The software described in this documentation is either in Extended Support or Sustaining Support. See https://www.oracle.com/us/support/library/enterprise-linux-support-policies-069172.pdf for more information.
Oracle recommends that you upgrade the software described by this documentation as soon as possible.
The NetworkManager service, Gnome graphical
applet, and the nm-connection-editor command
are included in the NetworkManager package.
The system-config-network utility is included
in the system-config-network-tui package.
The NetworkManager service dynamically detects
and configures network connections. It includes a GNOME
Notification Area applet (nm-applet)that
provides you with information about the network status and
graphical configuration tools to manage network interfaces and
connections.
The applet icon changes its appearance indicate the state of the network. Hover the mouse pointer over the icon to display more information as a tool tip. Clicking the icon displays a drop-down menu that allows you to restart or disconnect each named interface.
Right-clicking the icon displays a different drop-down menu:
- Enable Networking
Allows you to stop or start the network service.
- Enable Notifications
Controls whether
NetworkManagernotifies you of changes to the status of network connections.- Connection Information
Displays the Connection Information window, which lists the connection type, hardware address, IP address, and other useful information for each interface.
- Edit Connections
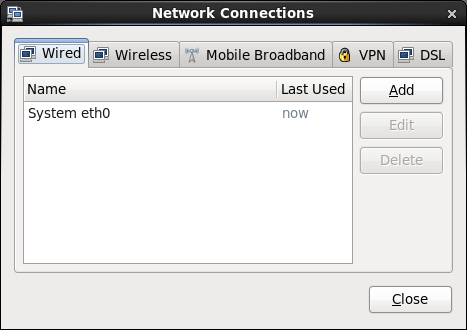
Displays the Network Connections window, which allows you to configure wired, wireless, mobile broadband, Virtual Private Network (VPN), and Digital Subscriber Link (DSL) interfaces. You can also open this window by using the nm-connection-editor command.
Figure 11.1 shows the Network Connections window with the Wired tab selected.
You can also use the system-config-network command, which provides a text-based user interface that allows you to configure network interface and DNS resolver settings.