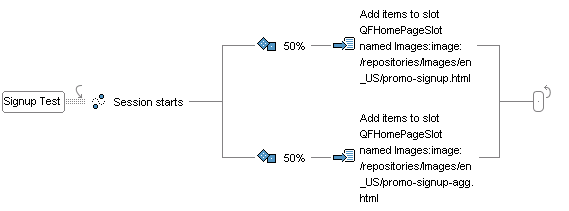
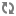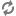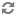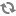To perform short term user sampling, you create a scenario that includes an element called a Randomizing Fork. This element acts in a similar way to a regular Fork element (see Using Fork Elements in Scenarios), except that the first element in the fork always divides the group of site visitors into segments according to a percentage you specify. For example, you could choose to divide the group into two equal segments, 50% in each group. The following image shows a Randomizing Fork element triggered by a Session Starts element:

The next elements in each branch define the object of the test. In the following example, the scenario contains two Action elements that show different promotions to the two groups of visitors:
You then add recorder elements that monitor the results of the test. In this example, you want to measure the success of the two promotions you show, so you add Event elements to account for possible visitor behavior after seeing the promotions (registers to become a member, leaves the site, or logs in). Then you add recorder elements to track the parts of the behavior that interest you:
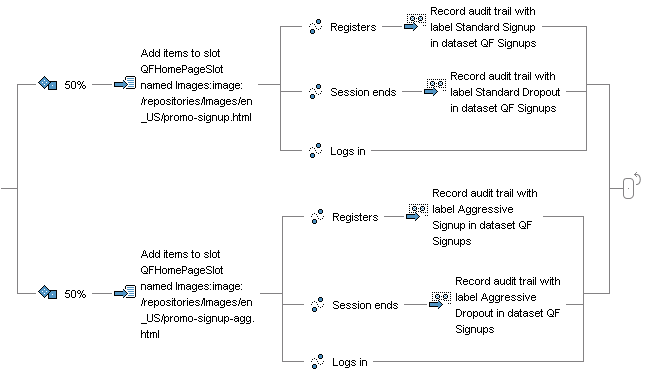
In this example, you add Audit Trail recorder elements to count the number of times that visitors respond to the two promotions either by registering or by leaving the site. The system stores this information in a dataset called QF Signups that you have created specifically for this test. (For information about Audit Trail elements, see Creating an Audit Trail.)
When the test period is complete, you can compare the data for the two groups of users by creating a report that displays the data that you tracked with the recorder elements.