("Michael", "Brown", "michael.brown@example.com"));
final HBox hb = new HBox();
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
Scene scene = new Scene(new Group());
stage.setTitle("Table View Sample");
stage.setWidth(450);
stage.setHeight(550);
final Label label = new Label("Address Book");
label.setFont(new Font("Arial", 20));
table.setEditable(true);
TableColumn firstNameCol = new TableColumn("First Name");
firstNameCol.setMinWidth(100);
firstNameCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("firstName"));
TableColumn lastNameCol = new TableColumn("Last Name");
lastNameCol.setMinWidth(100);
lastNameCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("lastName"));
TableColumn emailCol = new TableColumn("Email");
emailCol.setMinWidth(200);
emailCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("email"));
table.setItems(data);
table.getColumns().addAll(firstNameCol, lastNameCol, emailCol);
final TextField addFirstName = new TextField();
addFirstName.setPromptText("First Name");
addFirstName.setMaxWidth(firstNameCol.getPrefWidth());
final TextField addLastName = new TextField();
addLastName.setMaxWidth(lastNameCol.getPrefWidth());
addLastName.setPromptText("Last Name");
final TextField addEmail = new TextField();
addEmail.setMaxWidth(emailCol.getPrefWidth());
addEmail.setPromptText("Email");
final Button addButton = new Button("Add");
addButton.setOnAction(new EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(ActionEvent e) {
data.add(new Person(
addFirstName.getText(),
addLastName.getText(),
addEmail.getText()));
addFirstName.clear();
addLastName.clear();
addEmail.clear();
}
});
hb.getChildren().addAll(addFirstName, addLastName, addEmail, addButton);
hb.setSpacing(3);
final VBox vbox = new VBox();
vbox.setSpacing(5);
vbox.setPadding(new Insets(10, 0, 0, 10));
vbox.getChildren().addAll(label, table, hb);
((Group) scene.getRoot()).getChildren().addAll(vbox);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static class Person {
private final SimpleStringProperty firstName;
private final SimpleStringProperty lastName;
private final SimpleStringProperty email;
private Person(String fName, String lName, String email) {
this.firstName = new SimpleStringProperty(fName);
this.lastName = new SimpleStringProperty(lName);
this.email = new SimpleStringProperty(email);
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName.get();
}
public void setFirstName(String fName) {
firstName.set(fName);
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName.get();
}
public void setLastName(String fName) {
lastName.set(fName);
}
public String getEmail() {
return email.get();
}
public void setEmail(String fName) {
email.set(fName);
}
}
}
This application does not provide any filters to check if, for example, an email address was entered in an incorrect format. You can provide such functionality when you develop your own application.
The current implementation also does not check to determine if the empty values are entered. If no values are provided, clicking the Add button inserts an empty row in the table.
Figure 12-5 demonstrates how a user adds a new row of data.
Figure 12-5 Adding Contact Information to the Address Book
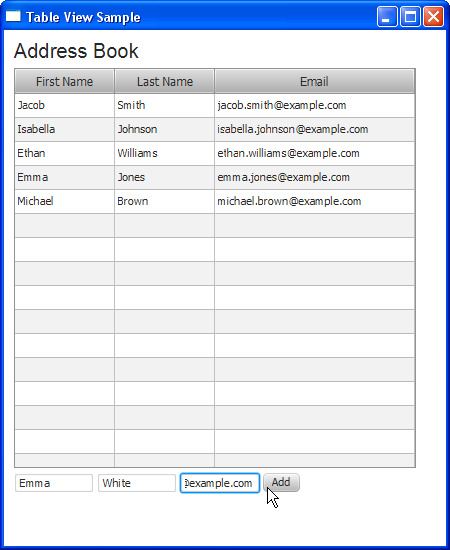
Description of "Figure 12-5 Adding Contact Information to the Address Book"
Figure 12-6 shows the table after the Add button is clicked. The contact details of Emma White now appear in the table.
Sorting Data in Columns
The TableView class provides built-in capabilities to sort data in columns. Users can alter the order of data by clicking column headers. The first click enables the ascending sorting order, the second click enables descending sorting order, and the third click disables sorting. By default, no sorting is applied.
Users can sort multiple columns in a table and specify the priority of each column in the sort operation. To sort multiple columns, the user presses the Shift key while clicking the header of each column to be sorted.
