BIOS Advanced Menu Selections
This section includes a screenshot of the BIOS Advanced Menu. The options that are
available from the Advanced Menu are described in the sections that follow. Options in the
tables that are marked as “(R/O)” are read-only information and cannot be
changed.
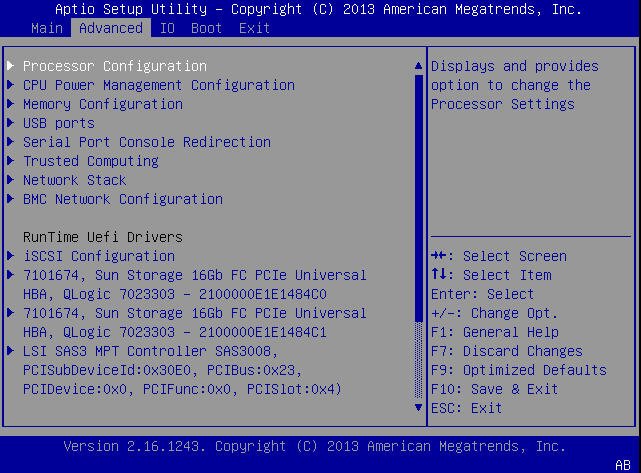
The following sections describe the BIOS Advanced Menu options:
BIOS Advanced Menu Processor Configuration Options
The following table describes the BIOS Advanced Menu processor configuration
options:
Table 19 BIOS Advanced Menu Processor Configuration
|
|
|
|
|
Hyper-threading
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Use to enable Hyper Threading. When enabled, two threads are available
per enabled core. When disabled, only one thread per enabled core is
available.
|
|
Active Processor Cores
|
A minimum of one up to the maximum number of cores available in the
processor package.
|
All
|
The number of cores to enable in each processor package.
|
|
Execute Disable Bit
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
When disabled, forces XD features flag to always return 0.
|
|
Hardware Prefetcher
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable the mid-level cache (MLC) streamer prefetcher (MSR 1A4h bit
[0]).
|
|
Adjacent Cache Prefetch
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable the mid-level cache (MLC) streamer prefetcher (MSR 1A4h bit
[1]).
|
|
DCU Streamer Prefetcher
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable DCU streamer prefetcher, which is a L1 data cache prefetcher
(MSR 1A4h [2]).
|
|
DCP IP Prefetcher
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable DCU IP prefetcher, which is a L1 data cache prefetcher (MSR
1A4h [3]).
|
|
Intel Virtualization Technology
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
When enabled, a Virtual Machine Manager (VMM) can utilize the
additional hardware capabilities provided by Intel Virtualization
Technology.
|
|
BIOS Advanced Menu CPU Power Management Configuration Options
The following table describes the BIOS Advanced Menu CPU power management
configuration options:
Table 20 BIOS Advanced Menu CPU Power Management Configuration
|
|
|
|
|
Power Technology
|
Disabled/Energy Efficient/Custom
|
Custom
|
Enables the power management features.
|
|
EIST (GV3)
|
Endabled/Disabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST).
|
|
Turbo Mode
|
Enabled/Disabled
|
Enabled
|
Enabled mode is supported only if Turbo Mode is supported in the CPU.
Enabled mode also requires that Enhanced Multi Threaded Thermal
Monitoring (EMTTM) be enabled on the CPU.
|
|
CPU C3 report
|
Enabled/Disabled
|
Disabled
|
Enable/disable the CPU C3 (ACPI C3) report to the operating
system.
|
|
CPU C6 report
|
Enabled/Disabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable/disable the CPU C6 (ACPI C3) report to the operating
system.
|
|
CPU C7 report
|
Enabled/Disabled
|
Disabled
|
Enable/disable the CPU C7 (ACPI C3) report to the operating
system.
|
|
Package C State limit
|
Endabled/Disabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable/disable Package C State limit.
|
|
Energy_PERF_BIAS_CFG mode
|
PERF/Balanced Perf/Balanced Power/Power
|
Balanced Perf
|
Use this option to select the Energy_PERF_BIAS_CFG mode.
