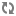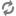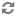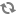The query response features described in this section provide information that allows users to refine their search. The following information is available:
Categories to which their query terms and/or results terms are related
Spelling correction
Additional keyword suggestions
Preconfigured query refinements
Categorization feedback, spelling suggestions, and query term feedback are all part of query refinement, that is, the process of modifying the search to make the results more precise. Categorization feedback allows users to restrict the search space to a relevant category. Spelling suggestions allows end users to correct mistakes or try alternative terms. And query term feedback allows users to add relevant terms to their query.
Categorization Feedback
ATG Search uses rules to place documents or queries into a taxonomy of categories (described briefly in the Categorization Process section of this guide, and in detail in the “Topic Sets” chapter of the ATG Search Administration Guide). During a query, ATG Search can apply these rules to the query and return the categories as part of the result. ATG Search can also review the candidate document results for a query and collect the most relevant or frequent categories and return them as part of the result. The categorization of the query and the candidate documents may not be the same, the former containing the categories most relevant to the query and the latter containing the categories most relevant to the results. Both represent feedback for the end-user to enable further refinement of the query.
Because the categories are organized in a taxonomy, ATG Search can extend the categorization feedback to contain a tree of the categories of the returned document results. Instead of a flat list of the most relevant categories, ATG Search returns the portion of the taxonomy that contains the most relevant categories. The user interface that receives this tree can display it along with the results.
The figure that follows illustrates the process of extracting the category result tree. On the left-side of the figure is the taxonomy, indented to show the hierarchical relationships, Cat1 has two children named Cat2 and Cat3. On the right-hand side are the final results for the query, whose index items belong to one or more categories as shown by the arrows. Categories without any references to results are eliminated from the result tree if none of their descendants have references (Cat4 and Cat6). Categories without any references to results are included if some of their descendents have references to results (Cat1). Thus, the result tree contains the minimum portion of the taxonomy which references the result list. Note that a result can be referenced by multiple categories (Result5) and a category can reference multiple results (Cat2).
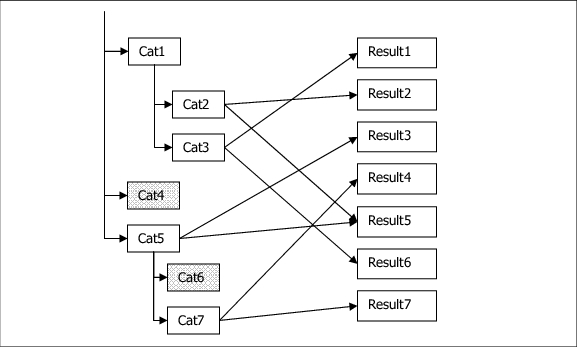
Category Result Tree
Spelling Feedback
ATG Search analyzes the query for spelling mistakes and can either suggest corrections or automatically correct the mistakes. In both cases, the ATG Search response contains feedback about this analysis, which helps explain unexpected results to end-users.
ATG Search provides one of the following feedback types for each query term:
No suggestion—Correct term, contained in the content
Corrected term—Misspelled term, correctable to term in the content
unk—Unknown term, uncorrectable, not in the contentnulx—Term not contained in the content, alternative (thesaurus) terms were availablenull—Term not contained in the content, no alternative (thesaurus) terms were available, so ignored in search
The first three types are self-explanatory and represent the traditional result of spelling checkers: correct, suggested correction, and unknown. The last two types reflect the common case of a user entering a valid term that does not appear in the content, so it cannot be used in the search. In the fourth type, the thesaurus could be used to substitute for the term in the query. In the final type, ATG Search has no alternatives for the term, so the term is ignored in the search. Both of the latter responses can lead to unexpected results for the user.
Query Term Feedback
During a query, ATG Search can review the matching statement candidates and return information about possible important secondary terms. This functionality is important because end-users typically enter short keyword queries, which often result in a large number of imprecise results. Allowing the user to quickly add promising additional terms to the query can further refine the results.
The following diagram illustrates the process of computing term feedback from a query. During retrieval, ATG Search collects a list of statement candidate results from which to select the final returned results. From these statements, non-query terms are collected and counted. A statistical formula is used to convert the frequency of these terms into a value representing the strength of its relationship with the query. The final list of related terms is sorted by this strength value.
The diagram also illustrates the process of computing phrase feedback from a query. From the same list of statement candidate as described above, sequences of non-query terms and adjacent query terms are collected and counted. A statistical formula is used to convert the frequency of these phrases into a value representing the strength of its relationship with the query. The final list of related phrases is sorted by this strength value.
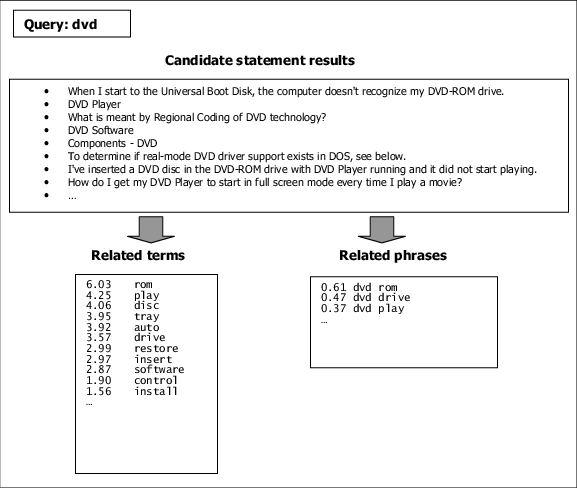
Query Term Feedback
Query Refinements
Another type of user feedback involves metadata properties of the retrieved index items. ATG Search can return properties and values which can segment the retrieval results. This refinement is controlled by configuration data defined by the administrator (see the ATG Search Administration Guide). The configuration data specifies which properties to use in refinement, the order in which they should be used, and various settings to control how to construct the refinement. For example, the configuration data might specify that manufacturer, product type, and price should be used, where price should be returned in ranges and the other two in enumerated lists, limited to the top three values.
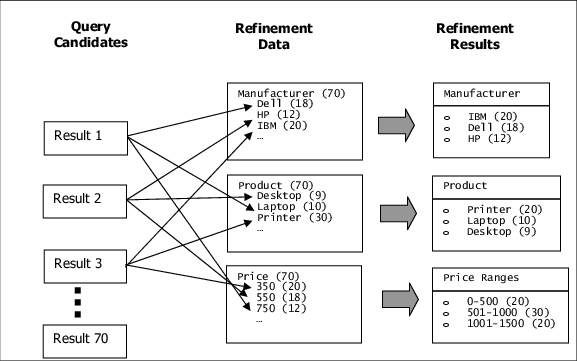
Query Refinement
As another example, the configuration data can specify that the country property will be used initially until all results are from the same country, then state, and then county, and so on. The property refinement is dynamic depending on the result set.