In Figure 12-7, an ascending sort order is applied to the first names, while last names are sorted in a descending order. Note that the first column has priority over the second column.
As the application developer, you can set sorting preferences for each column in your application by applying the setSortType method. You can specify both ascending and descending type. For example, use the following code line to set the descending type of sorting for the emailCol column: emailCol.setSortType(TableColumn.SortType.DESCENDING);.
You can also specify which columns to sort by adding and removing TableColumn instances from the TableView.sortOrder observable list. The order of columns in this list represents the sort priority (for example, the zero item has higher priority than the first item).
To prohibit sorting of data, call the setSortable(false) method on the column.
Editing Data in the Table
The TableView class not only renders tabular data, but it also provides capabilities to edit it. Use the setEditable method to enable editing of the table content.
Use the setCellFactory method to reimplement the table cell as a text field with the help of the TextFieldTableCell class. The setOnEditCommit method processes editing and assigns the updated value to the corresponding table cell. Example 12-9 shows how to apply these methods to process cell editing in the First Name, Last Name, and Email columns.
Example 12-9 Implementing Cell Editing
firstNameCol.setCellFactory(TextFieldTableCell.forTableColumn());
firstNameCol.setOnEditCommit(
new EventHandler<CellEditEvent<Person, String>>() {
@Override
public void handle(CellEditEvent<Person, String> t) {
((Person) t.getTableView().getItems().get(
t.getTablePosition().getRow())
).setFirstName(t.getNewValue());
}
}
);
lastNameCol.setCellFactory(TextFieldTableCell.forTableColumn());
lastNameCol.setOnEditCommit(
new EventHandler<CellEditEvent<Person, String>>() {
@Override
public void handle(CellEditEvent<Person, String> t) {
((Person) t.getTableView().getItems().get(
t.getTablePosition().getRow())
).setLastName(t.getNewValue());
}
}
);
emailCol.setCellFactory(TextFieldTableCell.forTableColumn());
emailCol.setOnEditCommit(
new EventHandler<CellEditEvent<Person, String>>() {
@Override
public void handle(CellEditEvent<Person, String> t) {
((Person) t.getTableView().getItems().get(
t.getTablePosition().getRow())
).setEmail(t.getNewValue());
}
}
);
The complete code of the application shown in Example 12-10.
Example 12-10 TableViewSample with Enabled Cell Editing
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.beans.property.SimpleStringProperty;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.event.ActionEvent;
import javafx.event.EventHandler;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn.CellEditEvent;
import javafx.scene.control.TableView;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.PropertyValueFactory;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.TextFieldTableCell;
import javafx.scene.layout.HBox;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class TableViewSample extends Application {
private TableView<Person> table = new TableView<Person>();
private final ObservableList<Person> data =
FXCollections.observableArrayList(
new Person("Jacob", "Smith", "jacob.smith@example.com"),
new Person("Isabella", "Johnson", "isabella.johnson@example.com"),
new Person("Ethan", "Williams", "ethan.williams@example.com"),
new Person("Emma", "Jones", "emma.jones@example.com"),
new Person("Michael", "Brown", "michael.brown@example.com"));
final HBox hb = new HBox();
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
Scene scene = new Scene(new Group());
stage.setTitle("Table View Sample");
stage.setWidth(450);
stage.setHeight(550);
final Label label = new Label("Address Book");
label.setFont(new Font("Arial", 20));
table.setEditable(true);
TableColumn firstNameCol = new TableColumn("First Name");
firstNameCol.setMinWidth(100);
firstNameCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("firstName"));
firstNameCol.setCellFactory(TextFieldTableCell.forTableColumn());
firstNameCol.setOnEditCommit(
new EventHandler<CellEditEvent<Person, String>>() {
@Override
public void handle(CellEditEvent<Person, String> t) {
((Person) t.getTableView().getItems().get(
t.getTablePosition().getRow())
).setFirstName(t.getNewValue());
}
}
);
TableColumn lastNameCol = new TableColumn("Last Name");
lastNameCol.setMinWidth(100);
lastNameCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("lastName"));
lastNameCol.setCellFactory(TextFieldTableCell.forTableColumn());
lastNameCol.setOnEditCommit(
new EventHandler<CellEditEvent<Person, String>>() {
