The software described in this documentation is either in Extended Support or Sustaining Support. See https://www.oracle.com/us/support/library/enterprise-linux-support-policies-069172.pdf for more information.
Oracle recommends that you upgrade the software described by this documentation as soon as possible.
Multiple paths to storage devices can provide connection redundancy, failover capability, load balancing, and improved performance. Device-Mapper Multipath (DM-Multipath) is a multipathing tool that allows you to represent multiple I/O paths between a server and a storage device as a single path.
You would be most likely to configure multipathing with a system that can access storage on a Fibre Channel-based storage area network (SAN). You can also use multipathing on an iSCSI initiator if redundant network connections exist between the initiator and the target.
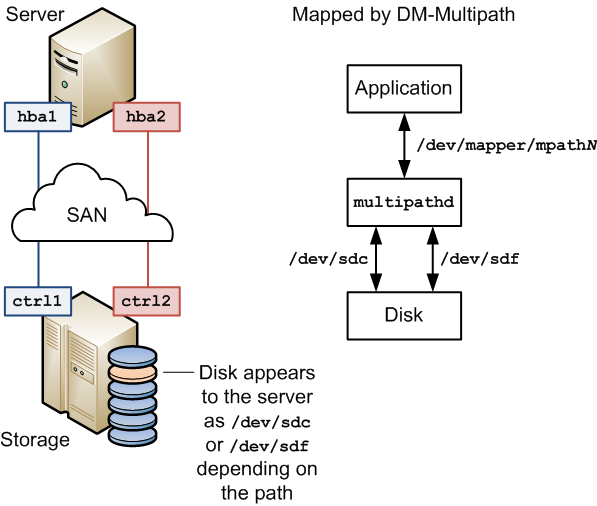
Figure 18.2 shows a simple DM-Multipath configuration where two I/O paths are configured between a server and a disk on a SAN-attached storage array:
Between host bus adapter
hba1on the server and controllerctrl1on the storage array.Between host bus adapter
hba2on the server and controllerctrl2on the storage array.
Without DM-Multipath, the system treats each path as being
separate even though it connects the server to the same storage
device. DM-Multipath creates a single multipath device,
/dev/mapper/mpath,
that subsumes the underlying devices, N/dev/sdc
and /dev/sdf.
You can configure the multipathing service
(multipathd) to handle I/O from and to a
multipathed device in one of the following ways:
- Active/Active
I/O is distributed across all available paths, either by round-robin assignment or dynamic load-balancing.
- Active/Passive (standby failover)
I/O uses only one path. If the active path fails, DM-Multipath switches I/O to a standby path. This is the default configuration.
DM-Multipath can provide failover in the case of path failure, such as in a SAN fabric. Disk media failure must be handled by using either a software or hardware RAID solution.