|
|
Uncore Frequency Scaling
|
Endabled/Disabled
|
Disabled
|
Enable/disable Uncore Frequency Scaling (USF).
|
|
BIOS Advanced Menu Memory Configuration Option
The following table describes the BIOS Advanced Menu memory configuration
option:
Table 21 BIOS Advanced Menu Memory Configuration Option
|
|
|
|
|
Numa
|
Enabled/Disabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable Non Uniform Memory Access (NUMA)
|
|
BIOS Advanced Menu USB Ports Options
The following table describes the BIOS Advanced Menu USB ports options:
Table 22 BIOS Advanced Menu USB Ports
|
|
|
|
|
EHCI Hand-off
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Enable or disable Enhanced Host Controller Interface (EHCI) hand-off
support. This is a workaround for operating systems without EHCI hand-off
support. The EHCI change of ownership should be claimed by the EHCI
driver.
|
|
Port 60/64 Emulation
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable I/O port 60h/64h emulation support. Enable this setting for the
complete USB keyboard legacy support for non-USB aware operating
systems.
|
|
EHCI Controller 1
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable EHCI Controller 1.
|
|
EHCI Controller 2
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable EHCI Controller 2.
|
|
Rear Port #0
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable USB Rear Port 0.
|
|
Rear Port #1
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable USB Rear Port 1.
|
|
Front Port #0
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable USB Front Port 0.
|
|
Front Port #1
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable USB Front Port 1.
|
|
Internal Port #0
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable USB Internal Port 0.
|
|
Internal Port #1
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable USB Internal Port 1.
|
|
BIOS Advanced Menu Serial Port Console Redirection Options
The following table describes the BIOS Advanced Menu serial port console redirection
options:
Table 23 BIOS Advanced Menu Serial Port Console Redirection Options
|
|
|
|
|
EMS Console Redirection
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Enable or disable console redirection for Windows Emergency Management
Service (EMS) administration.
|
|
Console Redirection
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable console redirection.
|
|
Terminal Type
|
VT100/VT100+/VT-UTF8/ANSI
|
VT100+
|
Select the emulation for the terminal:
-
VT100: ASCII character set.
-
VT100+: Extends VT100 to support color, function keys, etc.
-
VT-UTF8: Uses UTF8 encoding to map Unicode characters onto one
or more bytes.
-
ANSI: Extended ASCII character set.
|
|
Bits per Second
|
9600
19200
38400
57600
115200
|
9600
|
Select the serial port transmission speed. The speed must be matched
on the connecting serial device. Long or noisy lines require lower
speeds.
|
|
Data Bits
|
7/8
|
8
|
Select the data bits.
|
|
Parity
|
None/Even/Odd/Mark/Space
|
None
|
A parity bit can be sent with the data bits to detect some
transmission errors.
-
None: No parity bits are sent.
-
Even: Parity bit is 0 if the number of 1s in the data bits is
even.
-
Odd: Parity bit is 0 if the number of 1s in the data bits is
odd.
-
Mark: Parity bit is always 1.
-
Space: Parity bit is always 0.
Mark and Space parity do not allow for error detection. They can be
used as an additional data bit.
|
|
Stop Bits
|
1/2
|
1
|
Stop bits indicate the end of a serial data packet. (A start bit
indicates the beginning of a serial data packet.) The standard setting is
1 stop bit. Communication with slow devices may require more than 1 stop
bit.
|
|
Flow Control
|
None, Hardware RTS/CTS, Software Xon/Xoff
|
None
|
Flow control can prevent data loss from buffer overflow. When sending
data, if the receiving buffers are full, a 'stop' signal can be sent to
stop the data flow. Once the buffers are empty, a 'start' signal can be
sent to restart the flow. Hardware flow control uses two wires to send
start/stop signals.
|
|
BIOS Advanced Menu Trusted Computing Options
The following table describes the BIOS Advanced Menu trusted computing
options:
Table 24 BIOS Advanced Menu Trusted Computing Options
|
|
|
|
|
TPM Support
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Enable or disable Trusted Platform Module (TPM) support. Only UEFI
BIOS implements this setup option. If disabled, the OS will not show TPM.