@Override
public void handle(CellEditEvent<Person, String> t) {
((Person) t.getTableView().getItems().get(
t.getTablePosition().getRow())
).setLastName(t.getNewValue());
}
}
);
TableColumn emailCol = new TableColumn("Email");
emailCol.setMinWidth(200);
emailCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("email"));
emailCol.setCellFactory(TextFieldTableCell.forTableColumn());
emailCol.setOnEditCommit(
new EventHandler<CellEditEvent<Person, String>>() {
@Override
public void handle(CellEditEvent<Person, String> t) {
((Person) t.getTableView().getItems().get(
t.getTablePosition().getRow())
).setEmail(t.getNewValue());
}
}
);
table.setItems(data);
table.getColumns().addAll(firstNameCol, lastNameCol, emailCol);
final TextField addFirstName = new TextField();
addFirstName.setPromptText("First Name");
addFirstName.setMaxWidth(firstNameCol.getPrefWidth());
final TextField addLastName = new TextField();
addLastName.setMaxWidth(lastNameCol.getPrefWidth());
addLastName.setPromptText("Last Name");
final TextField addEmail = new TextField();
addEmail.setMaxWidth(emailCol.getPrefWidth());
addEmail.setPromptText("Email");
final Button addButton = new Button("Add");
addButton.setOnAction(new EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(ActionEvent e) {
data.add(new Person(
addFirstName.getText(),
addLastName.getText(),
addEmail.getText()));
addFirstName.clear();
addLastName.clear();
addEmail.clear();
}
});
hb.getChildren().addAll(addFirstName, addLastName, addEmail, addButton);
hb.setSpacing(3);
final VBox vbox = new VBox();
vbox.setSpacing(5);
vbox.setPadding(new Insets(10, 0, 0, 10));
vbox.getChildren().addAll(label, table, hb);
((Group) scene.getRoot()).getChildren().addAll(vbox);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static class Person {
private final SimpleStringProperty firstName;
private final SimpleStringProperty lastName;
private final SimpleStringProperty email;
private Person(String fName, String lName, String email) {
this.firstName = new SimpleStringProperty(fName);
this.lastName = new SimpleStringProperty(lName);
this.email = new SimpleStringProperty(email);
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName.get();
}
public void setFirstName(String fName) {
firstName.set(fName);
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName.get();
}
public void setLastName(String fName) {
lastName.set(fName);
}
public String getEmail() {
return email.get();
}
public void setEmail(String fName) {
email.set(fName);
}
}
}
In Figure 12-8, the user is editing the last name of Michael Brown. To edit a table cell, the user enters the new value in the cell, and then presses the Enter key. The cell is not modified until the Enter key is pressed. This behavior is determined by the implementation of the TextField class.
Note that the default implementation of the TextField control requires that users press the Enter key to commit the edit. You can redefine the TextField behavior to commit the edit on the focus change, which is an expected user experience. Try the modified code in to implement such an alternative behavior.
Example 12-11 Alternative Solution Of Cell Editing
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.beans.property.SimpleStringProperty;
import javafx.beans.value.ChangeListener;
import javafx.beans.value.ObservableValue;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.event.ActionEvent;
import javafx.event.EventHandler;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.TableCell;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn.CellEditEvent;
import javafx.scene.control.TableView;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.PropertyValueFactory;
import javafx.scene.layout.HBox;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Callback;
public class TableViewSample extends Application {
private TableView<Person> table = new TableView<Person>();
private final ObservableList<Person> data =
FXCollections.observableArrayList(
new Person("Jacob", "Smith", "jacob.smith@example.com"),
new Person("Isabella", "Johnson", "isabella.johnson@example.com"),
new Person("Ethan", "Williams", "ethan.williams@example.com"),
new Person("Emma", "Jones", "emma.jones@example.com"),
new Person("Michael", "Brown", "michael.brown@example.com"));
final HBox hb = new HBox();
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
Scene scene = new Scene(new Group());
stage.setTitle("Table View Sample");
stage.setWidth(450);
stage.setHeight(550);
final Label label = new Label("Address Book");
label.setFont(new Font("Arial", 20));
table.setEditable(true);
Callback<TableColumn, TableCell> cellFactory =
new Callback<TableColumn, TableCell>() {