Reset of the platform is required.
|
|
TPM State
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Displays whether TPM Support is enabled.
Note -
This option is available only if TPM Support is set to
enabled.
|
|
Pending Operation
|
None/Enable Take Ownership/Disable Take Ownership/TPM Clear
|
None
|
Used to schedule an operation for the security device.
Note -
Your computer will reboot during restart in order to change the
state of a security device.
|
|
Current Status Information
|
|
|
If TPM Support is disabled, Current Status Information displays
SUPPORT Turned OFF.”
|
|
TPM Enabled Status
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Use this option to provide the current capability state of the
security device.
Note -
This option is available only if TPM Support is set to
enabled.
|
|
TPM Active Status
|
Deactivated/Activated
|
Deactivated
|
Use this option to provide the current capability state of the
security device.
Note -
This option is available only if TPM Support is set to
enabled.
|
|
TPM Owner Status
|
Owned/Unowned
|
Unowned
|
Use this option to provide the current ownership state.
Note -
This option is available only if TPM Support is set to
enabled.
|
|
BIOS Advanced Menu Network Stack Options
The following table describes the BIOS Advanced Menu network stack options:
Table 25 BIOS Advanced Menu Network Stack Options
|
|
|
|
|
Network Stack
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable the UEFI network stack.
|
|
Ipv4 PXE Support
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Enabled
|
Enable or disable IPv4 PXE Boot support. If disable, the IPv4 Boot
Option will not be created.
|
|
Ipv6 PXE Support
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Enable or disable IPv6 PXE Boot support. If disable, the IPv6 Boot
Option will not be created.
|
|
BIOS Advanced Menu BMC Network Configuration Options
The following table describes the BIOS Advanced Menu BMC network configuration
options:
Table 26 BIOS Advanced Menu BMC Network Configuration Options
|
|
|
|
|
Current Active Management Port (R/O)
|
NA
|
NETMGT
|
The currently active management port.
|
|
Refresh
|
NA
|
NA
|
Refresh current BMC LAN information with the latest information from
the service processor.
|
|
Active Mgmt Port
|
NET MGT/NET0/NET1/NET2/NET3
|
NET MGT
|
Use to change the currently active network management port.
|
|
Commit
|
NA
|
NA
|
Commit the current BMC network LAN information.
|
|
IPv4 Configuration
|
NA
|
NA
|
Current configuration of the IPv4 settings is displayed.
|
|
Channel Number (R/O)
|
|
1
|
Current channel number is displayed.
|
|
Current IPv4 IP Assignment in BMC (R/O)
|
Static/Dynamic
|
Static
|
Set the IPV4 IP assignment to Static or Dynamic. This setting
determines whether the service processor is assigned a static IPv4
address or assigned a dynamic IPv4 address using Dynamic Host Control
Protocol (DHCP).
|
|
Current IPv4 address in BMC (R/O)
|
NA
|
NA
|
Displays the current IPv4 address in the BMC.
|
|
Current IPv4 MAC Address in BMC (R/O)
|
NA
|
NA
|
If IPv4 Assignment is set to Static, set the IPv4 address for the
service processor.
Example: 172.31.255.255
|
|
Current IPv4 Subnet Mask in BMC (R/O)
|
NA
|
NA
|
If the IPv4 Assignment is set to Static, set the IPv4 subnet
mask.
Example: 255.255.255.0
|
|
Current IPv4 Default Gateway in BMC
|
NA
|
NA
|
If the IPv4 Assignment is set to Static, set the IPv4 default
gateway
Example: 172.31.255.255
|
|
Refresh
|
|
|
Refresh the current BMC LAN information.
|
|
IPv4 IP Assignment
|
Static/Dynamic
|
Static
|
Current IPv4 assignment.
|
|
IPv4 Address
|
NA
|
NA
|
If set, current IPv4 address is displayed.
|
|
IPv4 Subnet Mask
|
NA
|
NA
|
If set, current IPv4 Subnet Mask is displayed.
|
|
IPv4 Default Gateway
|
NA
|
NA
|
If set, current IPv4 Default Gateway is displayed.
|
|
Commit
|
|
|
Commit the current BMC LAN information.
|
|
IPv6 Configuration
|
|
|
Current configuration of the IPv6 settings is displayed.