public TableCell call(TableColumn p) {
return new EditingCell();
}
};
TableColumn firstNameCol = new TableColumn("First Name");
firstNameCol.setMinWidth(100);
firstNameCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("firstName"));
firstNameCol.setCellFactory(cellFactory);
firstNameCol.setOnEditCommit(
new EventHandler<CellEditEvent<Person, String>>() {
@Override
public void handle(CellEditEvent<Person, String> t) {
((Person) t.getTableView().getItems().get(
t.getTablePosition().getRow())
).setFirstName(t.getNewValue());
}
}
);
TableColumn lastNameCol = new TableColumn("Last Name");
lastNameCol.setMinWidth(100);
lastNameCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("lastName"));
lastNameCol.setCellFactory(cellFactory);
lastNameCol.setOnEditCommit(
new EventHandler<CellEditEvent<Person, String>>() {
@Override
public void handle(CellEditEvent<Person, String> t) {
((Person) t.getTableView().getItems().get(
t.getTablePosition().getRow())
).setLastName(t.getNewValue());
}
}
);
TableColumn emailCol = new TableColumn("Email");
emailCol.setMinWidth(200);
emailCol.setCellValueFactory(
new PropertyValueFactory<Person, String>("email"));
emailCol.setCellFactory(cellFactory);
emailCol.setOnEditCommit(
new EventHandler<CellEditEvent<Person, String>>() {
@Override
public void handle(CellEditEvent<Person, String> t) {
((Person) t.getTableView().getItems().get(
t.getTablePosition().getRow())
).setEmail(t.getNewValue());
}
}
);
table.setItems(data);
table.getColumns().addAll(firstNameCol, lastNameCol, emailCol);
final TextField addFirstName = new TextField();
addFirstName.setPromptText("First Name");
addFirstName.setMaxWidth(firstNameCol.getPrefWidth());
final TextField addLastName = new TextField();
addLastName.setMaxWidth(lastNameCol.getPrefWidth());
addLastName.setPromptText("Last Name");
final TextField addEmail = new TextField();
addEmail.setMaxWidth(emailCol.getPrefWidth());
addEmail.setPromptText("Email");
final Button addButton = new Button("Add");
addButton.setOnAction(new EventHandler<ActionEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(ActionEvent e) {
data.add(new Person(
addFirstName.getText(),
addLastName.getText(),
addEmail.getText()));
addFirstName.clear();
addLastName.clear();
addEmail.clear();
}
});
hb.getChildren().addAll(addFirstName, addLastName, addEmail, addButton);
hb.setSpacing(3);
final VBox vbox = new VBox();
vbox.setSpacing(5);
vbox.setPadding(new Insets(10, 0, 0, 10));
vbox.getChildren().addAll(label, table, hb);
((Group) scene.getRoot()).getChildren().addAll(vbox);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
public static class Person {
private final SimpleStringProperty firstName;
private final SimpleStringProperty lastName;
private final SimpleStringProperty email;
private Person(String fName, String lName, String email) {
this.firstName = new SimpleStringProperty(fName);
this.lastName = new SimpleStringProperty(lName);
this.email = new SimpleStringProperty(email);
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName.get();
}
public void setFirstName(String fName) {
firstName.set(fName);
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName.get();
}
public void setLastName(String fName) {
lastName.set(fName);
}
public String getEmail() {
return email.get();
}
public void setEmail(String fName) {
email.set(fName);
}
}
class EditingCell extends TableCell<Person, String> {
private TextField textField;
public EditingCell() {
}
@Override
public void startEdit() {
if (!isEmpty()) {
super.startEdit();
createTextField();
setText(null);
setGraphic(textField);
textField.selectAll();
}
}
@Override
public void cancelEdit() {
super.cancelEdit();
setText((String) getItem());
setGraphic(null);
}
@Override
public void updateItem(String item, boolean empty) {
super.updateItem(item, empty);
if (empty) {
setText(null);
setGraphic(null);
} else {
if (isEditing()) {
if (textField != null) {
textField.setText(getString());
}
setText(null);
setGraphic(textField);
} else {
setText(getString());
setGraphic(null);
}
}
}
private void createTextField() {
textField = new TextField(getString());
textField.setMinWidth(this.getWidth() - this.getGraphicTextGap()* 2);
textField.focusedProperty().addListener(new ChangeListener<Boolean>(){
@Override
public void changed(ObservableValue<? extends Boolean> arg0,
Boolean arg1, Boolean arg2) {
if (!arg2) {
commitEdit(textField.getText());
}
}
});
}
private String getString() {
return getItem() == null ? "" : getItem().toString();
}
}
}
Note that this approach might become redundant in future releases as the TextFieldTableCell implementation is being evolved to provide better user experience.
Adding Maps of Data to the Table
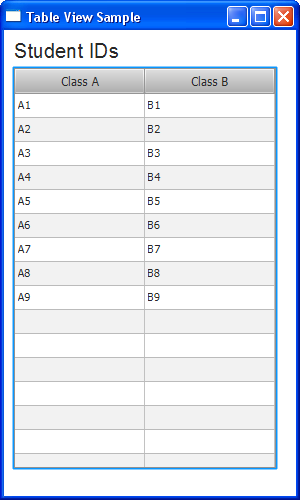
Starting JavaFX SDK 2.2, you can add the Map data to the table. Use the MapValueFactory class as shown in Example 12-12 to display the map of student IDs in the table.
Example 12-12 Adding Map Data to the Table
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Label;
import javafx.scene.control.TableCell;
import javafx.scene.control.TableColumn;
import javafx.scene.control.TableView;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.MapValueFactory;
import javafx.scene.control.cell.TextFieldTableCell;
import javafx.scene.layout.VBox;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Callback;
import javafx.util.StringConverter;
public class TableViewSample extends Application {
public static final String Column1MapKey = "A";
public static final String Column2MapKey = "B";
public static void main(String[] args) {
launch(args);
}
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
Scene scene = new Scene(new Group());
stage.setTitle("Table View Sample");
stage.setWidth(300);
stage.setHeight(500);
final Label label = new Label("Student IDs");
label.setFont(new Font("Arial", 20));
TableColumn<Map, String> firstDataColumn = new TableColumn<>("Class A");
TableColumn<Map, String> secondDataColumn = new TableColumn<>("Class B");
firstDataColumn.setCellValueFactory(new MapValueFactory(Column1MapKey));
firstDataColumn.setMinWidth(130);
secondDataColumn.setCellValueFactory(new MapValueFactory(Column2MapKey));
secondDataColumn.setMinWidth(130);
TableView table_view = new TableView<>(generateDataInMap());
table_view.setEditable(true);
table_view.getSelectionModel().setCellSelectionEnabled(true);
table_view.getColumns().setAll(firstDataColumn, secondDataColumn);
Callback<TableColumn<Map, String>, TableCell<Map, String>>
cellFactoryForMap = new Callback<TableColumn<Map, String>,
TableCell<Map, String>>() {
@Override
public TableCell call(TableColumn p) {
return new TextFieldTableCell(new StringConverter() {
@Override
public String toString(Object t) {
return t.toString();
}
@Override
public Object fromString(String string) {
return string;
}
});
}
};
firstDataColumn.setCellFactory(cellFactoryForMap);
secondDataColumn.setCellFactory(cellFactoryForMap);
final VBox vbox = new VBox();
vbox.setSpacing(5);
vbox.setPadding(new Insets(10, 0, 0, 10));
vbox.getChildren().addAll(label, table_view);
((Group) scene.getRoot()).getChildren().addAll(vbox);
stage.setScene(scene);
stage.show();
}
private ObservableList<Map> generateDataInMap() {
int max = 10;
ObservableList<Map> allData = FXCollections.observableArrayList();
for (int i = 1; i < max; i++) {
Map<String, String> dataRow = new HashMap<>();
String value1 = "A" + i;
String value2 = "B" + i;
dataRow.put(Column1MapKey, value1);
dataRow.put(Column2MapKey, value2);
allData.add(dataRow);
}
return allData;
}
}
The MapValueFactory class implements the Callback interface, and it is designed specifically to be used within cell factories of table columns. In Example 12-12, the dataRow hash map presents a single row in the TableView object. The map has two String keys: Column1MapKey and Column2MapKey to map the corresponding values in the first and second columns. The setCellValueFactory method called for the table columns populates them with data matching with a particular key, so that the first column contains values that correspond to the "A" key and second column contains the values that correspond to the "B" key.
When you compile and run this application, it produces the output shown in Figure 12-9.
Related API Documentation
 Alla is a technical writer for Oracle. She lives in St. Petersburg, Russia, and develops tutorials and technical articles for Java and JavaFX technologies. Prior to her assignment at Oracle, she worked as a technical writer in different IT companies.
Alla is a technical writer for Oracle. She lives in St. Petersburg, Russia, and develops tutorials and technical articles for Java and JavaFX technologies. Prior to her assignment at Oracle, she worked as a technical writer in different IT companies.