IPv6 addresses are written with hexadecimal digits and colon
separators. For example:
2001:0db0:000:82a1:0000:0000:1234:abcd.
IPv6 addresses are composed of two parts: a 64-bit subnet prefix and a
64-bit host interface ID. To shorten the IPv6 address, you can (1) omit
all leading zeros, and (2) replace one consecutive group of zeros with a
double colon (::). For example:
2001:db0:0:82a1::1234:abcd.
|
|
Channel Number (R/O)
|
|
1
|
Current channel number is displayed.
|
|
Current IPv6 State (R/O)
|
Enabled/Disabled
|
Enabled
|
Current IPv6 state is displayed.
|
|
Current IPv6 Auto Configuration (R/O)
|
Stateful/Stateless
|
Stateless
|
Current IPv6 autoconfiguration parameters are displayed.
|
|
Link Local IPv6 Address (R/O)
|
|
|
Current link local IPv6 address is displayed.
Example: fe80::214:4fff:feca:5f7e/64
|
|
Static IPv6 Address (R/O)
|
|
|
Current static IPv6 address is displayed.
Example:
2001:0db0:000:82a1:0000:0000:1234:abcd
|
|
IPv6 Gateway (R/O)
|
|
|
Current IPv6 gateway address is displayed.
Example: fe80::211:5dff:febe:5000/128
|
|
Dynamic IPv6 Address 1-n (R/O)
|
|
|
Current dynamic IPv6 addresses are displayed.
Example: fec0:a:8:b7:214:4fff:feca:5f7e/64
|
|
Refresh
|
|
|
Select Refresh to update to the current settings.
|
|
IPv6 State
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Set the IPv6 state to enabled or disabled.
|
|
Auto IPv6 Configuration
|
Disabled/
Stateless/
Dhcpv6_stateless/
Dhcpv6_stateful
|
Disabled
|
Autoconfiguration options are:
-
Disabled: When autoconfiguration is disabled, only the Link
Local address is set. None of the autoconfiguration options to
configure an IPv6 address are run.
-
Stateless: When enabled, the IPv6 Stateless autoconfiguration is
run to learn the IPv6 addresses for the device.
-
Dhcpv6_stateless: When enabled, the Dhcpv6_stateless
autoconfiguration is run to learn the DNS and domain information
for the device.
-
Dhcpv6_stateful: When enabled, the Dhcpv6_stateful
autoconfiguration is run to learn the IP addresses and DNS
information for the device.
|
|
Static IPv6 Address (R/O)
|
|
|
Set the static IPv6 address.
Example:
2001:0db0:000.82a1:0000:0000:1234:abcd
|
|
Commit
|
|
|
Commit the current BMC LAN information.
|
|
BIOS Advanced Menu iSCSI Configuration Options
The following table describes the BIOS Advanced Menu iSCSI configuration
options:
Table 27 BIOS Advanced Menu iSCSI Configuration Options
|
|
|
|
|
iSCSI Initiator Name
|
NA (must be specified)
|
None
|
The worldwide unique name of the iSCSI Initiator. Only IQN format is
accepted.
|
|
Add an Attempt
|
|
|
|
|
iSCSI Attempt Name
|
NA (must be specified)
|
None
|
The readable name that you assigned to this attempt.
|
|
iSCSI Mode
|
Disabled/Enabled/Enabled for MPIO
|
Disabled
|
Set to Enabled for multipath I/O (MPIO). MPIO can boost the
performance of an application by load balancing traffic across multiple
ports.
|
|
Internet Protocol
|
IP4/IP6/Autoconfigure
|
IP4
|
Can be set to IP4, IP6, or Autoconfigure. The initiator IP address is
assigned by the system to IP6. In Autoconfigure mode, the iSCSI driver
attempts to connect to the iSCSI target using the IPv4 stack. If this
fails, then the iSCSI driver attempt to connect using the IPv6
stack.
|
|
Connection Retry Count
|
0 to 16
|
0
|
The count range is 0 to 16. If set to 0, there are no retries.
|
|
Connection Establishing Timeout
|
NA
|
1,000
|
The timeout value in milliseconds. The minimum value is 100
milliseconds and the maximum is 20 seconds.
|
|
Configure ISID
|
Derived from the MAC address
|
The default value is derived from the Mac Address
|
The OUI-format ISID is 6 bytes. The default value is derived from the
MAC address. Only the last 3 bytes are configurable.
Example: Update 0ABBCCDDEEFF to 0ABBCCF07901 by inputting
F07901
|
|
Enable DHCP
|
Disabled/Enabled
|
Disabled
|
Enable or disable DHCP
|
|
Initiator IP Address
|
NA
|
0.0.0.0
|
Use to set initiator IP address in dotted-decimal notation.
|
|
Initiator Subnet Mask
|
NA
|
0.0.0.0
|
Use to set initiator subnet mask IP address in dotted-decimal
notation.
|
|
Gateway
|
NA
|
0.0.0.0
|
Use to set initiator gateway IP address in dotted-decimal
notation.
|
|
Target Name
|
NA
|
NA
|
The worldwide unique name of the target. Only IQN format is
accepted.
|
|
Target IP address
|
0.0.0.0
|
None
|
Use to set target IP address in dotted-decimal notation.
|
|
Target Port
|
|
3260
|
Use to change target port number.
|
|
Boot LUN
|
|
0
|
Use to set the hexadecimal representation of the boot logical unit
number (LUN).
Example: 4752-3A4F-6b7e-2F99
|
|
Authentication Type
|
CHAP/None
|
CHAP
|
Define the Challenge-Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP).
Available settings are CHAP, Kerberos, and None.
|
|
CHAP Type
|
One Way/Mutual
|
One Way
|
Use to set CHAP type to either One Way or Mutual.
|
|
CHAP Name
|
NA
|
None
|
Use to set CHAP name.
|
|
CHAP Secret
|
NA
|
None
|
Use to set the CHAP secret password. The secret length range is 12 to
16 bytes.
|
|
Delete Attempts
|
NA
|
NA
|
Use to delete one or more attempts.
|
|
Change Attempt Order
|
NA
|
NA
|
Use to change the order of attempts. Use arrow keys to select the
attempt, then press +/- keys to move the attempt up/down in the attempt
order list.
|
|
BIOS Advanced Menu Ethernet Controller Options
The following table describes the BIOS Advanced Menu Ethernet controller
options:
Table 28 BIOS Advanced Menu Ethernet Controller Options
|
|
|
|
|
Port Configuration Menu
|
|
|
|
|
NIC configuration
|
|
|
Use to configure the network device port.
|
|
Link Speed (R/O)
|
Supported port speeds/Auto Negotiate
|
NA
|
Specifies the port speed used for the selected boot protocol.
Note -
This option is not supported.
|
|
Wake on LAN
|
Disable/Enabled
|
NA
|
Enable or disable wake on LAN.
Note -
This option is not supported.
|
|
Blink LEDs
|
0/1/2/3
|
0
|
Use to identify the physical network port by blinking the associated
LED.
|
|
Port Configuration Information
|
|
|
Displays and specifies the port settings for the network
device.
|
|
UEFI Driver (R/O)
|
NA
|
NA
|
Identifies the UEFI driver.
|
|
Adapter PBA (R/O)
|
NA
|
NA
|
Product board adapter (PBA) number. You can use the Intel Network
Adapter PBA number to search for the adapter's model number. The PBA
number is a nine digit number that is the last part of the adapter board
serial number. The PBA number is presented in this format:
xxxxxxx-xxx, for example, C80222-001.
|
|
Chip Type (R/O)
|
NA
|
NA
|
Manufacturer and model number
|
|
PCI Device ID (R/O)
|
|
1528
|
Device identifier
|
|
PCI Address (R/O)
|
NA
|
NA
|
Bus device function identifier
Example format: Bus:Device:Function
|
|
Link Status
|
Connected/Disconnected
|
Disconnected
|
Specifies the link status of the network port.
|
|
MAC Address (R/O)
|
NA
|
None
|
Lists the MAC address of the network interface card (NIC).
|
|
